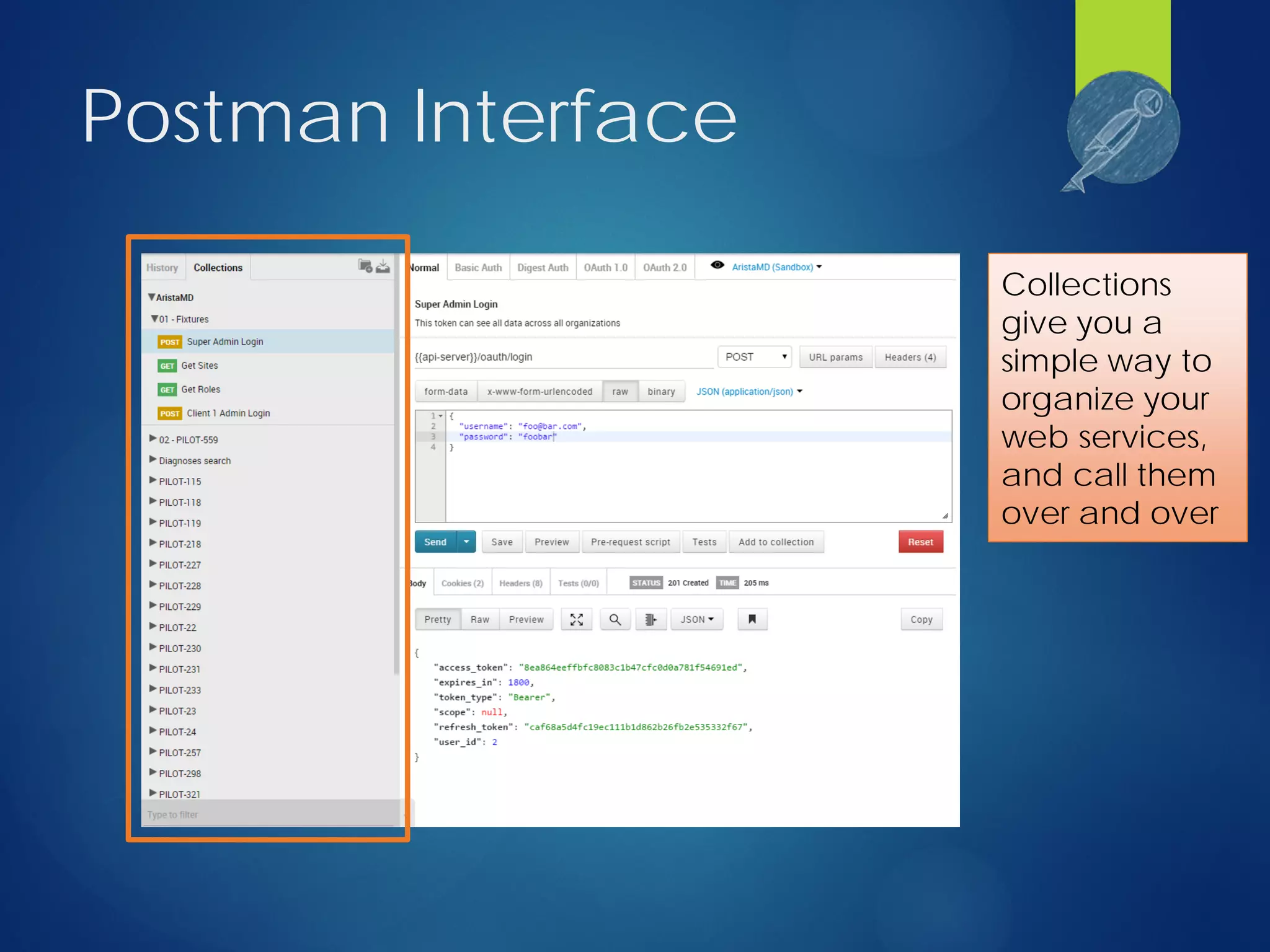
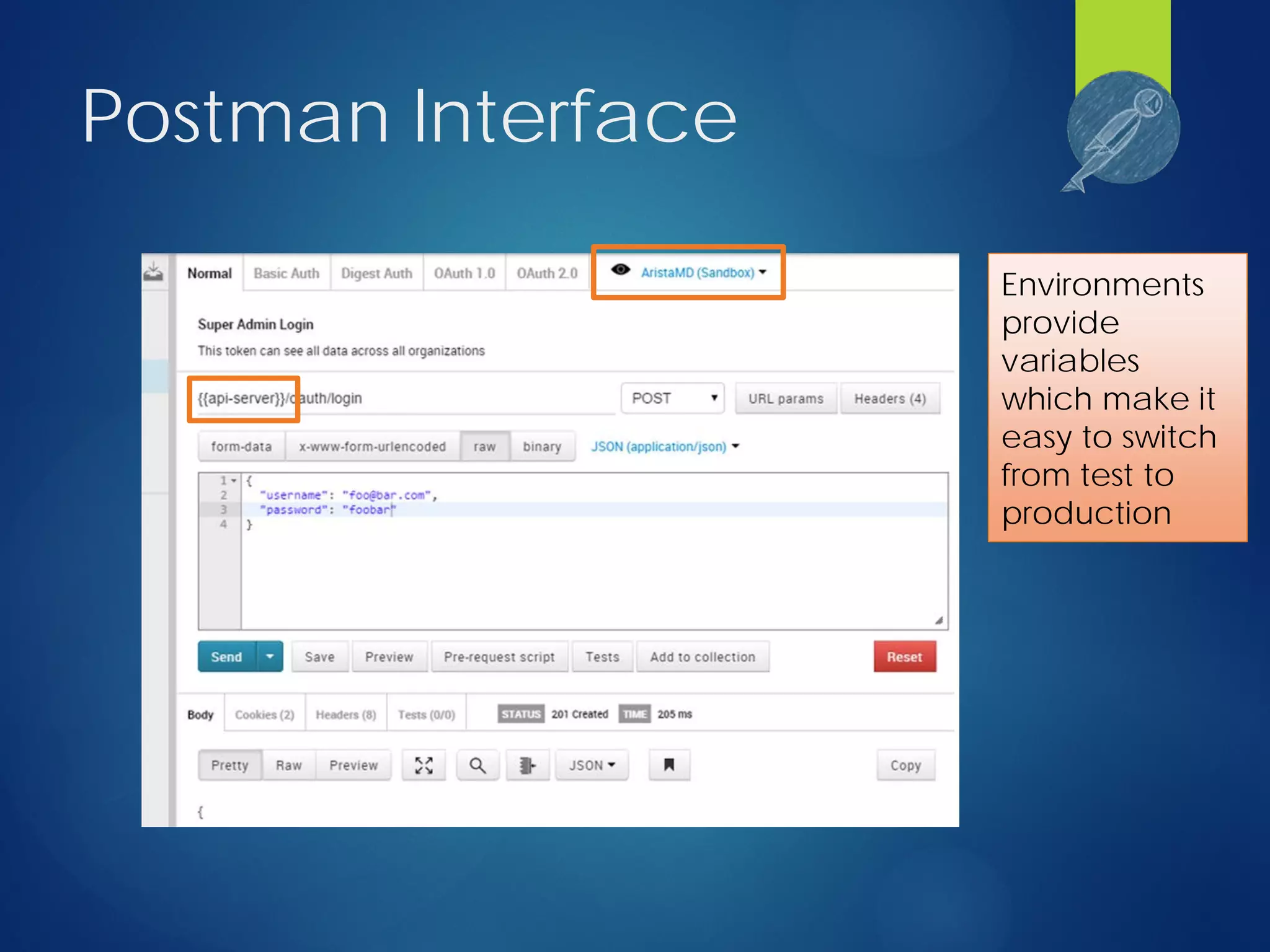
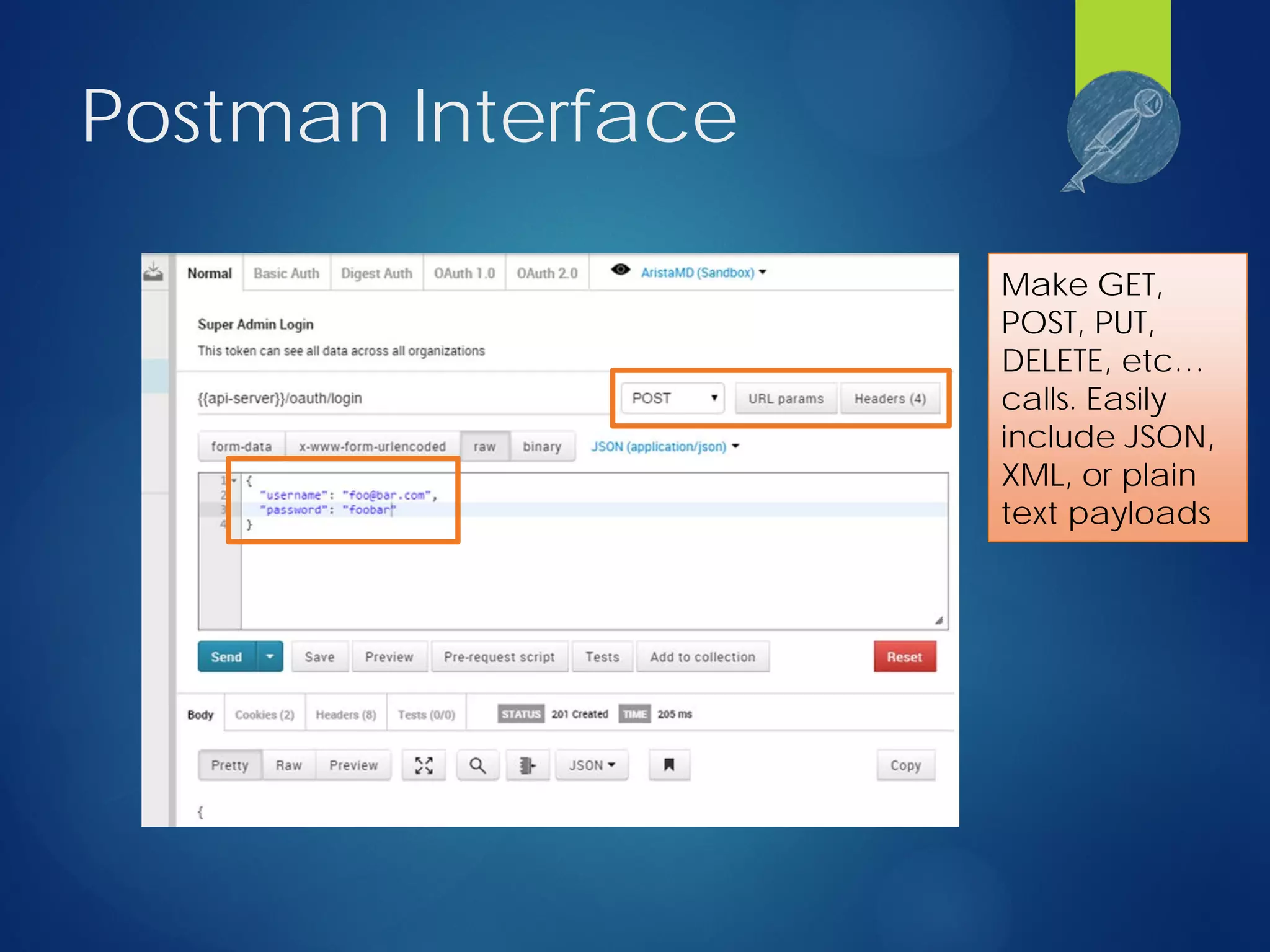
