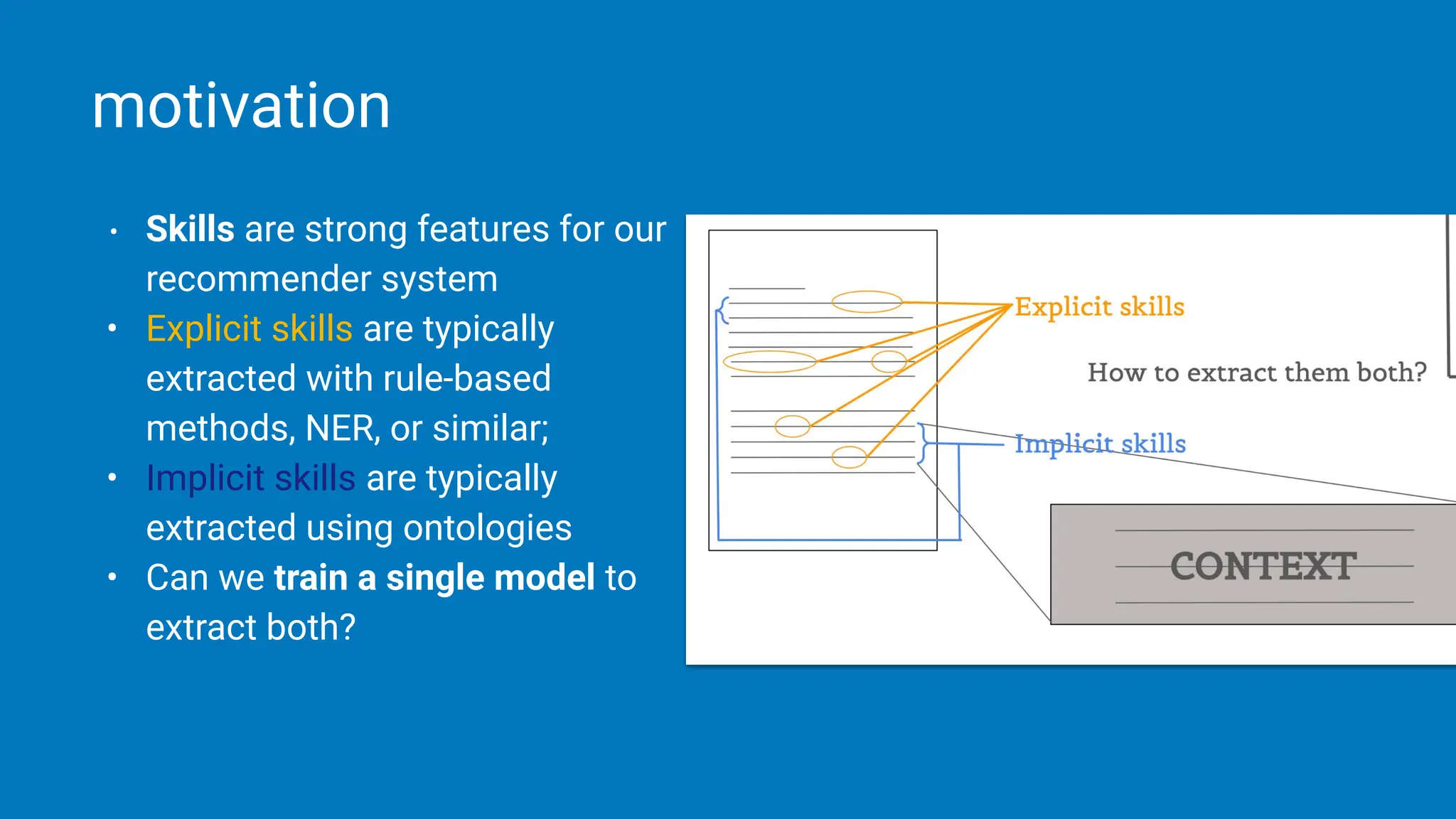
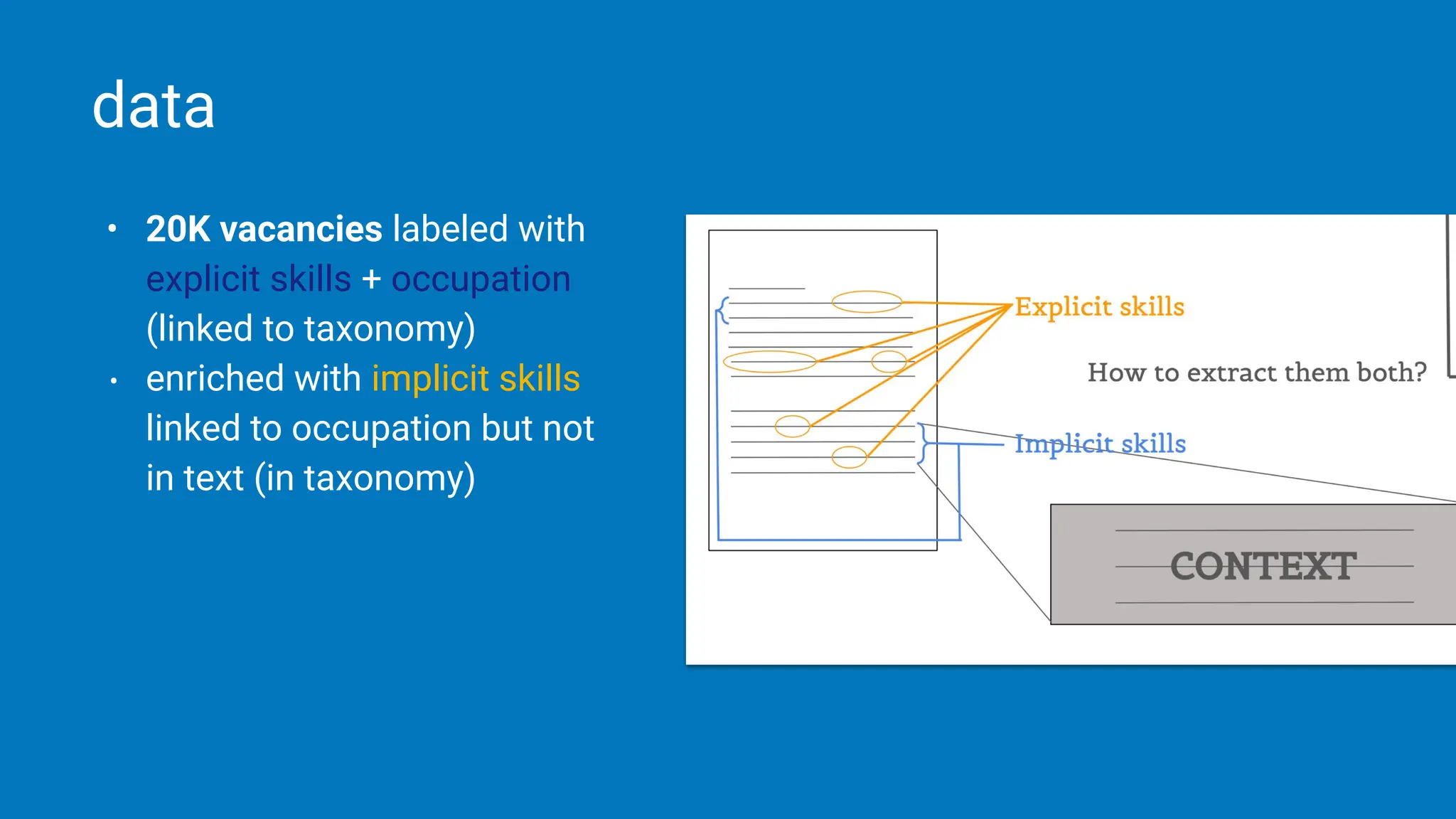
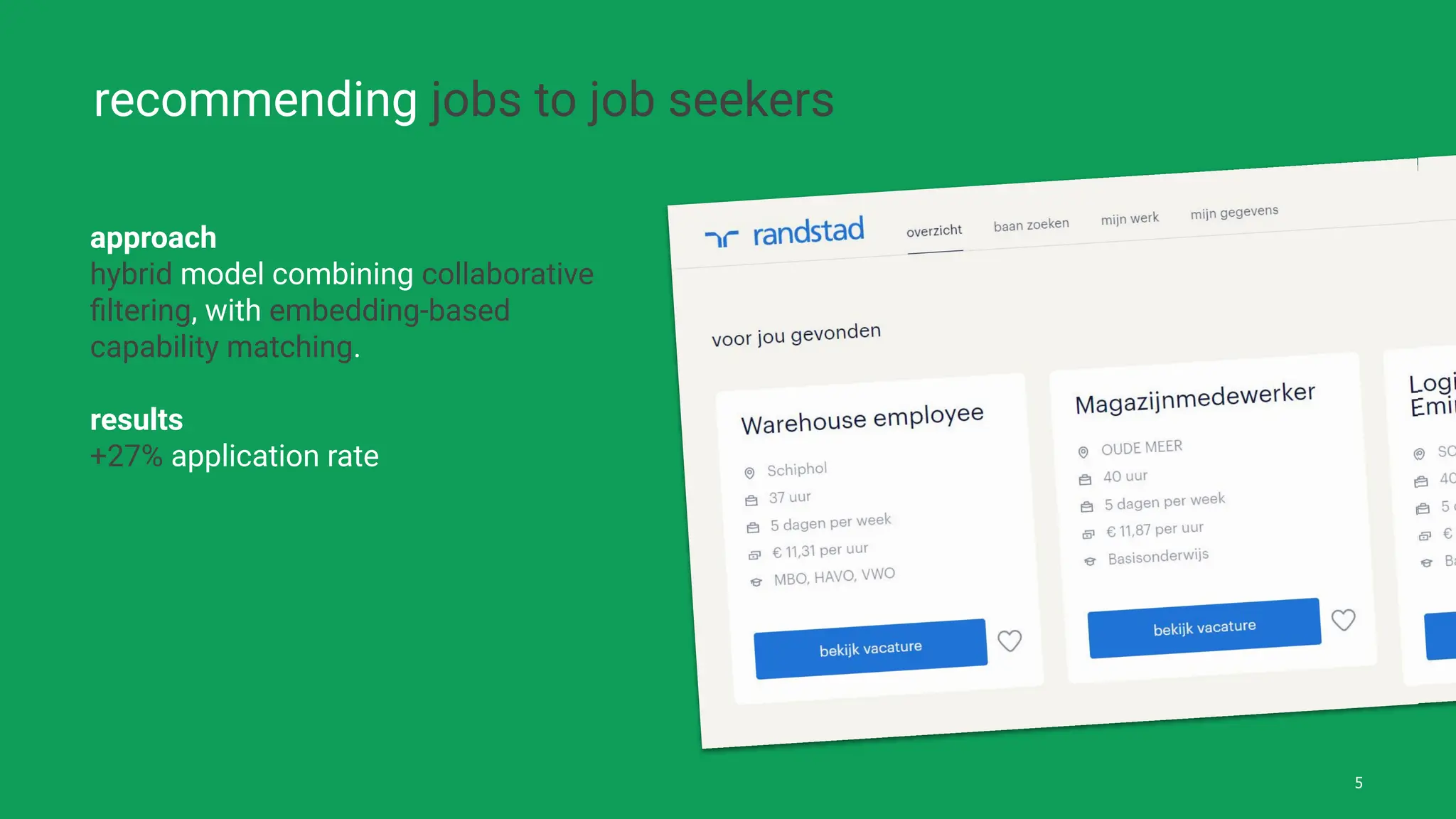
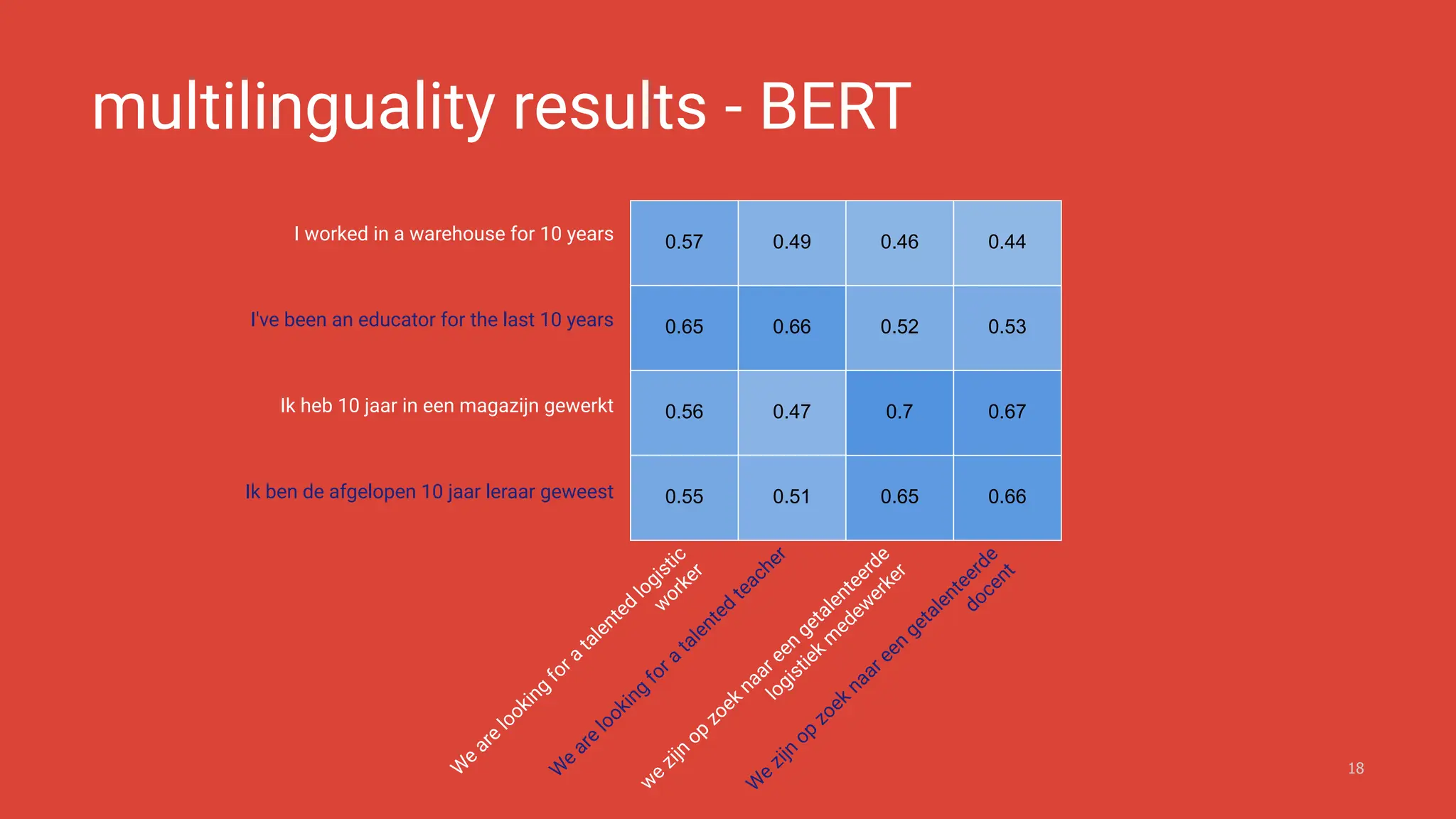
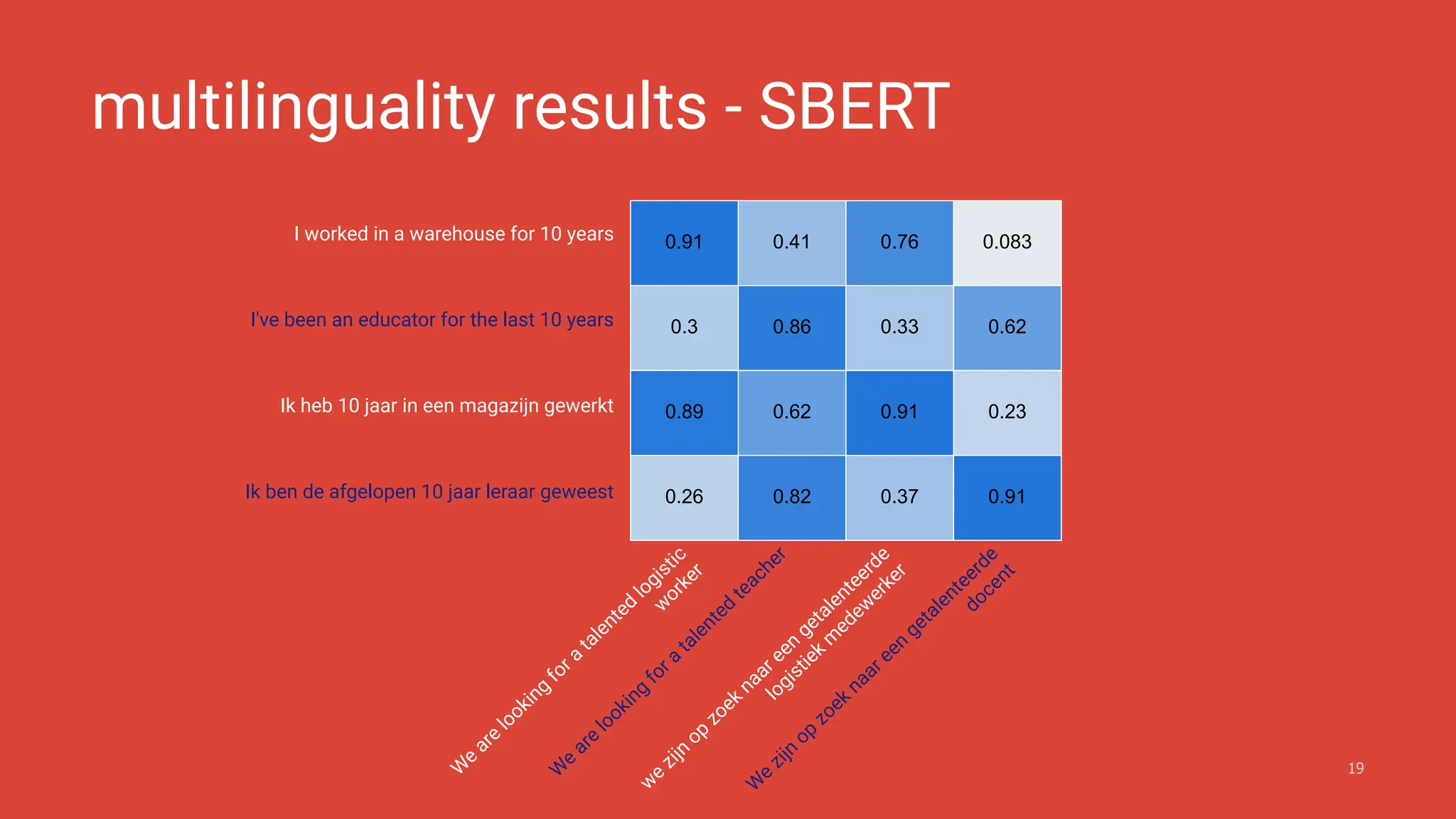
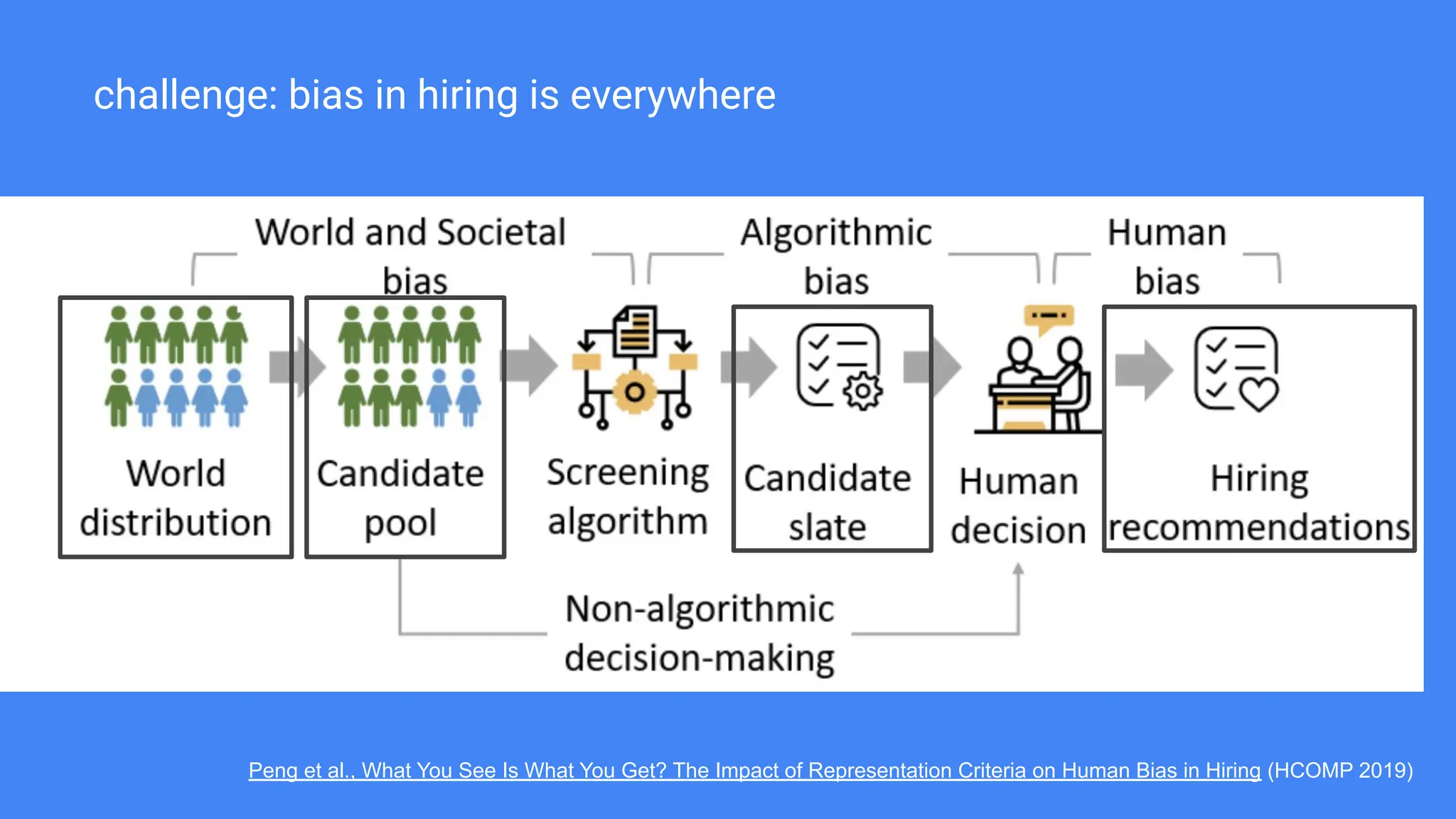
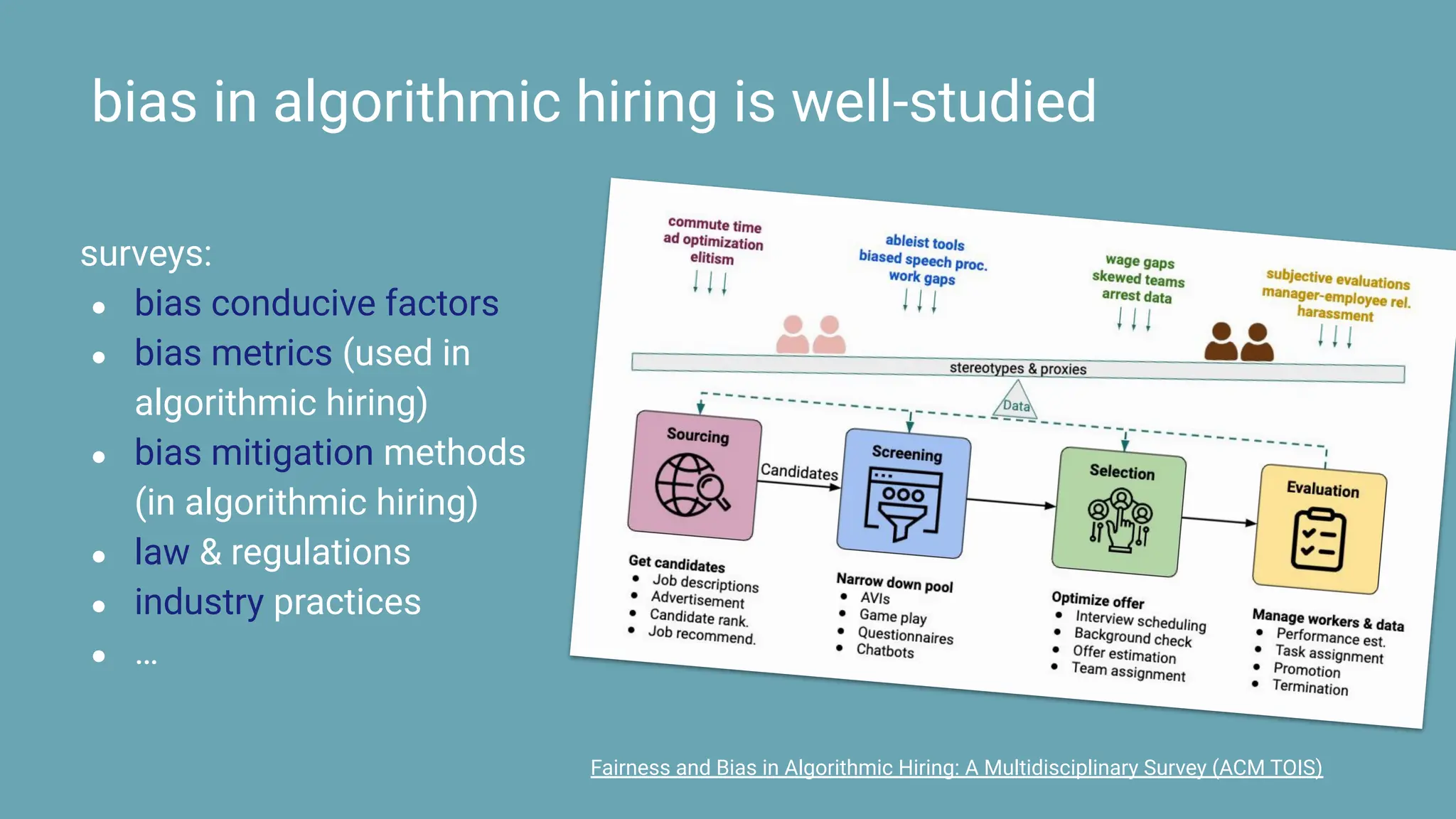
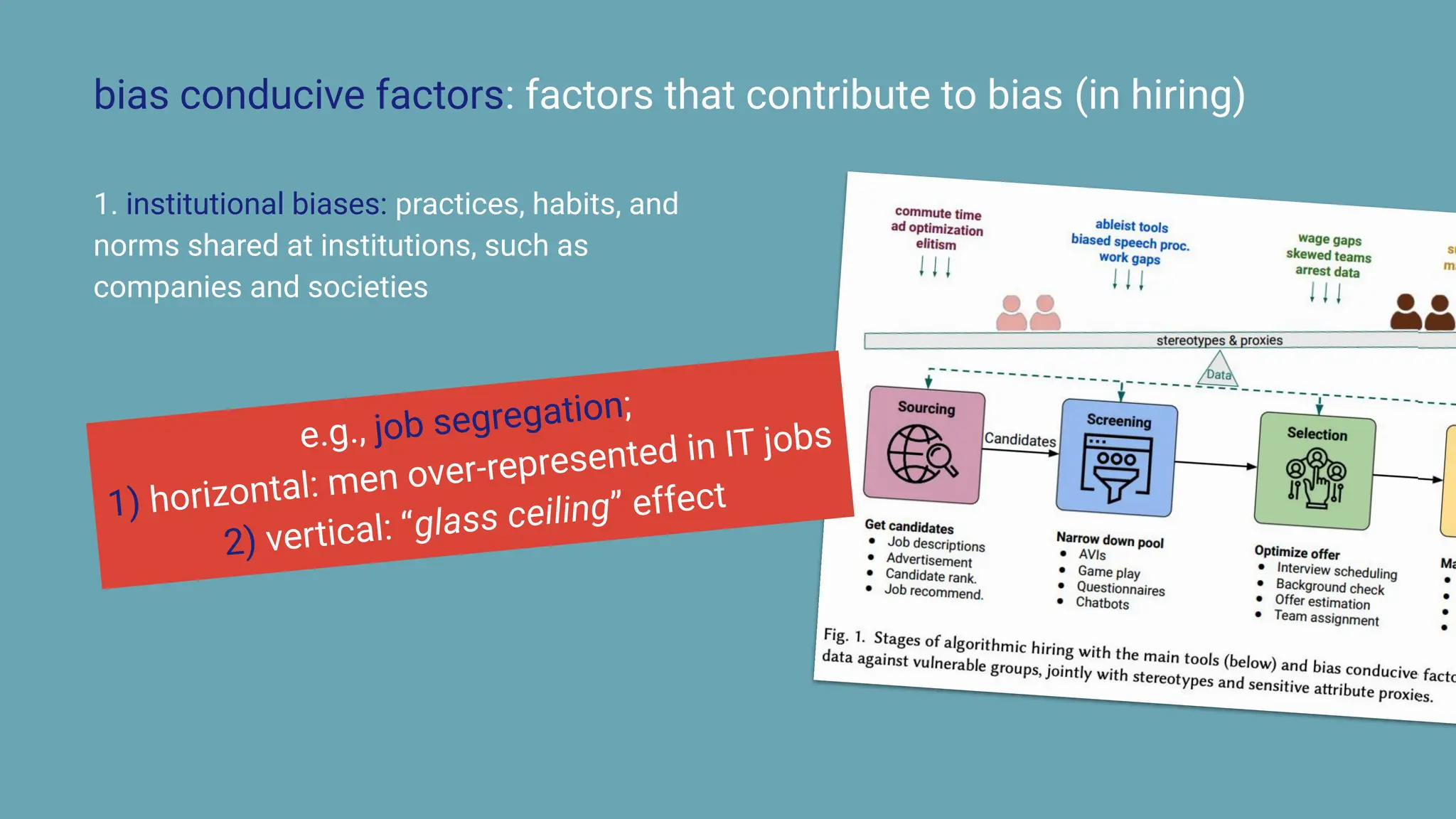
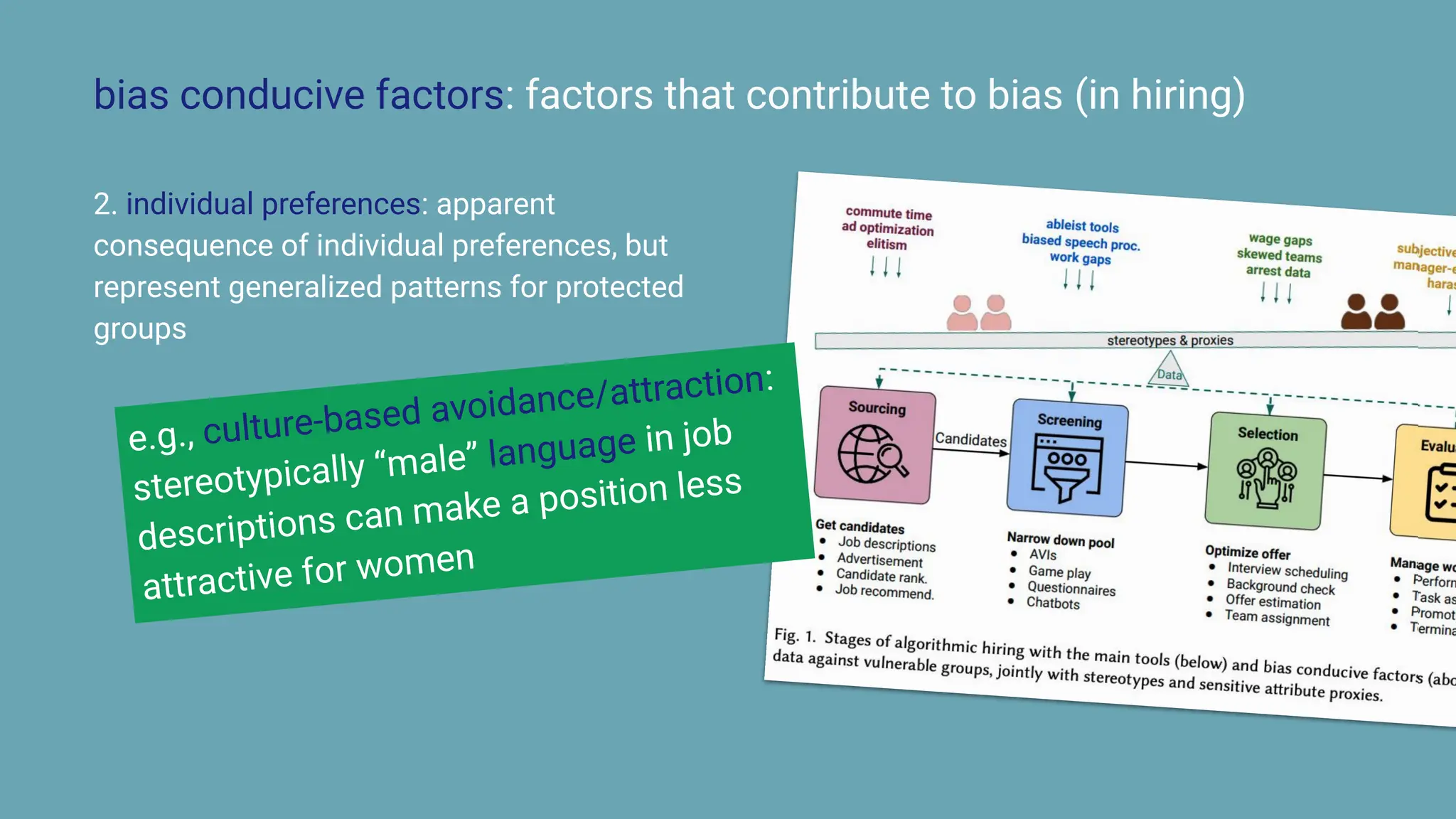
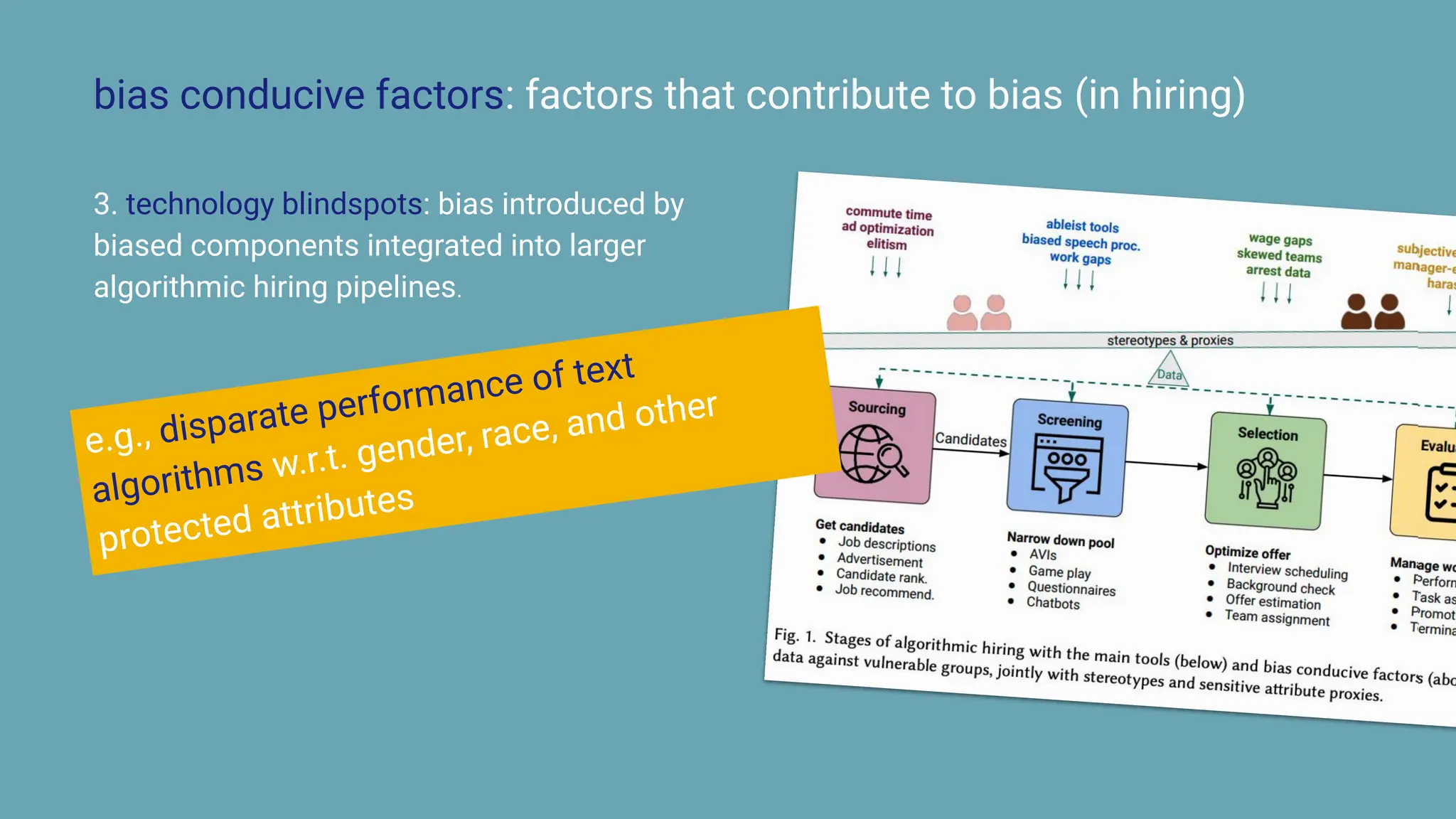
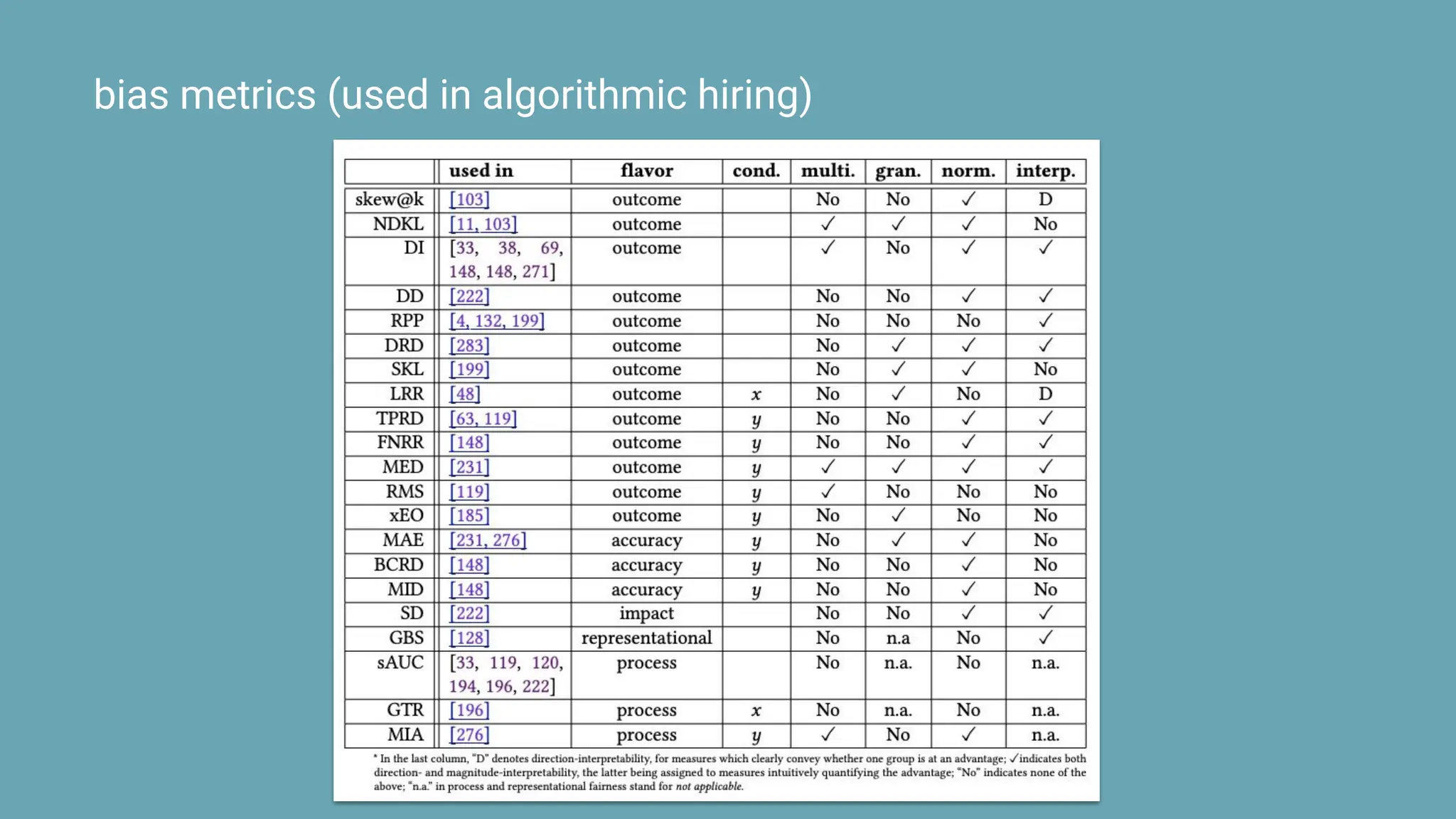
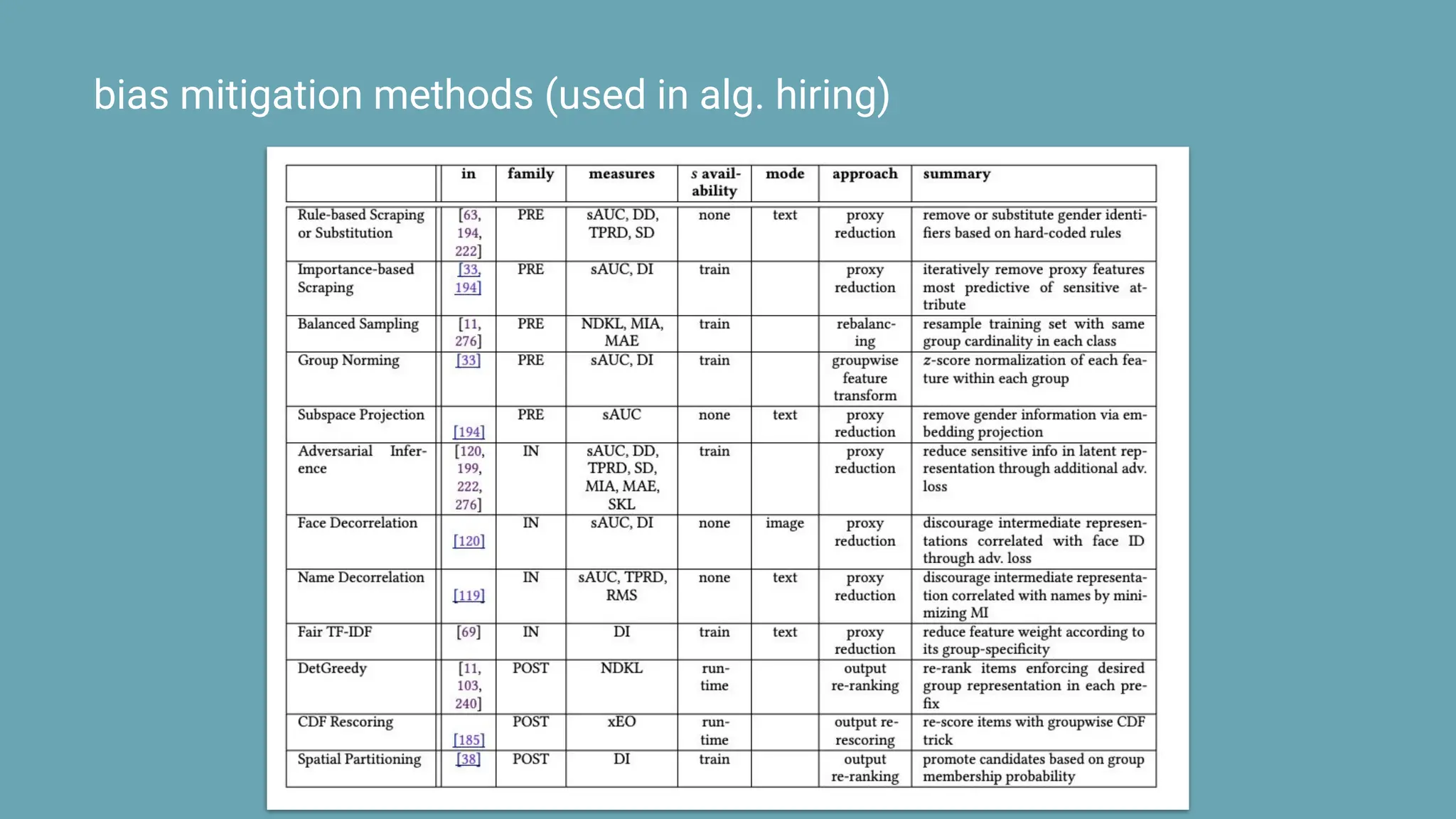
The document discusses the challenges and solutions of bias in hiring, specifically pertaining to recommender systems and natural language