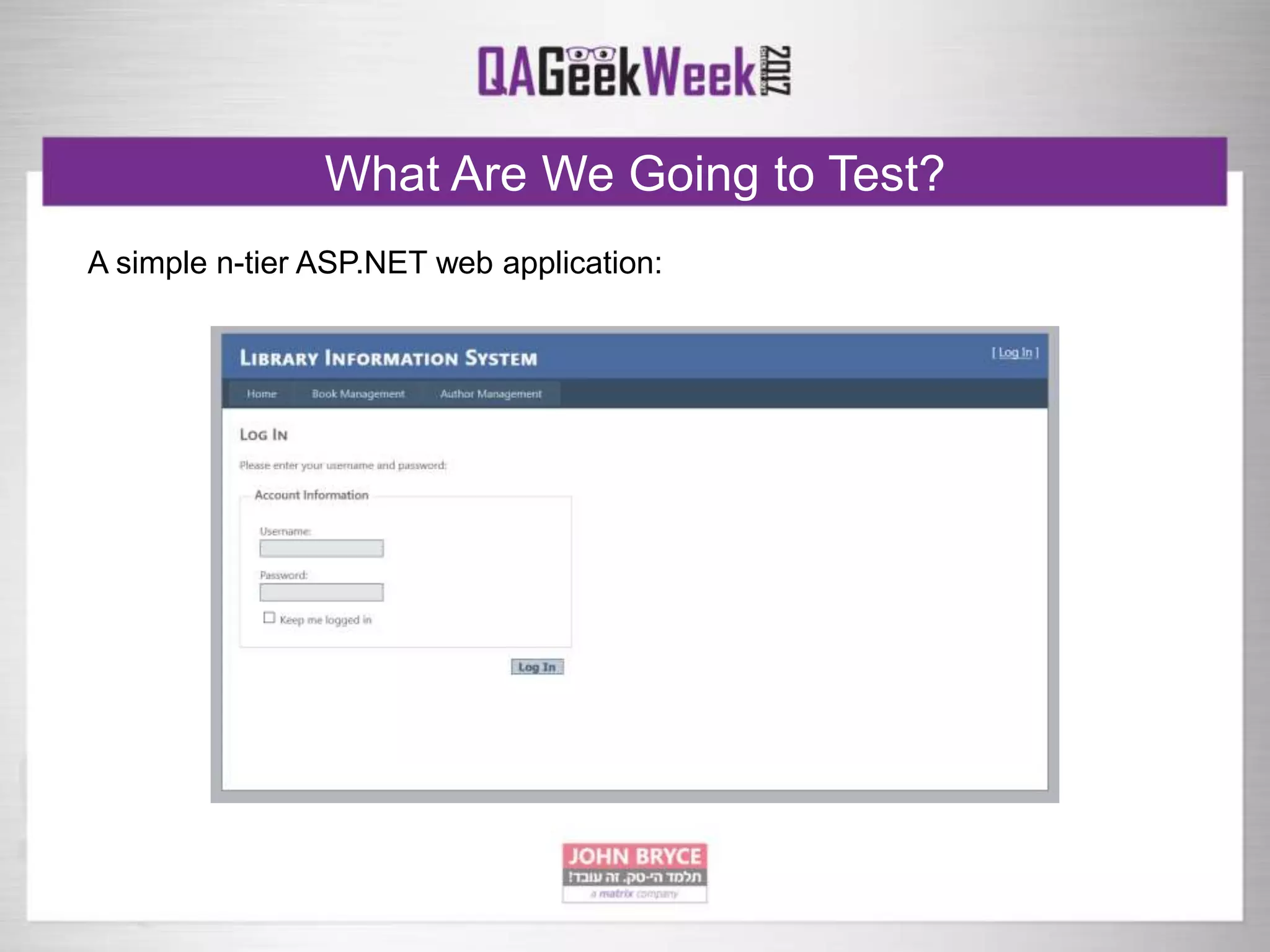
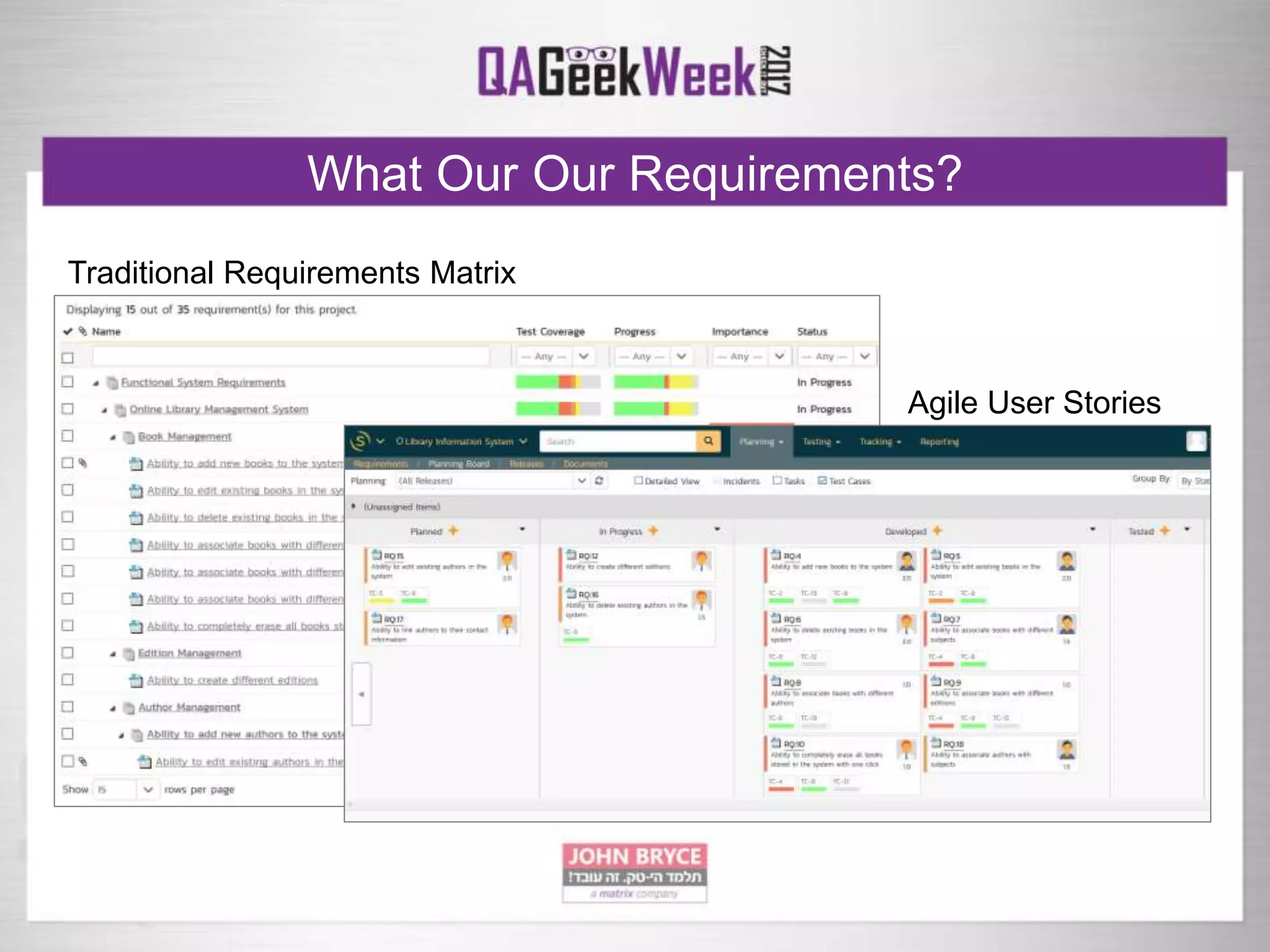