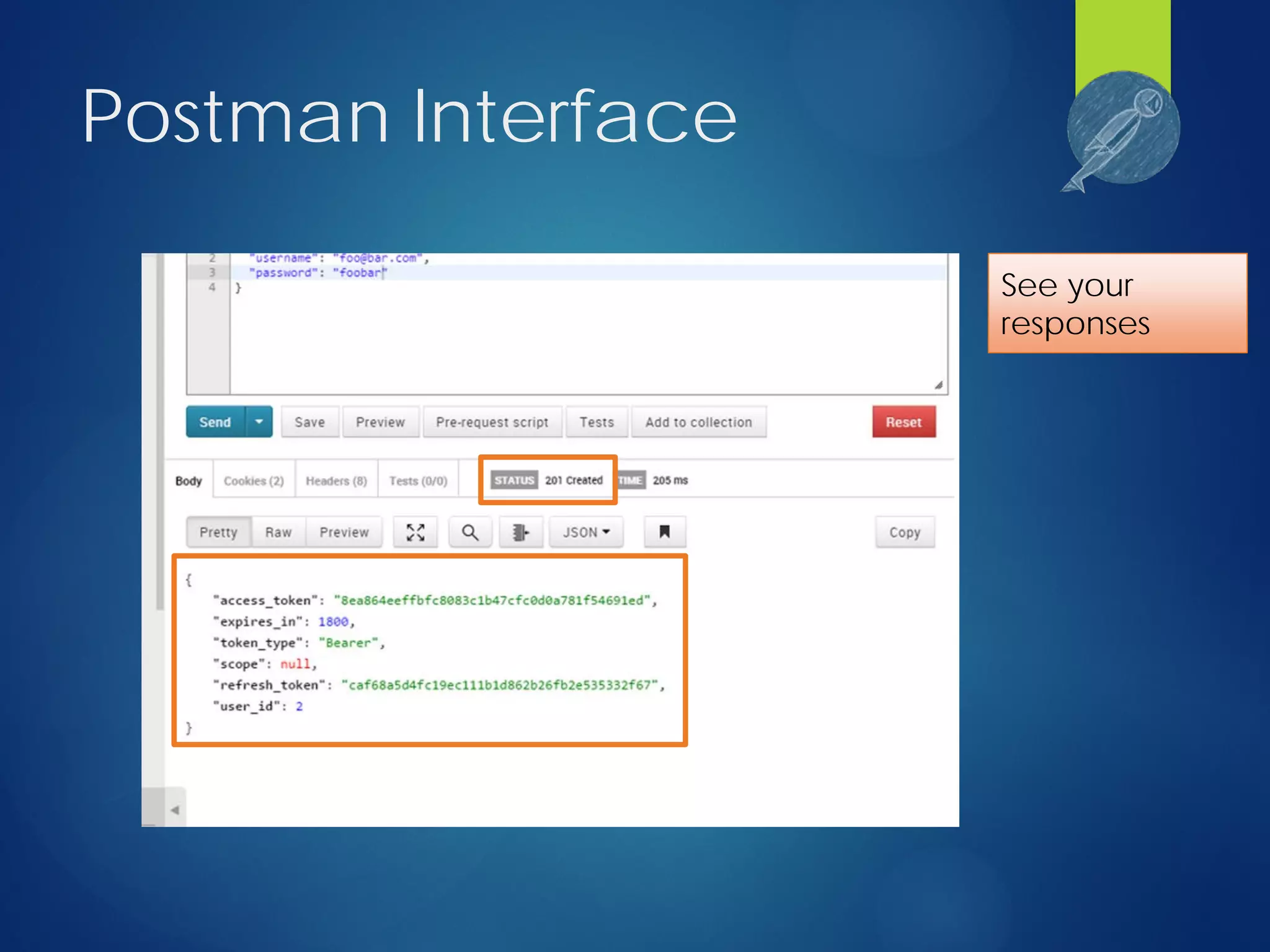
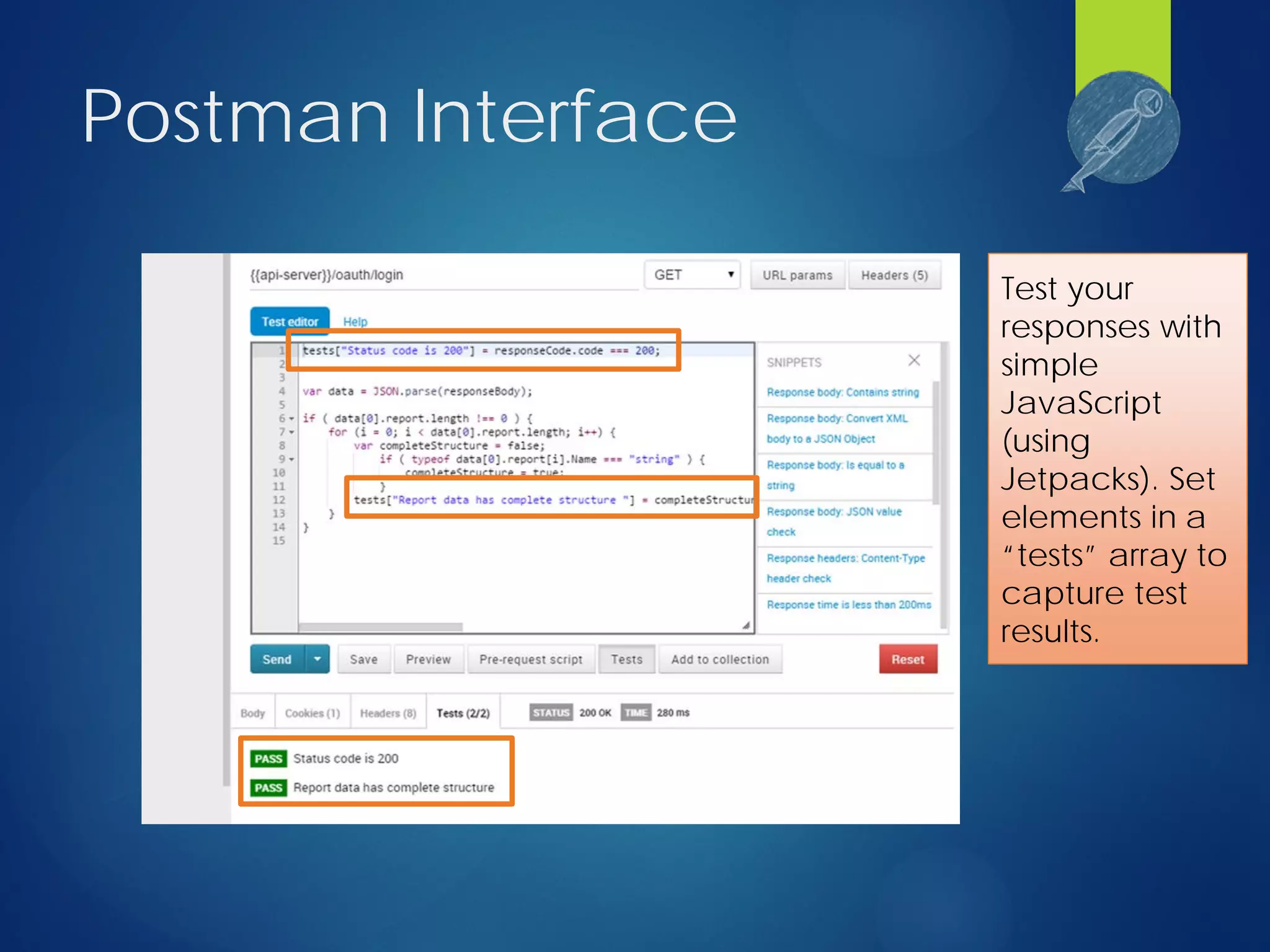
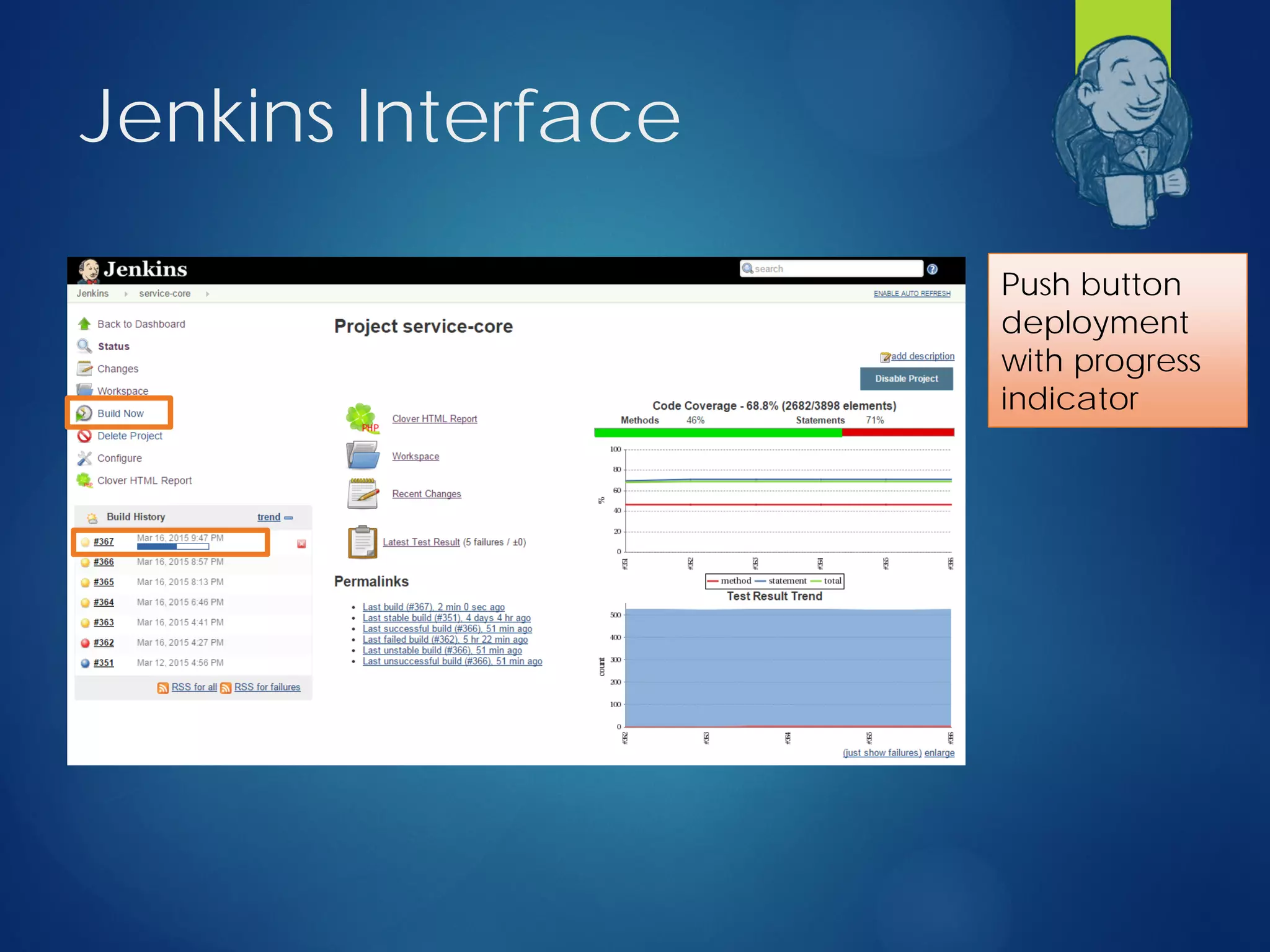