processing (NLP). It highlights the impact of bias in job applications, with examples of disparities based on gender and race, and presents various bias mitigation strategies including synthetic data generation and fairness-aware ranking. Additionally, it covers advancements in multilingual text processing for improved skill extraction and recommends adopting collaborative models to enhance algorithmic fairness in hiring practices.










![in humans...
“Given CVs from real-life
scientists [...] with names
changed to traditional male and
female names”
Turns out that both men and
women were more likely to
hire male job applicants than
female with an identical
record.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illcrecommendersystemsbiasandbiasmitigationinhiring1-241211194001-6874dfd9/75/recommender-systems-bias-and-bias-mitigation-in-hiring-22-2048.jpg)
![in humans...
“White” names received 50%
more callbacks for interviews
[than “African-American”
names]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illcrecommendersystemsbiasandbiasmitigationinhiring1-241211194001-6874dfd9/75/recommender-systems-bias-and-bias-mitigation-in-hiring-23-2048.jpg)
![Amazon’s system [...]
penalized résumés that
included the word
“women’s”, as in “women’s
chess club captain”. And it
downgraded graduates of
two all-women’s colleges.
…in “AI tools”...
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illcrecommendersystemsbiasandbiasmitigationinhiring1-241211194001-6874dfd9/75/recommender-systems-bias-and-bias-mitigation-in-hiring-24-2048.jpg)





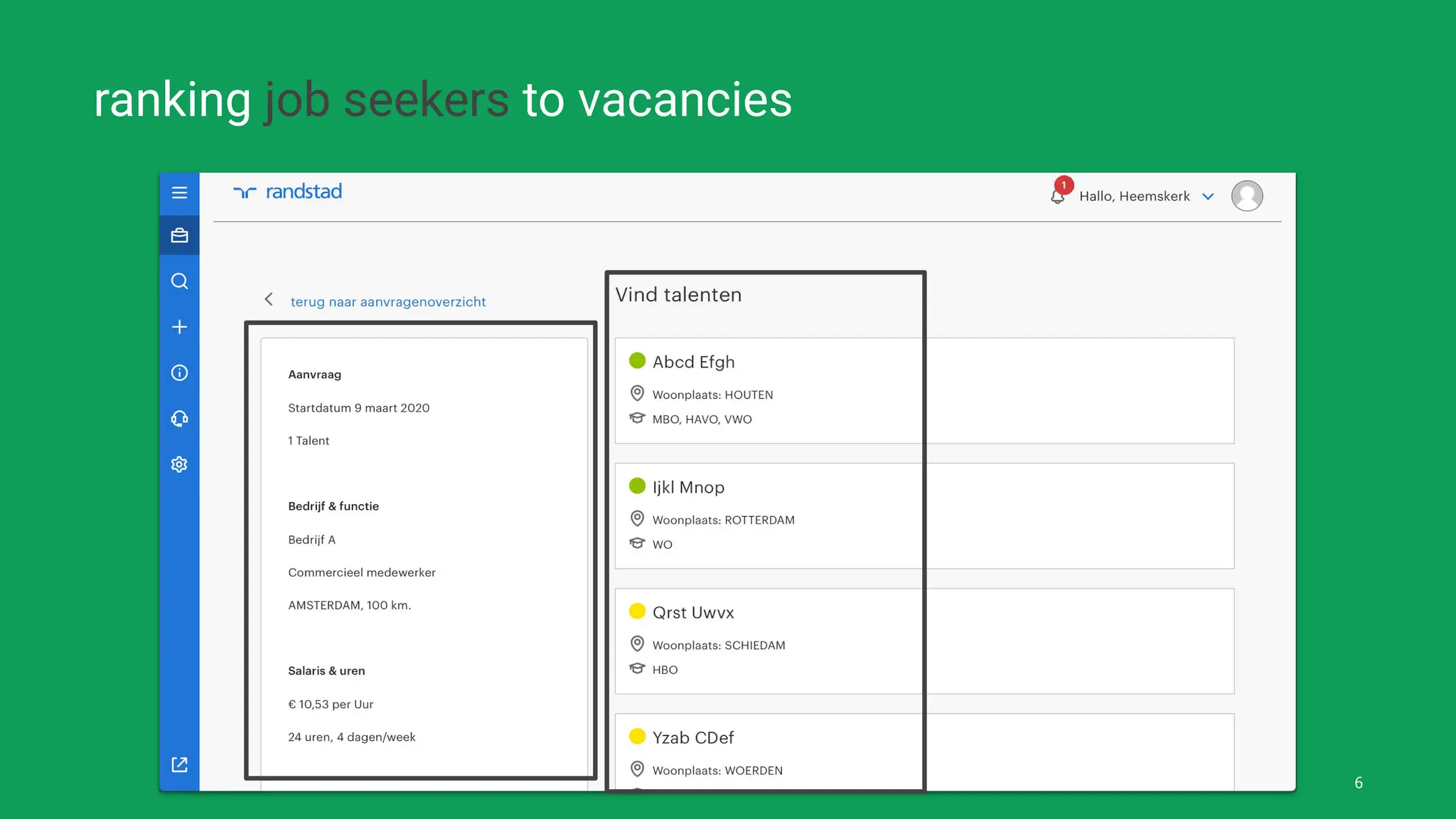
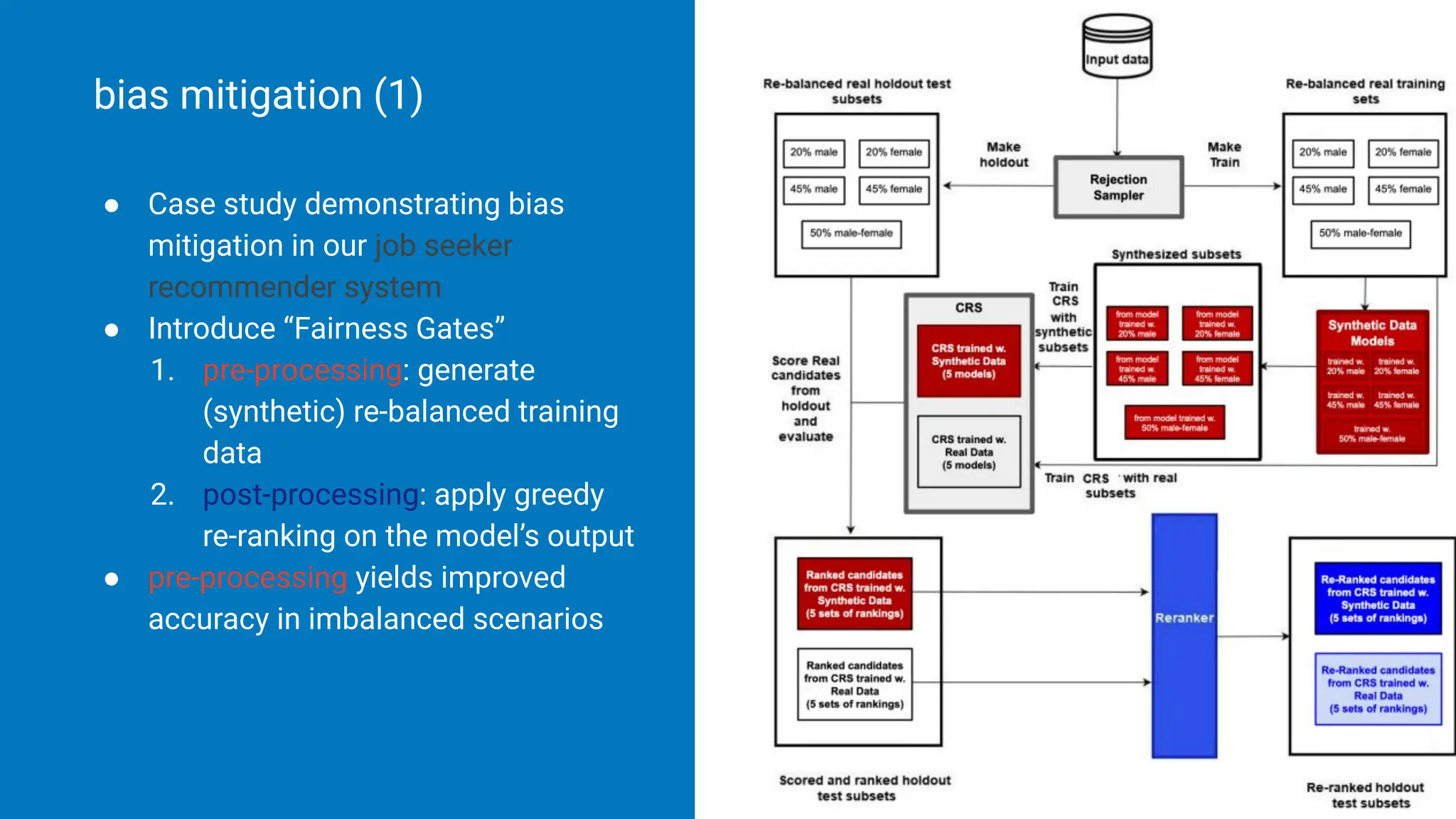
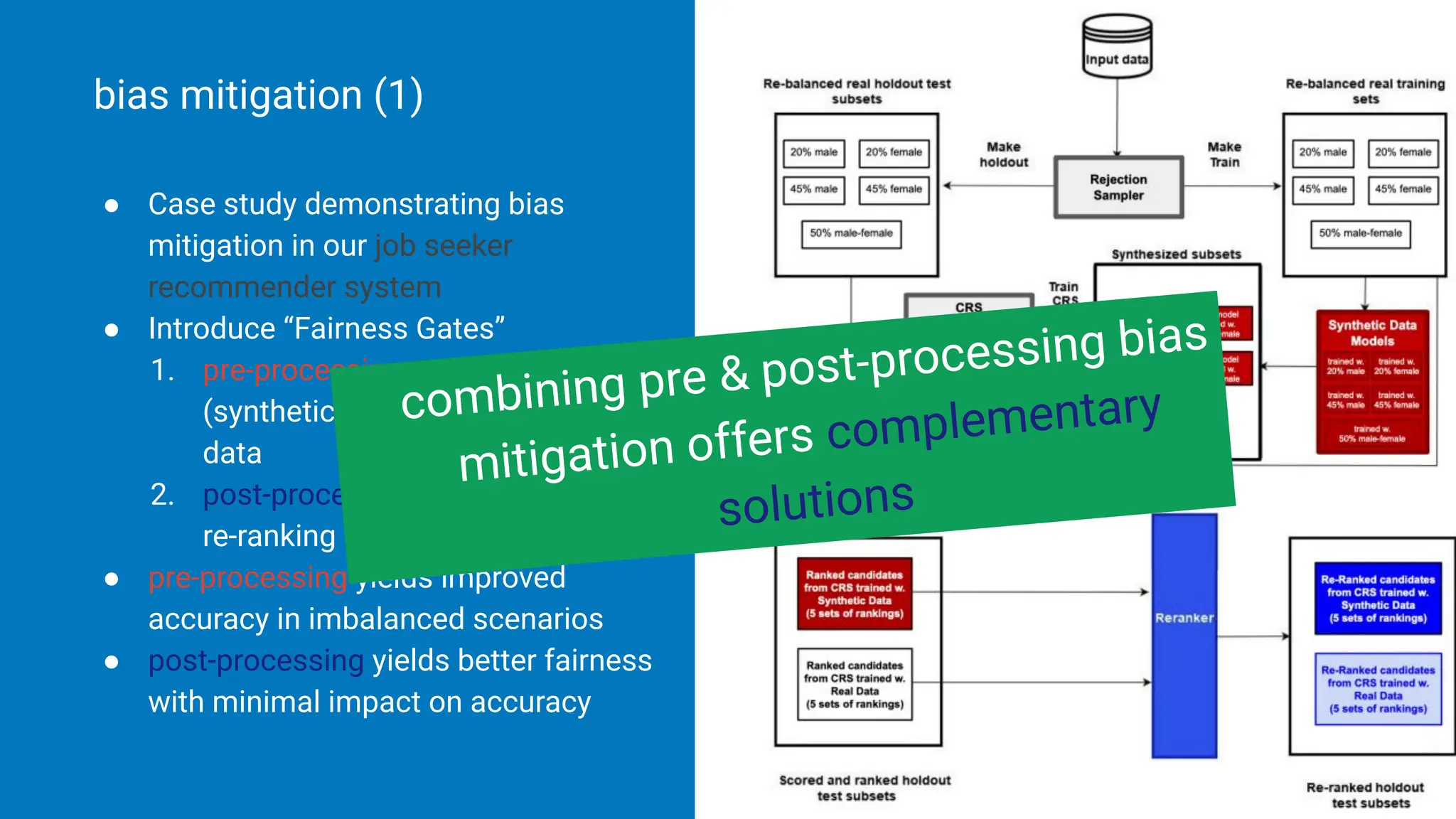
![● Case study demonstrating bias
mitigation in our job seeker
recommender system
● Introduce “Fairness Gates”
1. pre-processing: generate
(synthetic) re-balanced training
data
2. post-processing: apply greedy