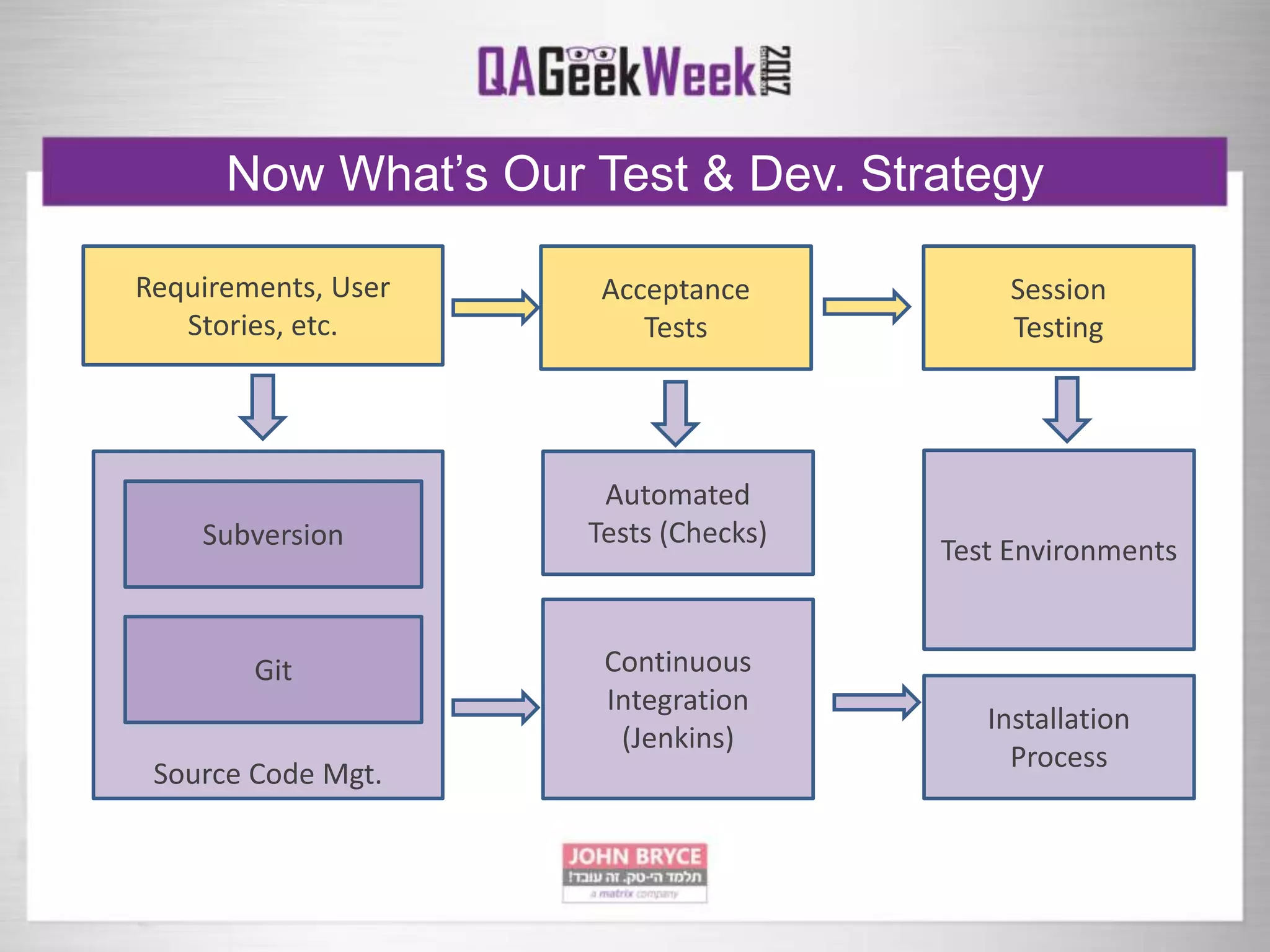