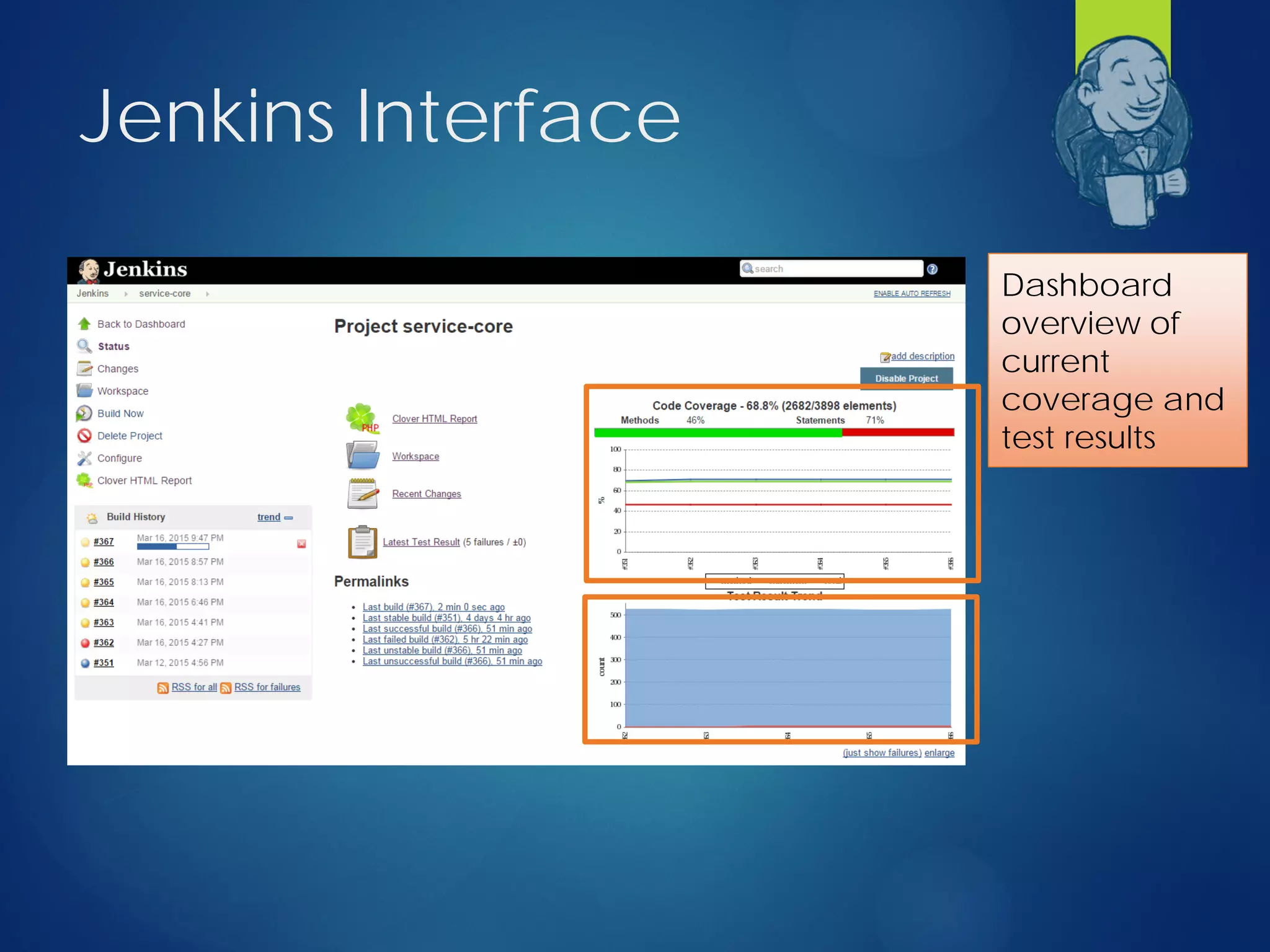
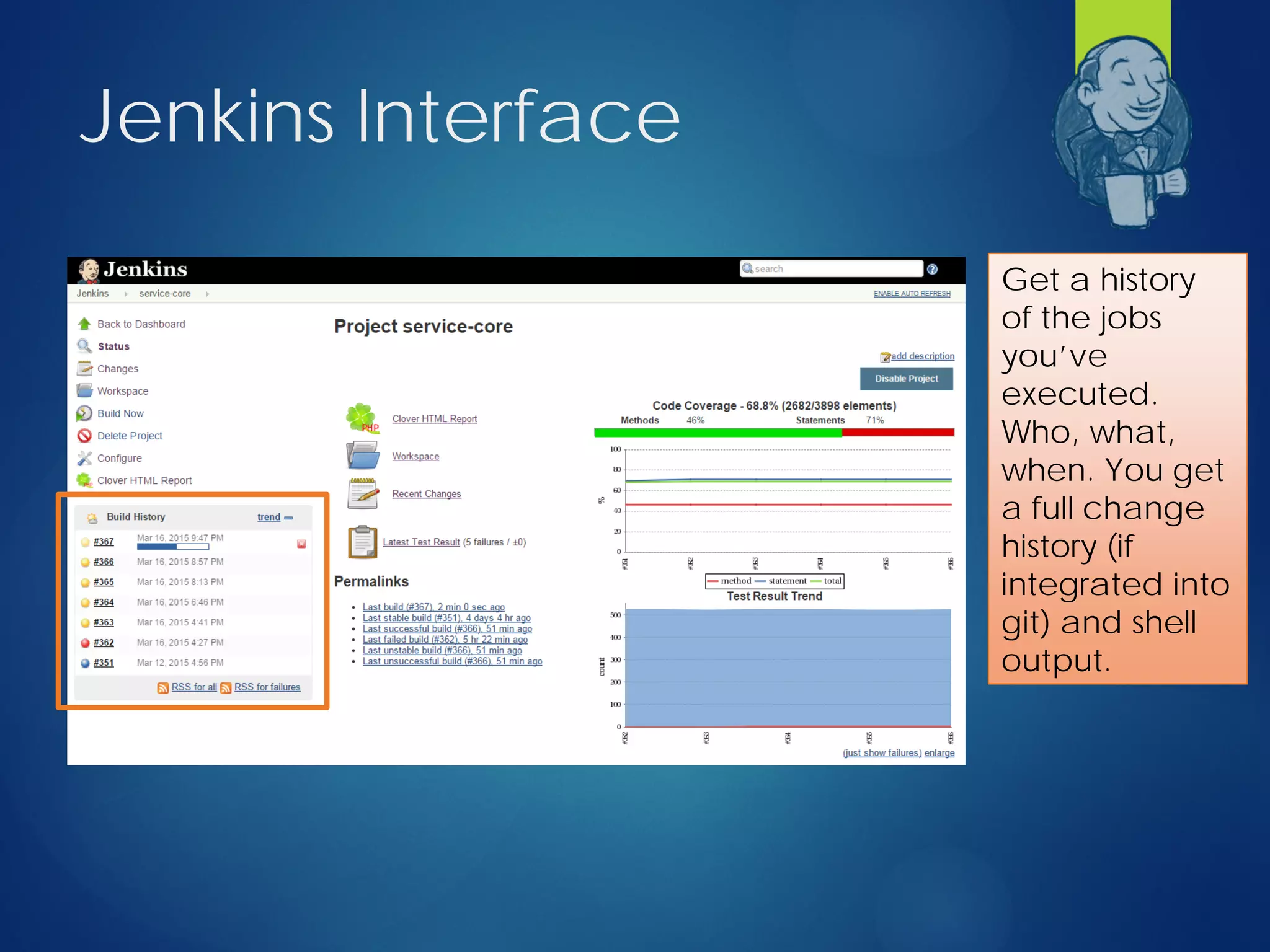
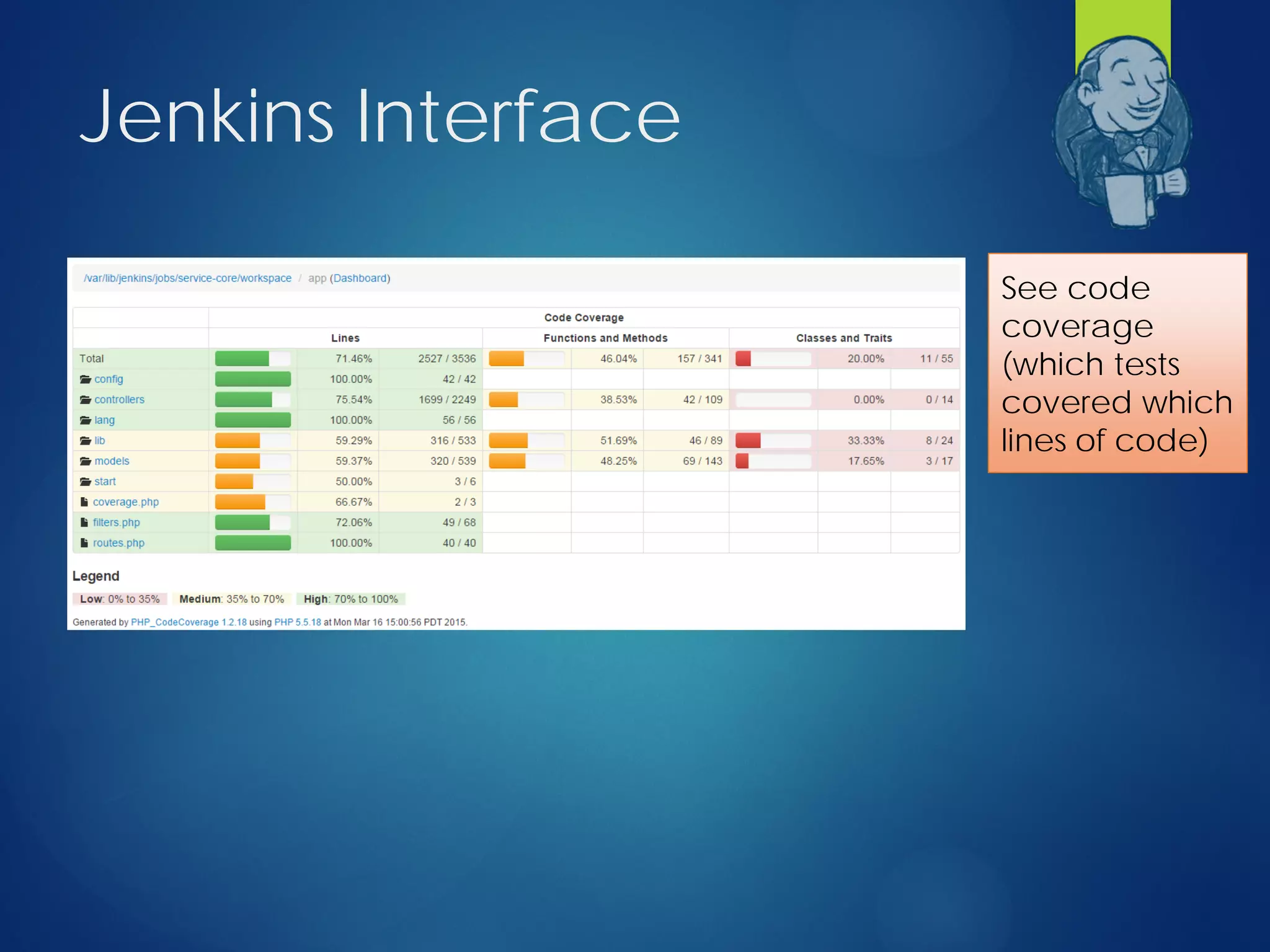
This document discusses integrating test automation and code coverage for web service applications. It introduces Postman for calling web services and testing responses, and Jenkins for build automation and tracking test results over time. It then demonstrates setting up a test automation workflow using these tools on a sample Laravel application, including starting and stopping coverage collection, running tests from Postman and PHPUnit, and merging the results. Some best practices and philosophies around test automation and code coverage are also discussed.