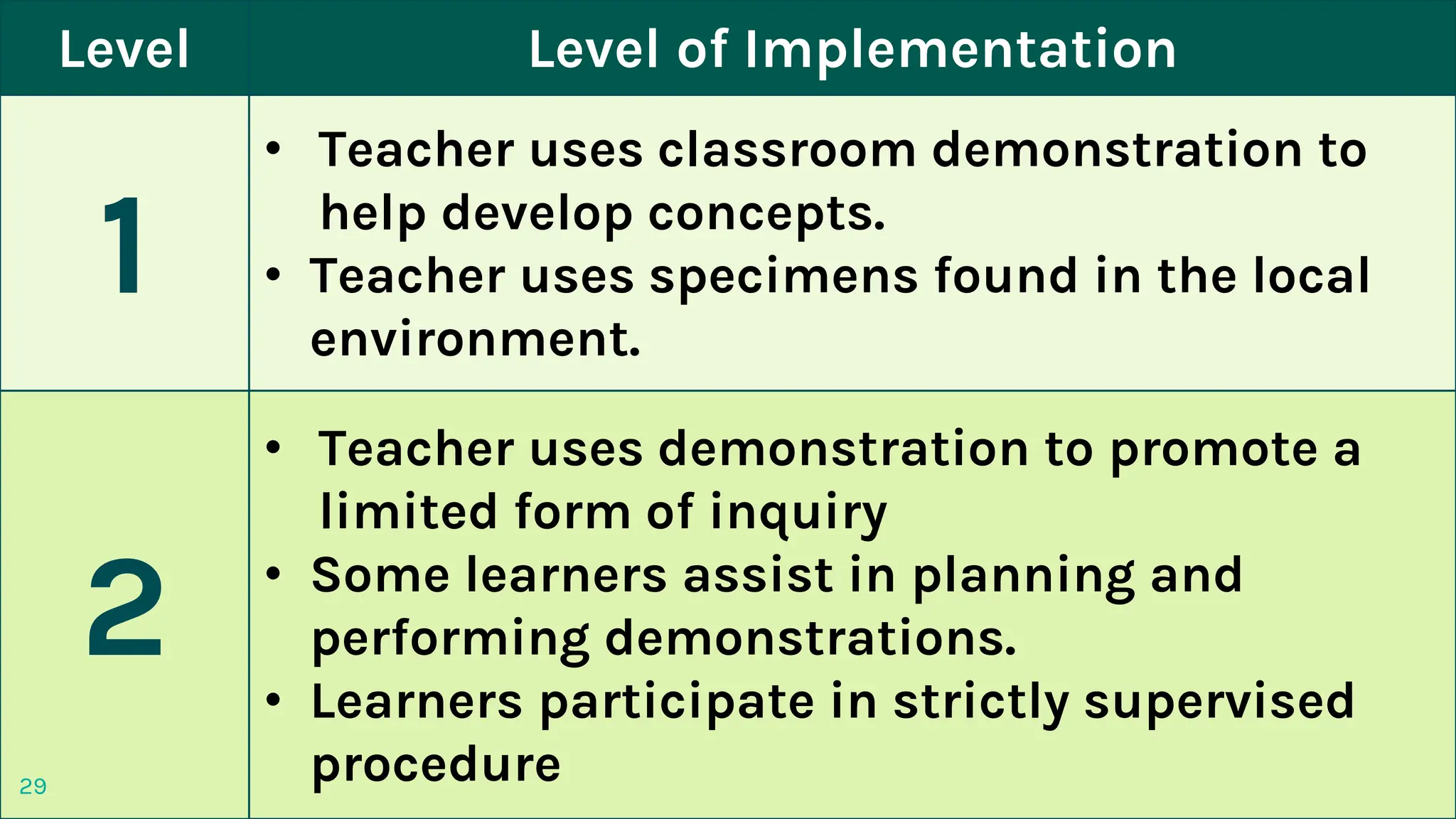
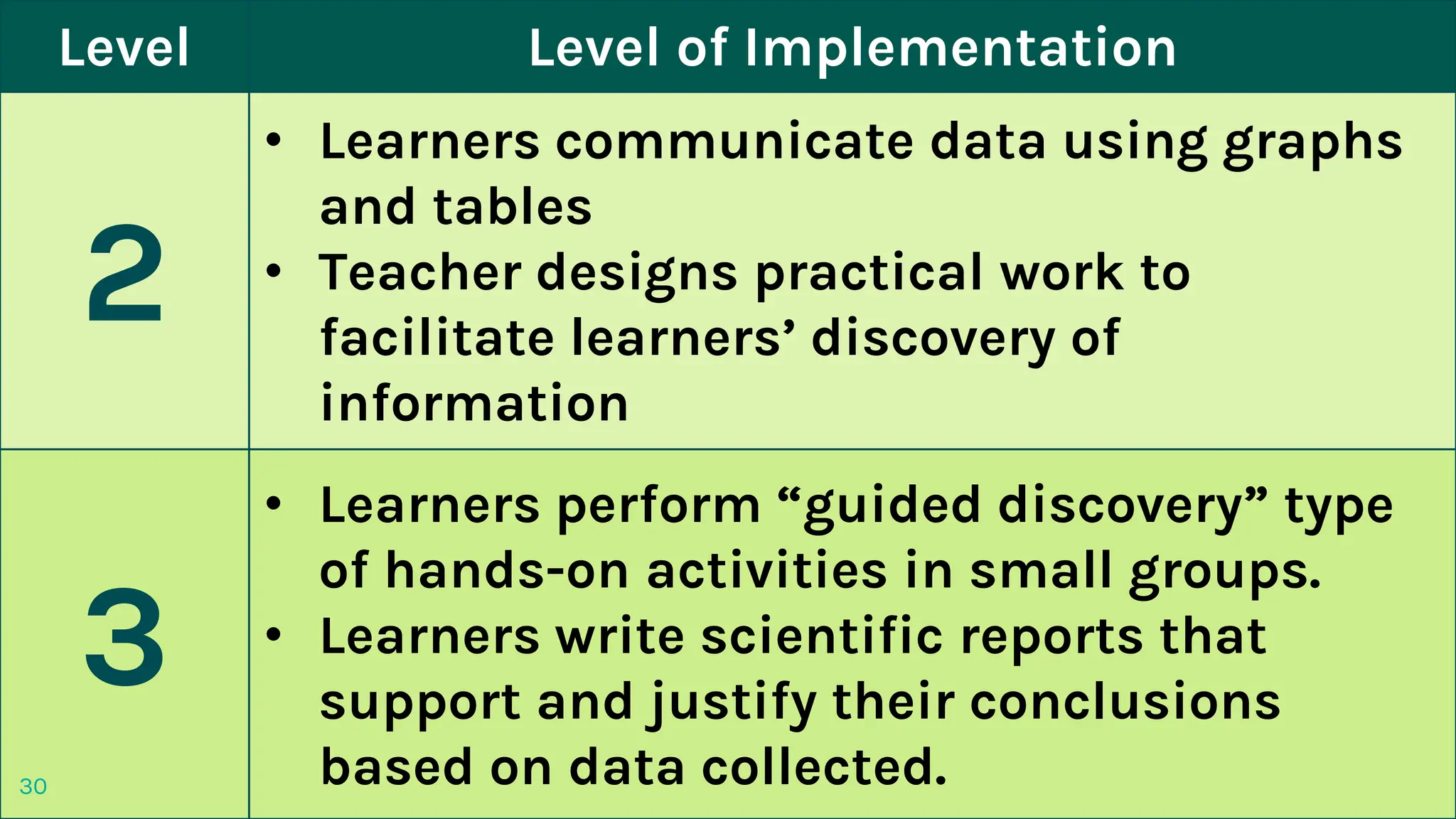
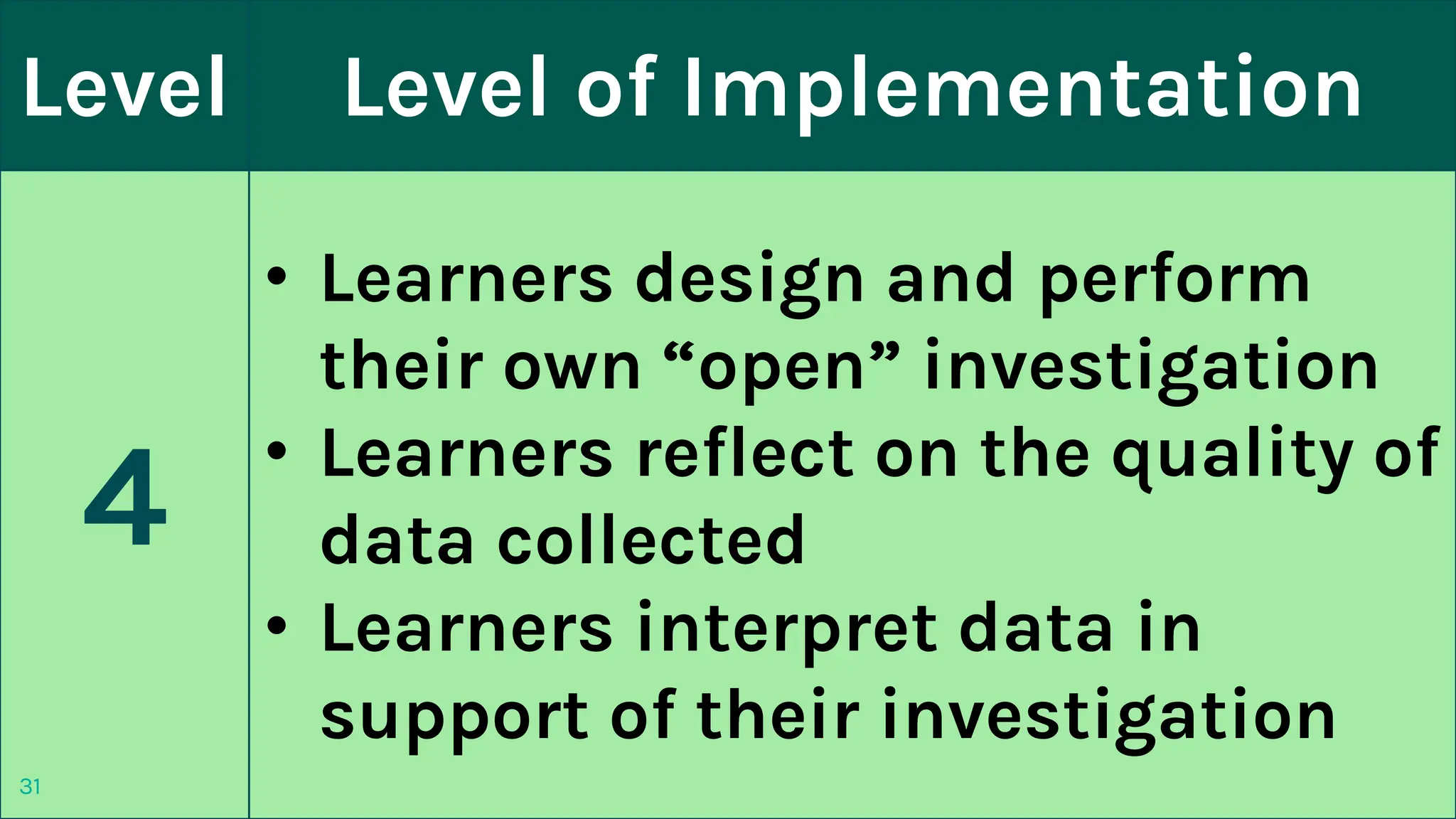
The document discusses two methods of teaching mathematics - the discovery approach and the practical work approach.
The discovery approach encourages students to explore concepts independently and discover patterns and relationships on their own. The teacher acts as a coach to guide students in exploring examples and scenarios. The practical work approach involves students manipulating real-world objects and performing hands-on activities to understand mathematical concepts. This allows active participation and exposure to relevant environments to facilitate comprehension. Both approaches aim to make learning more experiential and student-centered compared to traditional instruction.