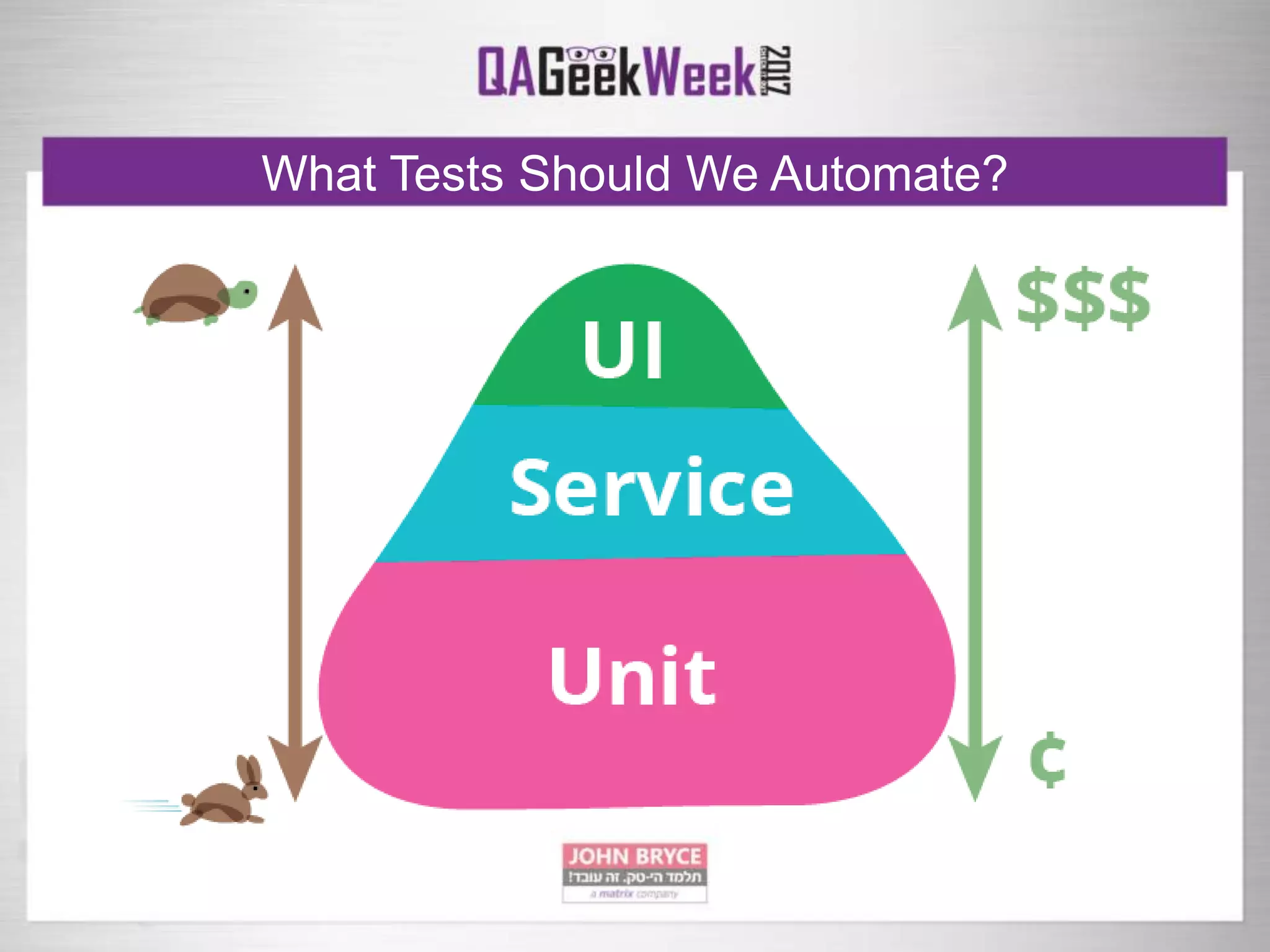
