The document discusses the design and implementation of recommendation systems, focusing on functional and non-functional requirements, data collection strategies, and the handling of challenges like cold starts and sparsity. It outlines a step-by-step approach to developing these systems, including the use of collaborative filtering and content-based algorithms, along with the importance of A/B testing and user feedback for optimization. The presentation emphasizes a hybrid recommendation strategy and involves leveraging embeddings and data processing techniques to enhance relevance and personalization.





![5
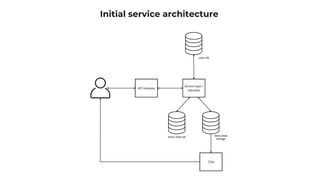
Functional requirements
Provide a set of the most relevant items for a user.
Handle cold start and the sparsity problems.
Support multiple platforms.
Control recommendation diversity.
Ensure real-time updates of recommendation results.
Present the approach with a step-by-step process.
API:
- getRelevantItems(userProfile, count) -> [ItemId]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recsys-230806173119-00782006/85/Recommendation-systems-6-320.jpg)


![10
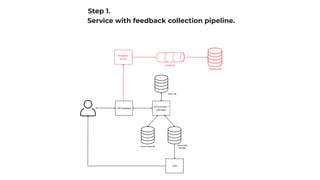
Feedback collection
It's essential to understand how users interact with items.
Usually, the pace of data collection is rapid.
Data includes implicit feedback (e.g., items listened to or viewed).
Data also includes explicit feedback (e.g., movie ratings or e-commerce item reviews).
Data is a primary source for most recommendation algorithms.
Consider implementing batching for data processing.
API: recordFeedback([(userId, itemId, feedback, ts)]) -> void](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recsys-230806173119-00782006/85/Recommendation-systems-12-320.jpg)

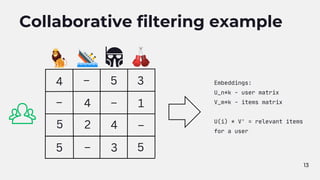
![14
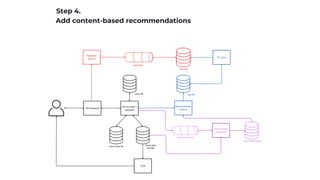
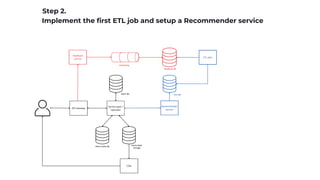
Implement collaborative filtering
Having the feedback collection already in place we can analyze (user, item)
interactions in past history.
Given this pairs we want to compute embeddings for users and items.
Can be done using Matrix factorization.
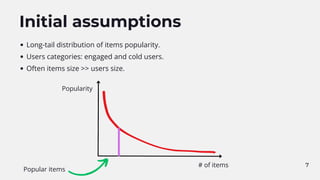
Mostly works only for popular items and engaged users (remember the long tail chart).
Deploy and measure (A/B test).
Embeddings (same length "latent" vectors):
user_n = [0.12, 0.234, 0.34, ..., 0.893]
item_n = [0.843, 0.553, 0.123, ..., 0.23]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recsys-230806173119-00782006/85/Recommendation-systems-18-320.jpg)

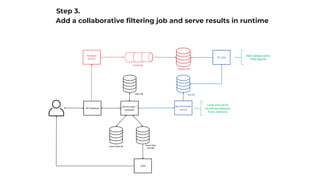
![16
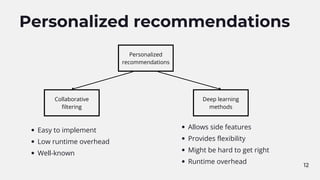
Tackling long tail problem
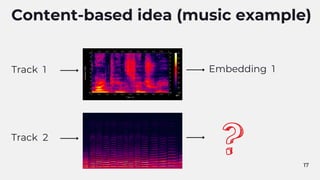
Content-based algorithms are popular in this field.
It's possible to learn content features based on well-known collaborative filtering data.
For example, if a track sounds close to an another track their embeddings should be
similar.
We can produce embeddings based on content features even without users'
interaction.
Use a vector database to find a set of similar items for an item given.
Deploy and measure (A/B test).
Vector DB API: getSimilarItems(itemId, count) -> [ItemId]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recsys-230806173119-00782006/85/Recommendation-systems-21-320.jpg)