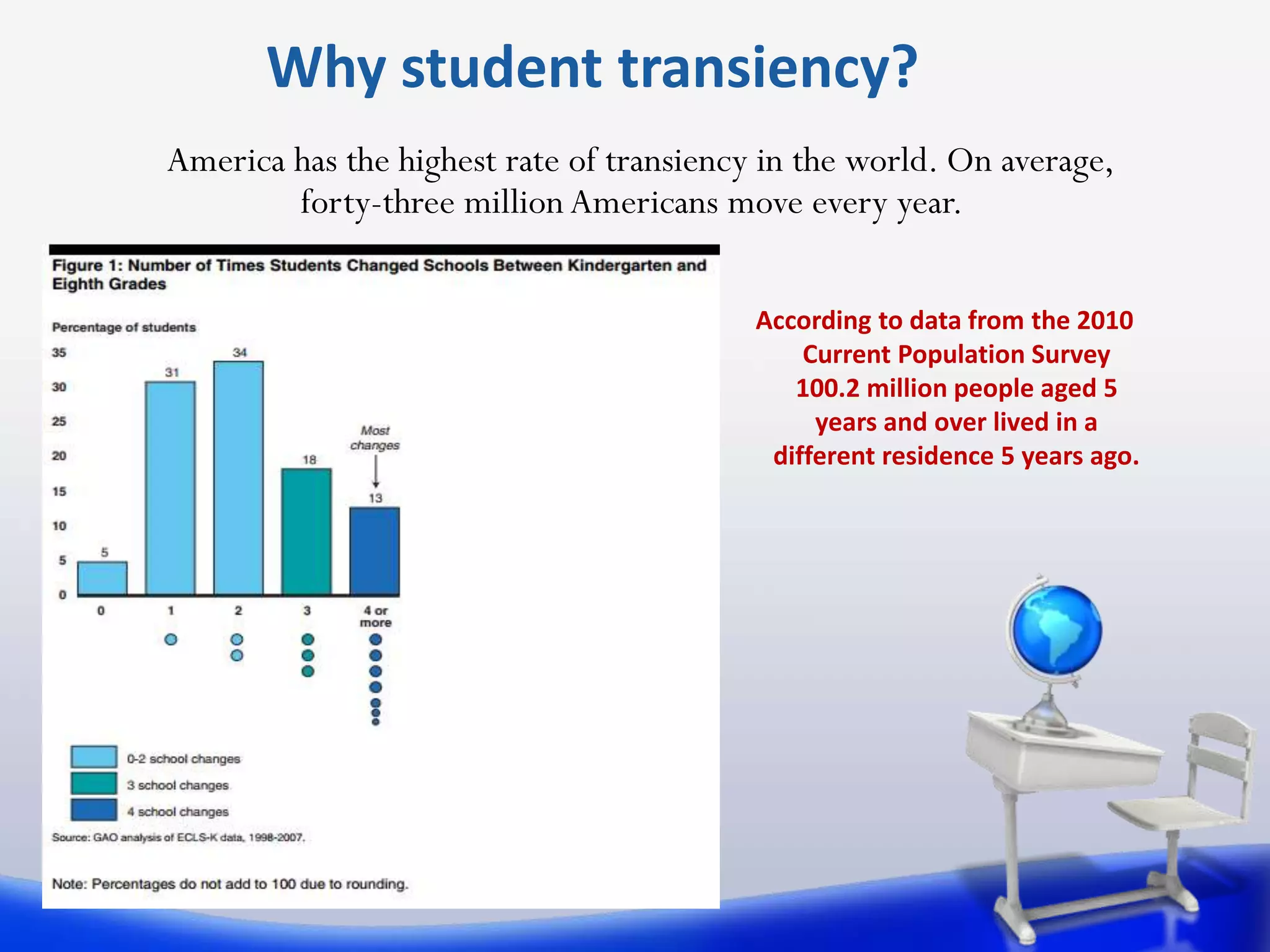
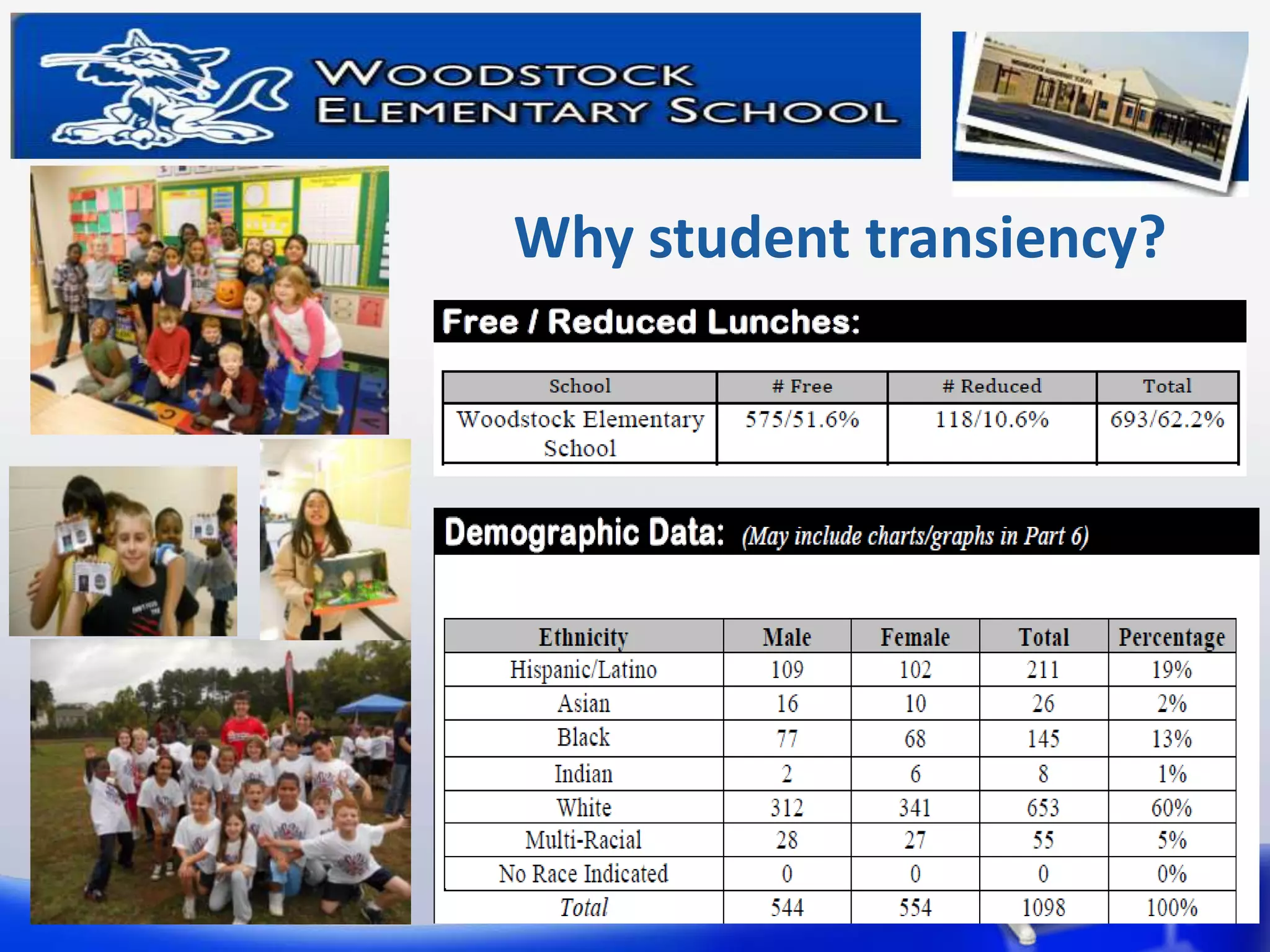
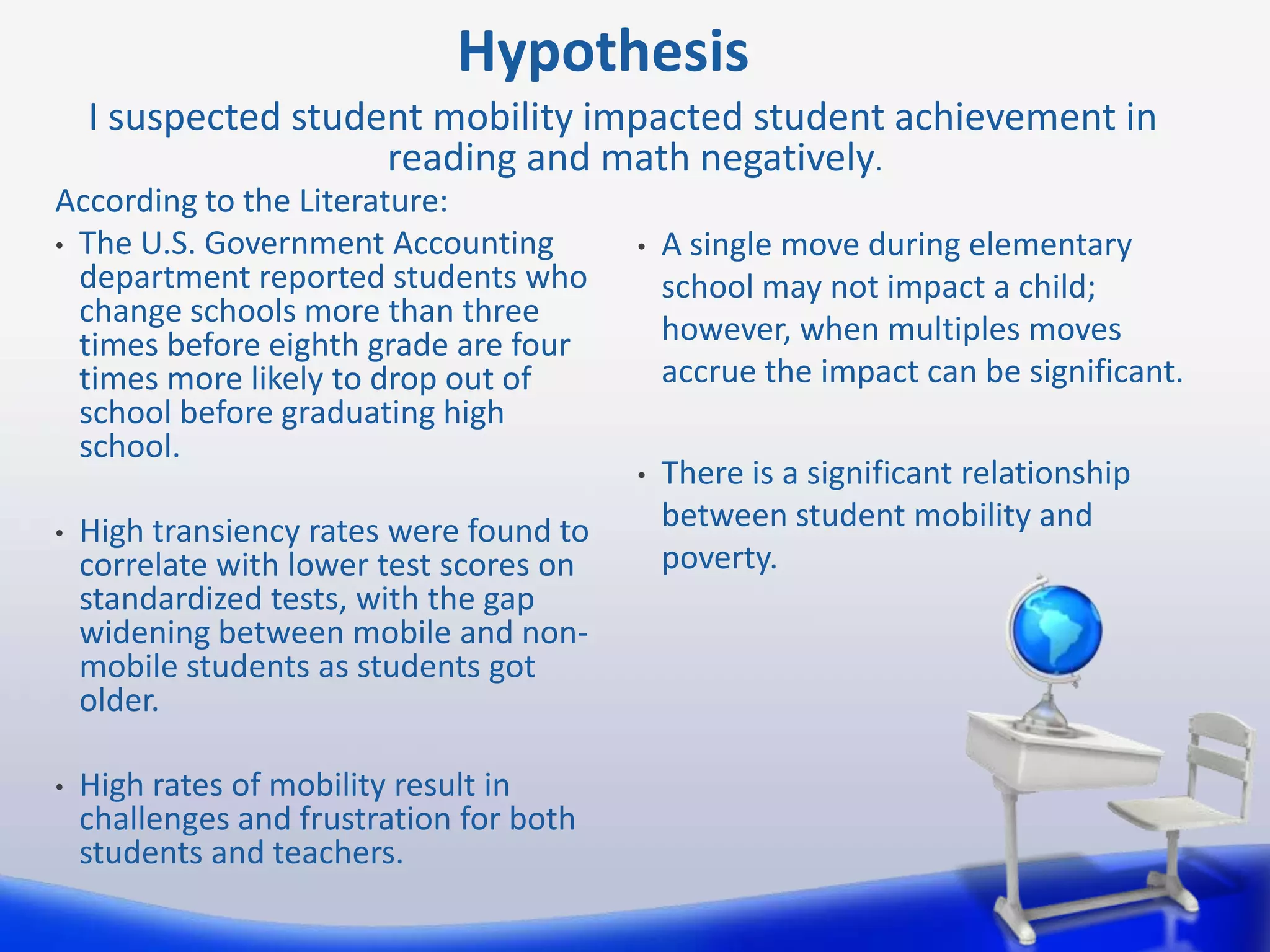
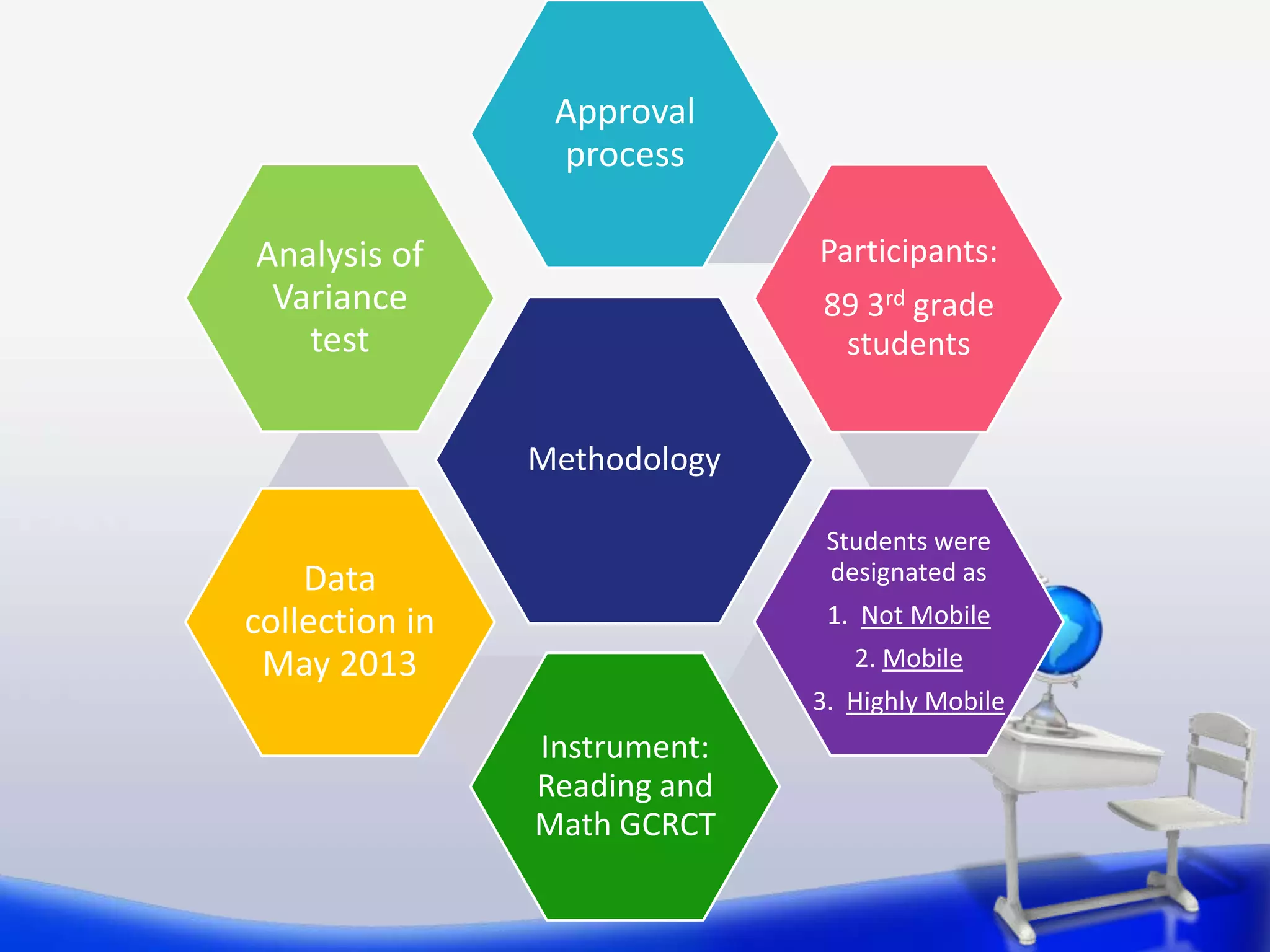