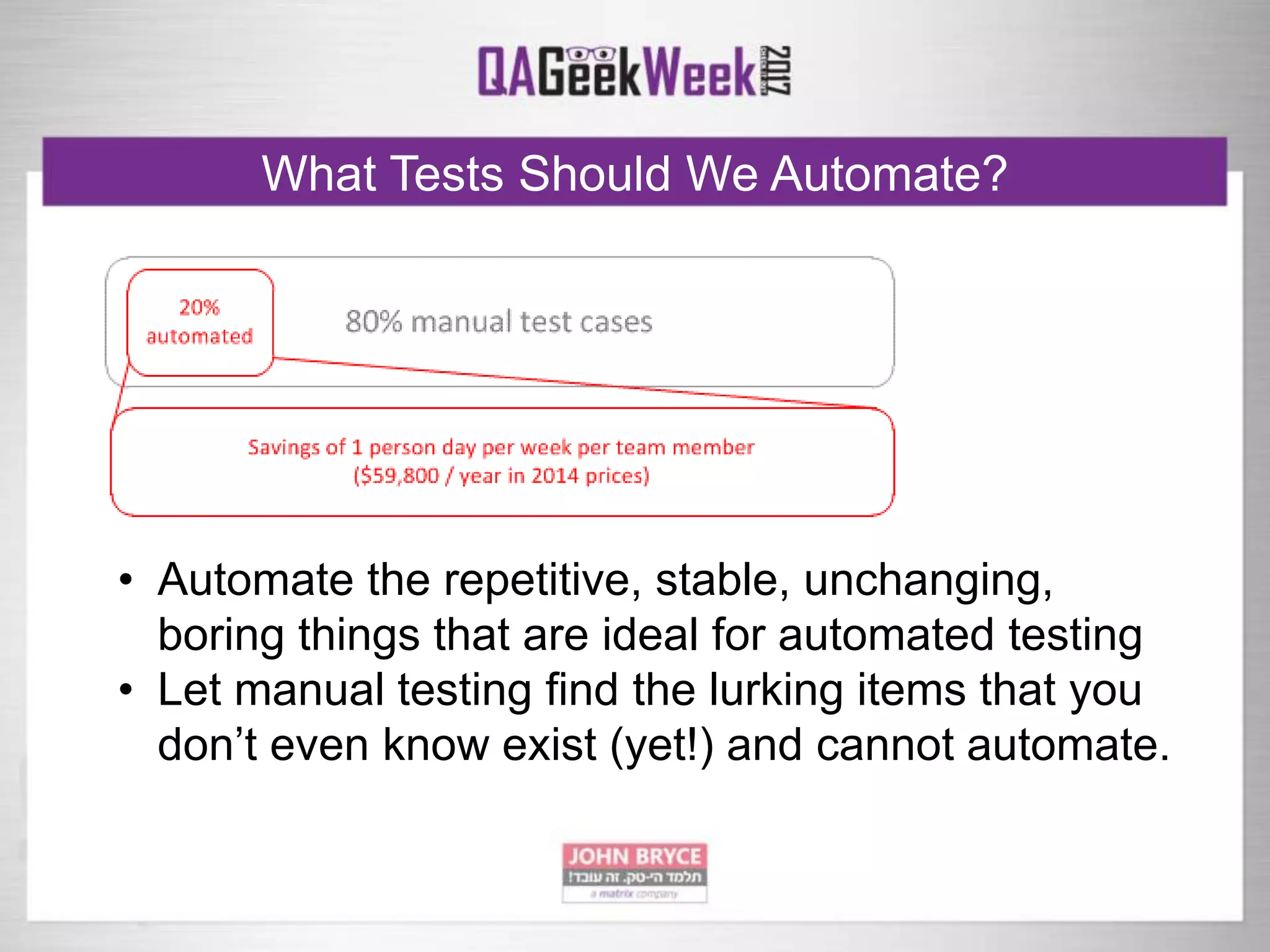
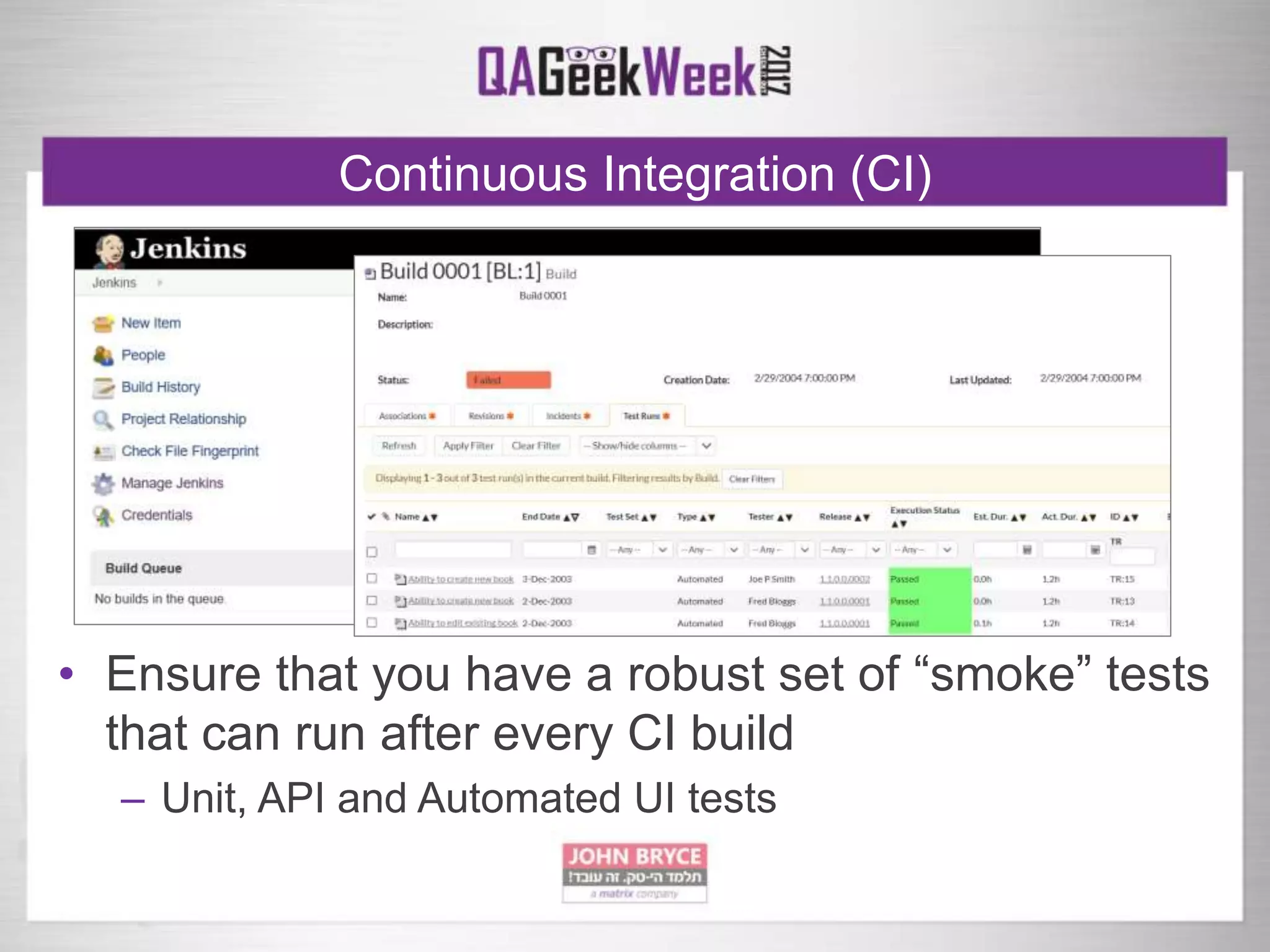