re-ranking on the model’s output [1]
bias mitigation (1)
[2] Fairness-Aware Ranking in Search & Recommendation Systems
with Application to LinkedIn Talent Search](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illcrecommendersystemsbiasandbiasmitigationinhiring1-241211194001-6874dfd9/75/recommender-systems-bias-and-bias-mitigation-in-hiring-36-2048.jpg)


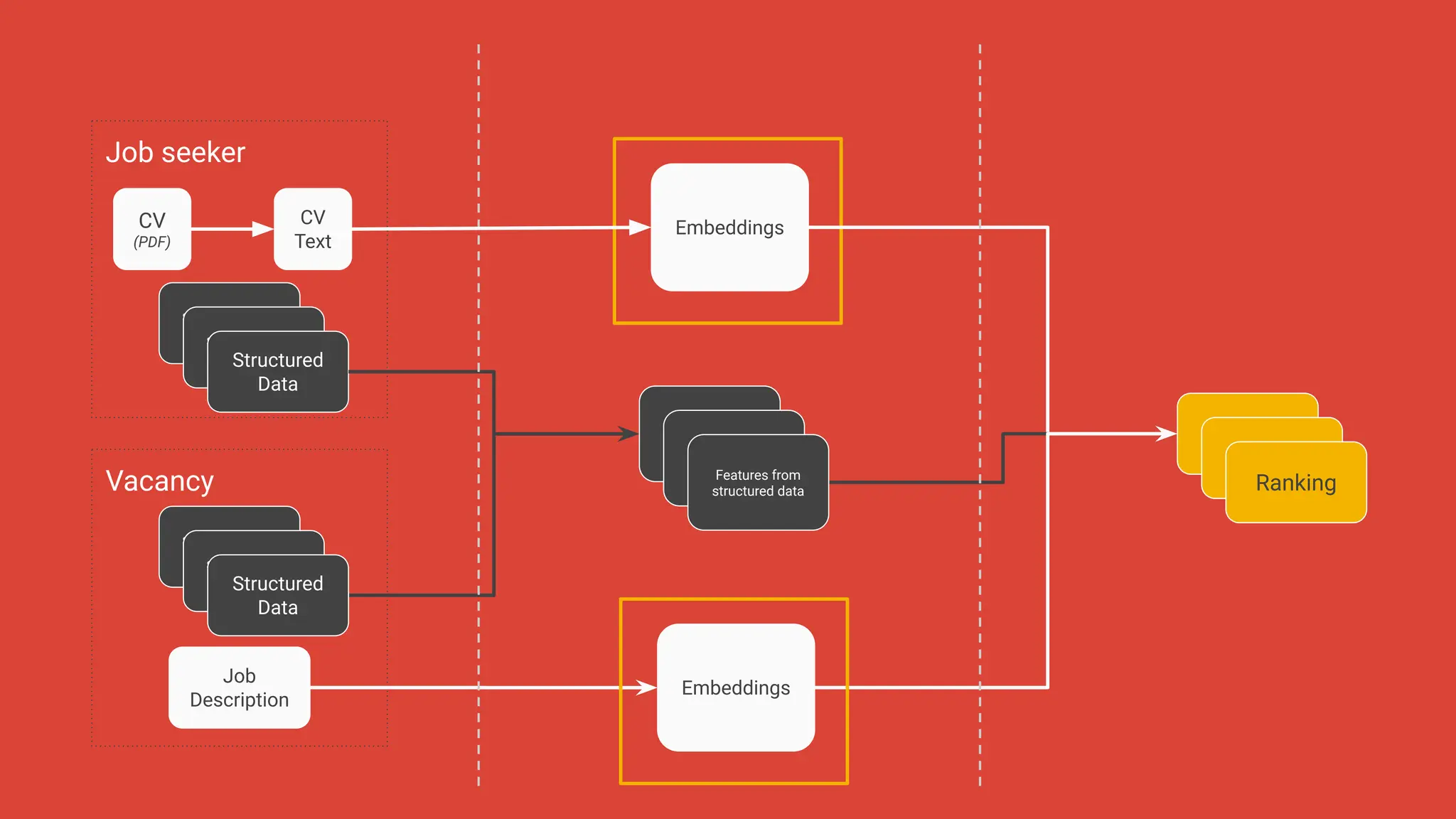
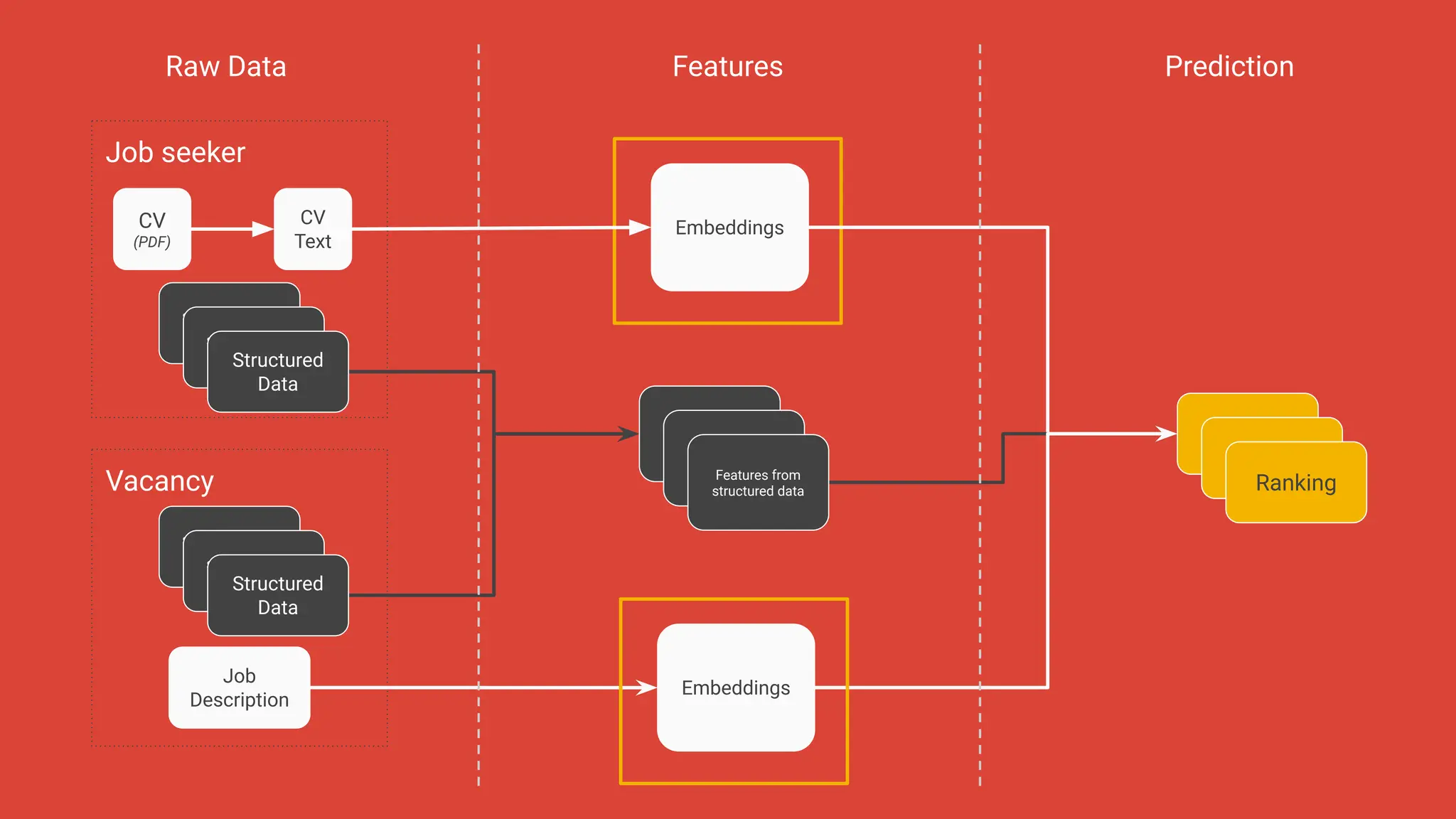
![Job seeker
CV
(PDF)
CV
Text
Structured Data (e.g location)
Structured Data (e.g location)
Structured Data
age 32
gender M
phone +311234567890
John Doe
+311234567890
