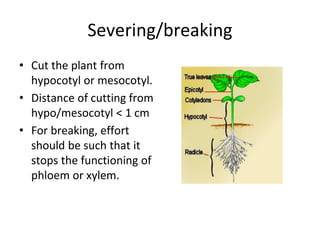
The document discusses various mechanical weeding methods including uprooting, severing, and burial techniques suitable for different soil types and conditions. It outlines specific methods like tillage, hoeing, hand weeding, digging, sickling, mowing, burning, and flooding, highlighting their effectiveness, costs, and labor requirements. Additionally, it emphasizes factors affecting the success of these methods such as soil type, weed characteristics, and crop rotation.