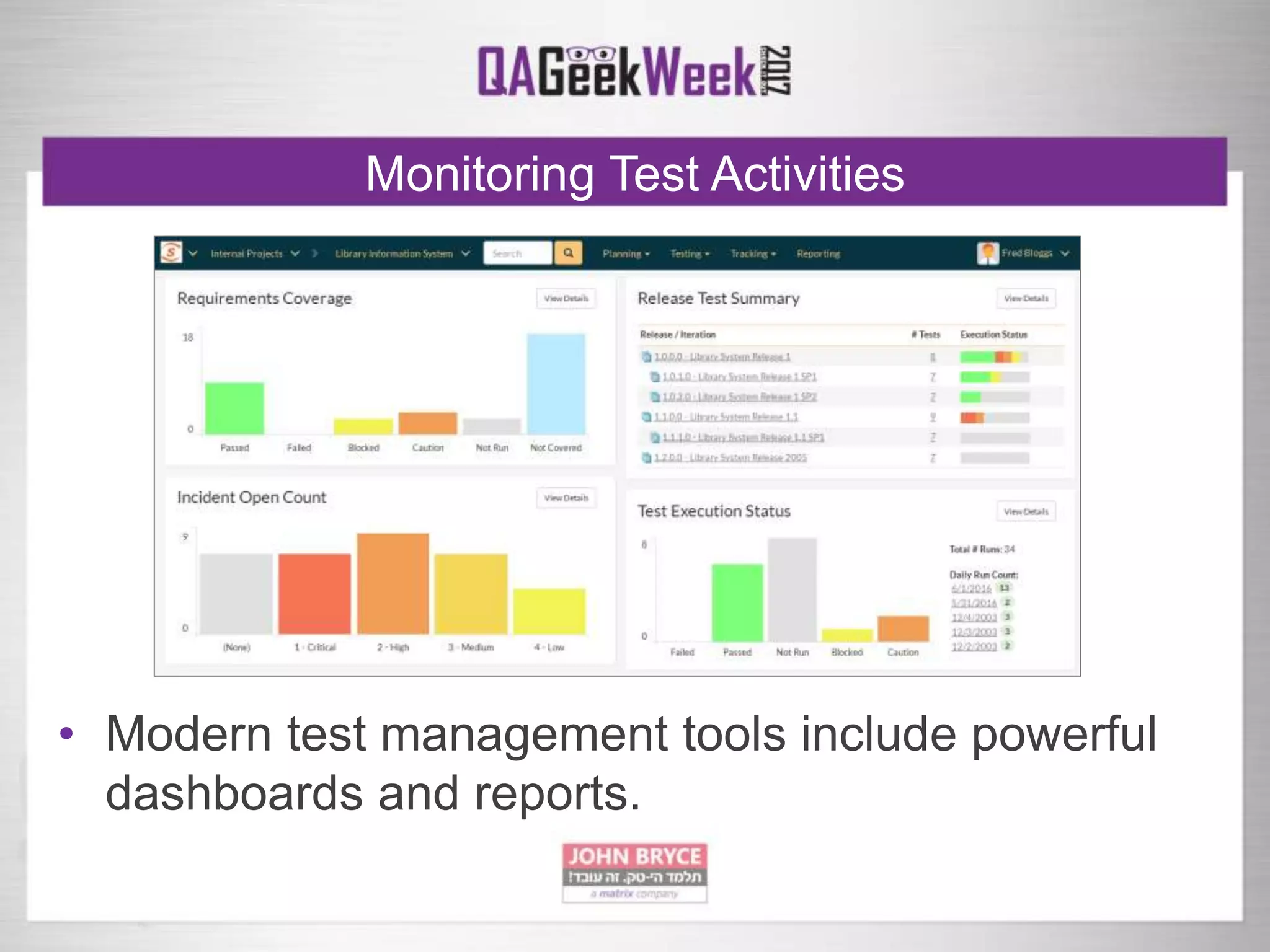
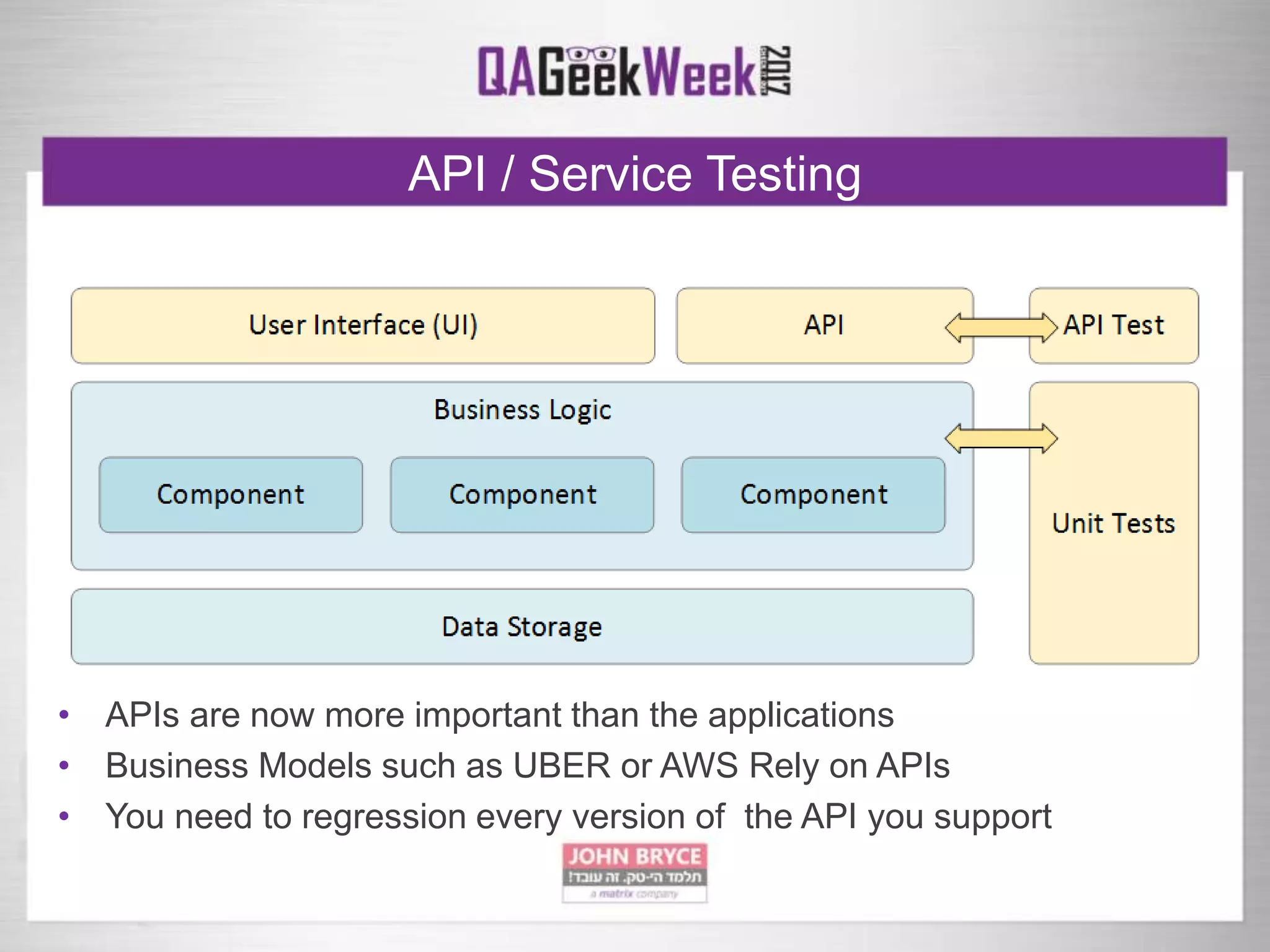
