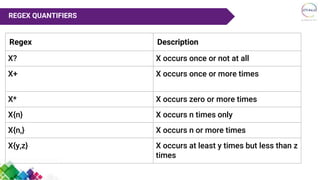
The document discusses regular expressions (regex) in Java. It provides 3 key points:
1. The java.util.regex package provides classes and interfaces for defining regex patterns and matching strings against patterns, including the Pattern, Matcher, and MatchResult classes.
2. The Pattern class compiles a regex into a pattern that can be used for matching. It has methods like compile(), matcher(), and matches() for working with patterns.
3. Examples demonstrate how to use the Pattern and Matcher classes to define patterns, compile them, and match strings against patterns in Java.







![PATTERN METHODS
static Pattern compile(String regex)
Compiles the given regular expression
into a pattern
Matcher matcher(CharSequence input)
Creates a matcher that will match the
given input against this pattern
static boolean matches(String regex, CharSequence
input)
Compiles the given regular expression
and attempts to match the given input
against it
String[] split(CharSequence input)
Splits the given input sequence around
matches of this pattern.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regex1-231013103057-009b694b/85/Regex1-1-pptx-8-320.jpg)




![EXAMPLE
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(".xx.");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher("MxxY");
System.out.println("Input String matches regex -
"+matcher.matches());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regex1-231013103057-009b694b/85/Regex1-1-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![EXAMPLE -2 (REGEX EXAMPLE IN JAVA)
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]){
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(".s");
Matcher m = p.matcher("as");
boolean b = m.matches();
boolean b2=Pattern.compile(".s").matcher("as").matches();
boolean b3 = Pattern.matches(".s", "as");
System.out.println(b+" "+b2+" "+b3);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regex1-231013103057-009b694b/85/Regex1-1-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![The . (dot) represents a single character.
REGULAR EXPRESSION .
import java.util.regex.*;
class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(Pattern.matches(".s", "as"));
System.out.println(Pattern.matches(".s", "mk"));
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regex1-231013103057-009b694b/85/Regex1-1-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![REGEX CHARACTER CLASSES
[abc] a, b, or c (simple class)
[^abc] Any character except a, b, or c (negation)
[a-d[m-p]] a through d, or m through p: [a-dm-p]
(union)
[a-z&&[def]] d, e, or f (intersection)
[a-z&&[^bc]] a through z, except for b and c: [ad-z]
(subtraction)
[a-z&&[^m-p]] a through z, and not m through p: [a-lq-
z](subtraction)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regex1-231013103057-009b694b/85/Regex1-1-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![REGEX META CHARACTERS
. Any character (may or may not
match line terminators)
d A digit: [0-9]
D A non-digit: [^0-9]
s A whitespace character: [
tnx0Bfr]
S A non-whitespace character: [^s]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regex1-231013103057-009b694b/85/Regex1-1-pptx-17-320.jpg)