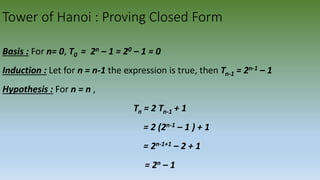
The document discusses three recurrent problems: the Tower of Hanoi problem, the lines in the plane problem, and the Josephus problem. It explains that recurrent problems can be solved using recursion, where the solution to a problem relies on previously solved smaller instances of the same problem. It provides details on the recursive solutions and recurrence relations for calculating the number of moves in the Tower of Hanoi problem and the maximum number of regions created by lines in a plane. It also outlines the general steps to solve a recurrent problem by finding a closed-form expression through a recurrence relation and mathematical induction.