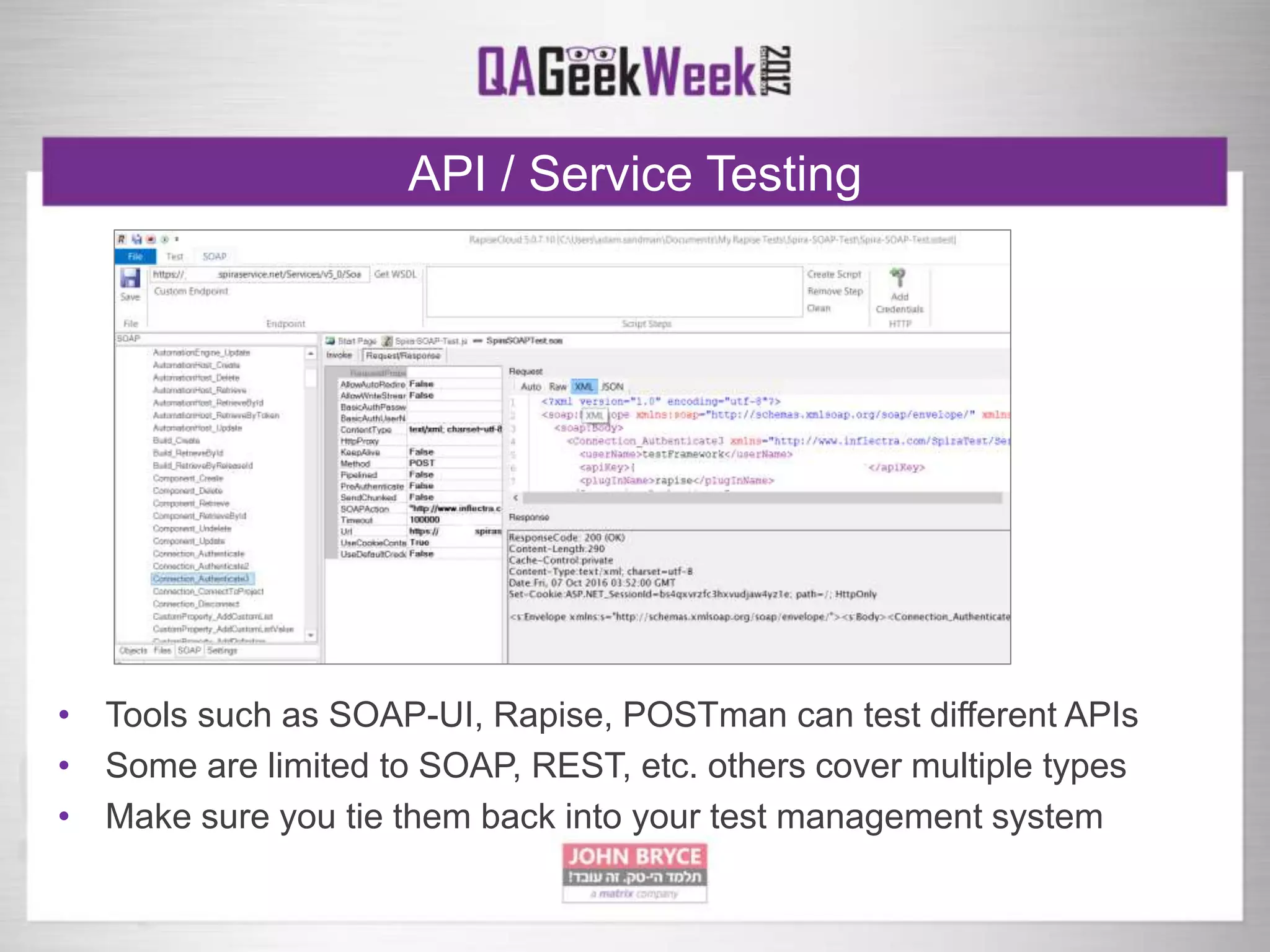