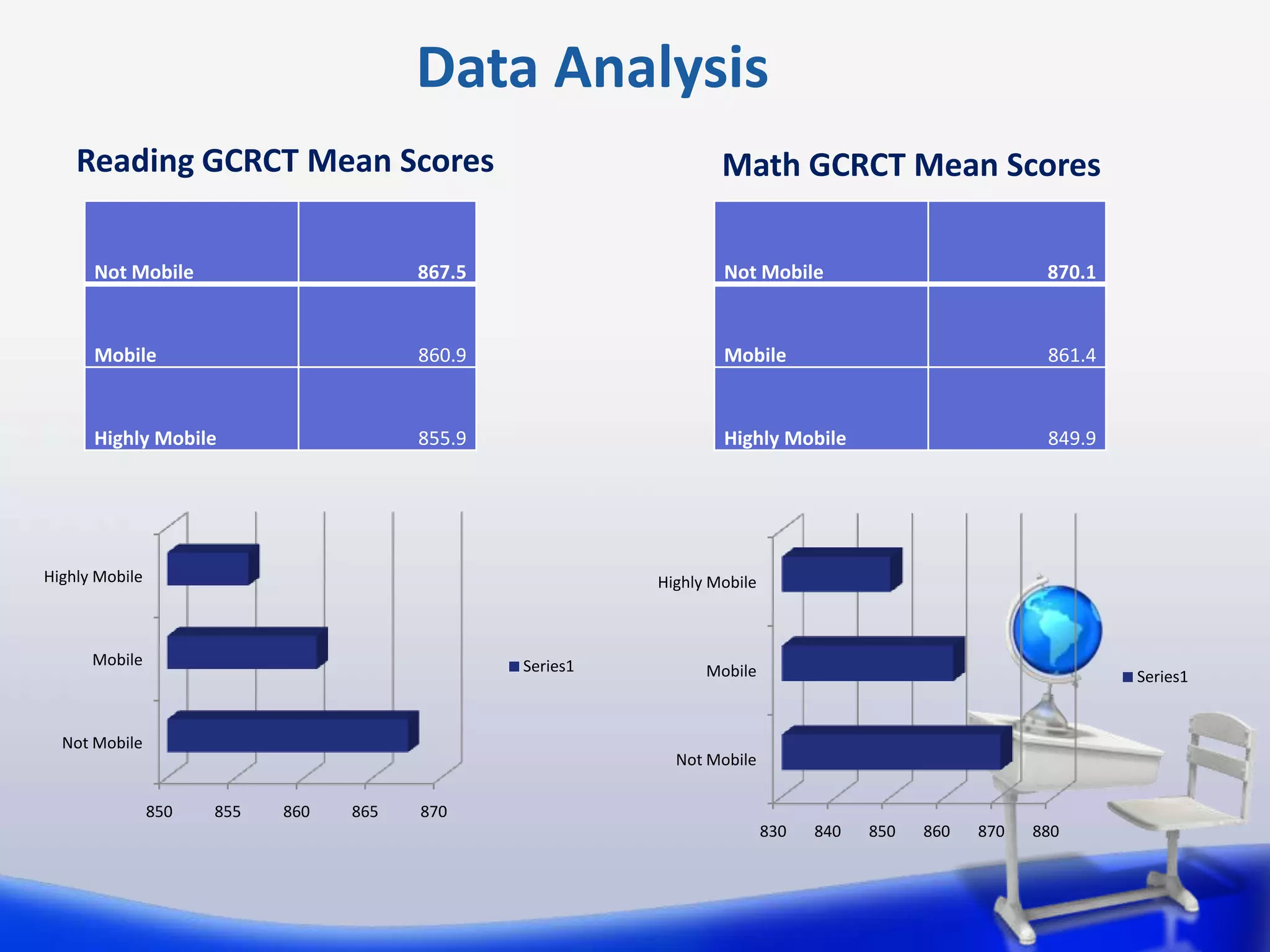
This document summarizes a study on the relationship between student transiency (mobility) and academic performance. The study aimed to determine if transiency negatively impacts student achievement in reading and math. It hypothesized that increased student mobility would correlate with lower test scores. The study analyzed test scores of 89 3rd grade students, categorizing them as non-mobile, mobile, or highly mobile. It found no statistically significant differences in reading or math scores between the three groups. Therefore, the study concluded that transiency did not significantly impact 3rd grade student achievement as measured by standardized tests in this sample.