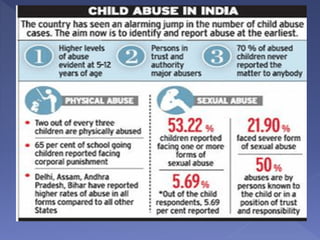
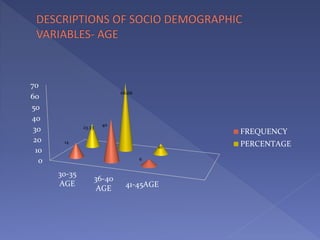
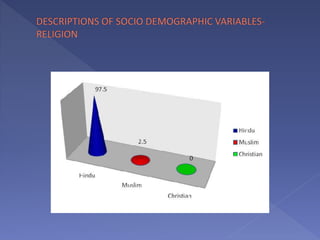
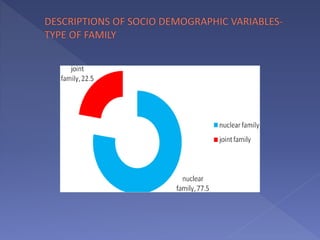
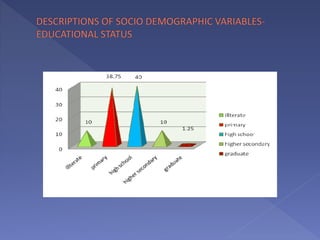
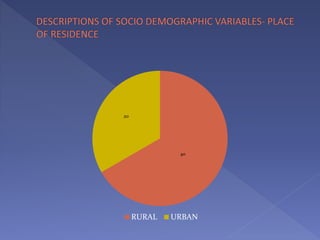
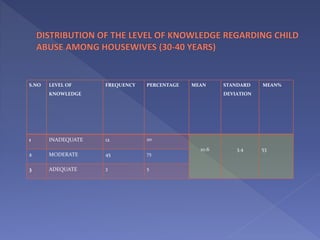
This study assesses the knowledge of housewives aged 30-45 about child abuse in selected villages in Cuddalore, noting that 75% had moderate knowledge. It highlights alarming statistics on child abuse cases in India, including physical and emotional abuse predominantly inflicted by parents. The study indicates that knowledge of child abuse is significantly associated with education and prior awareness, while other socio-demographic variables showed no significant correlation.