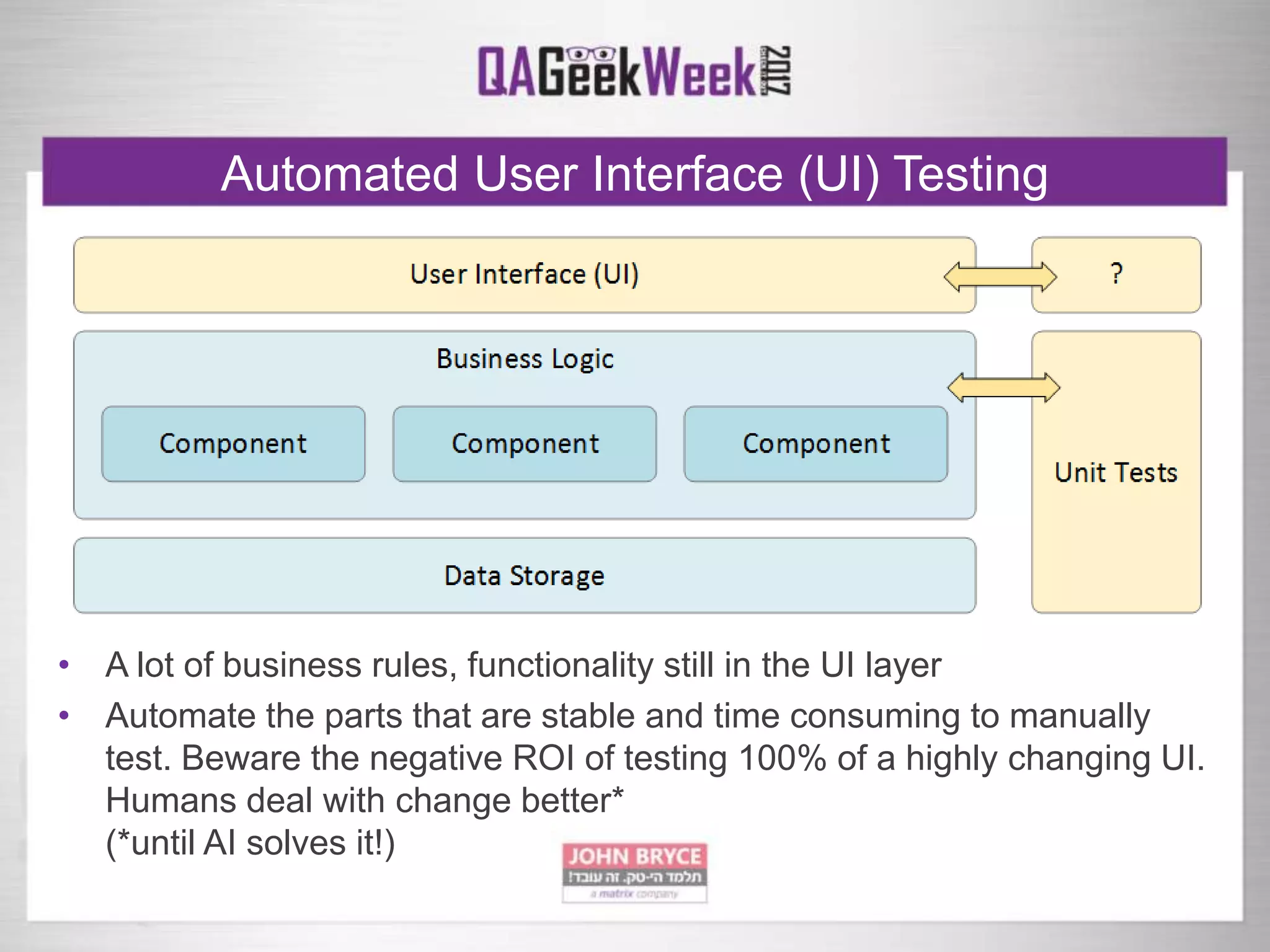