Work History:
- Company XYZ - Senior Software
Engineer - 2018-2022 Developed
software solutions for clients.
Collaborated with team members on
project planning and execution.
- Company ABC - Software Developer -
2015-2018 Designed and implemented
software features. Conducted code
reviews and provided feedback to team
members [...].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illcrecommendersystemsbiasandbiasmitigationinhiring1-241211194001-6874dfd9/75/recommender-systems-bias-and-bias-mitigation-in-hiring-42-2048.jpg)
![2-stage approach:
1. (para)phrase questions
John Doe
+311234567890
Work History:
Company XYZ - Senior Software
Engineer - 2018-2022 Developed
software solutions for clients.
Collaborated with team members
on project planning and
execution.
Company ABC - Software
Developer - [...].
questions
what is your age?
what is your gender?
what is your phone number?
attribute answer
age 32
gender M
phone +311234567890
mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer
mT5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illcrecommendersystemsbiasandbiasmitigationinhiring1-241211194001-6874dfd9/75/recommender-systems-bias-and-bias-mitigation-in-hiring-43-2048.jpg)
![2-stage approach:
1. (para)phrase questions
2. fine-tune mT5
John Doe
+311234567890
Work History:
Company XYZ - Senior Software
Engineer - 2018-2022 Developed
software solutions for clients.
Collaborated with team members
on project planning and
execution.
Company ABC - Software
Developer - [...].
questions
what is your age?
what is your gender?
what is your phone number?
attribute answer
age 32
gender M
phone +311234567890
mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer
mT5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/illcrecommendersystemsbiasandbiasmitigationinhiring1-241211194001-6874dfd9/75/recommender-systems-bias-and-bias-mitigation-in-hiring-44-2048.jpg)