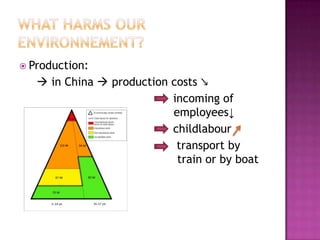
The document discusses regional and seasonal sustainable development. It defines regional as related to a large geographic area near one's home/country, while seasonal refers to products that grow during a certain season. Buying regional and seasonal products supports sustainable development by reducing transportation costs, pollution, and unnatural growing conditions compared to importing out-of-season or distant products. The document also discusses how eco-friendly tourism can support sustainability by reducing waste of natural resources like water, light, fuel, and materials through conservation and recycling.