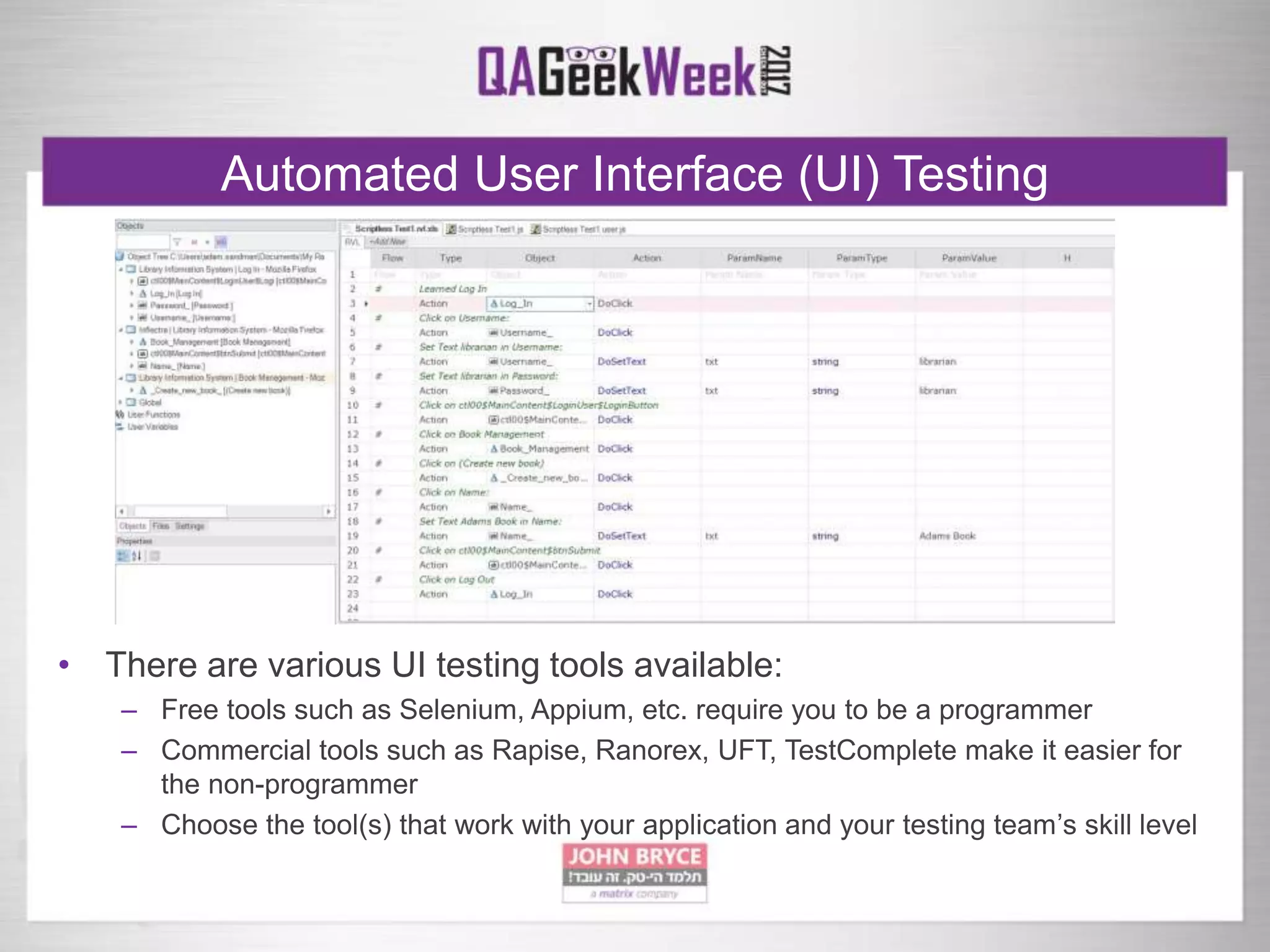
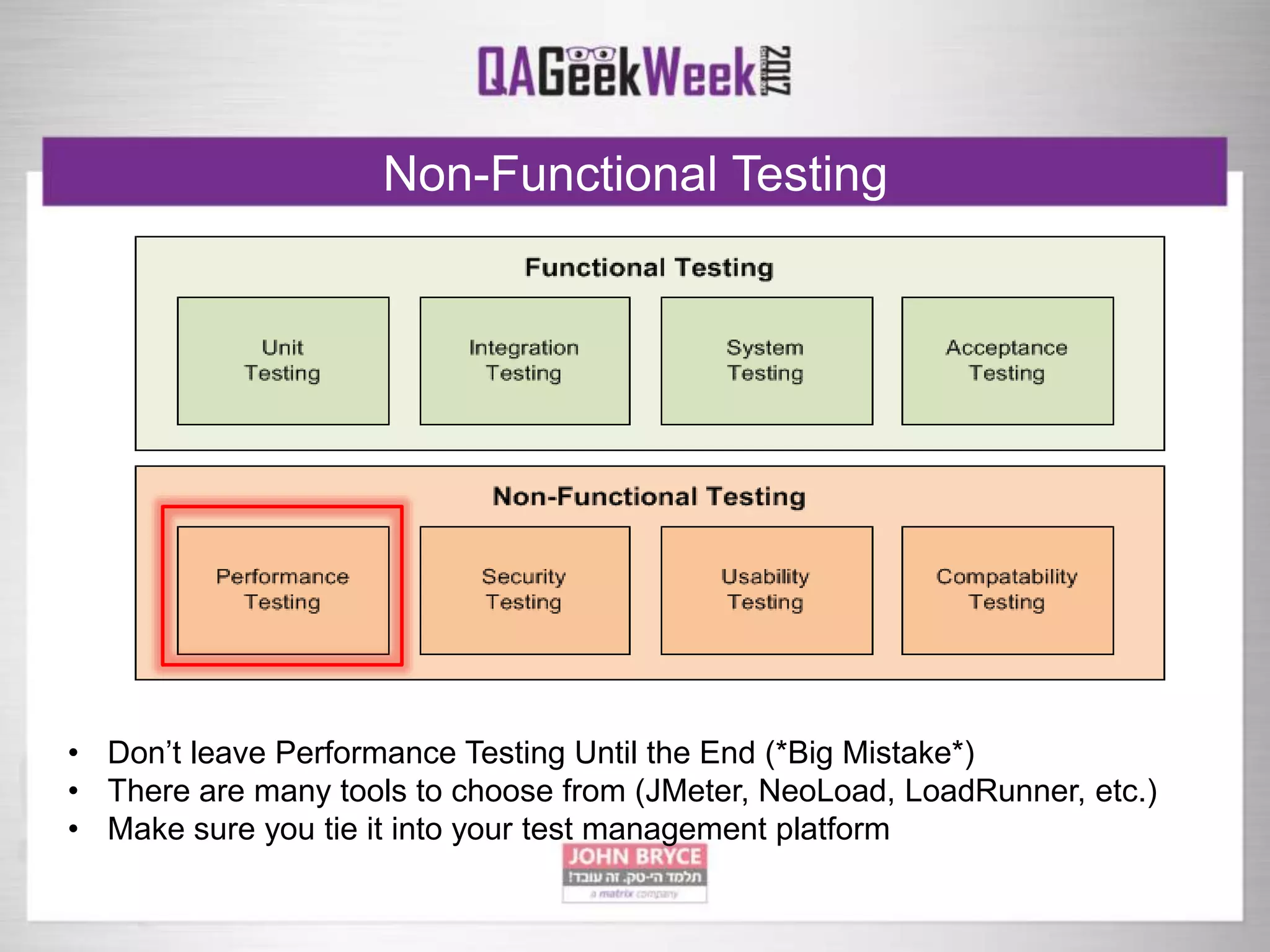
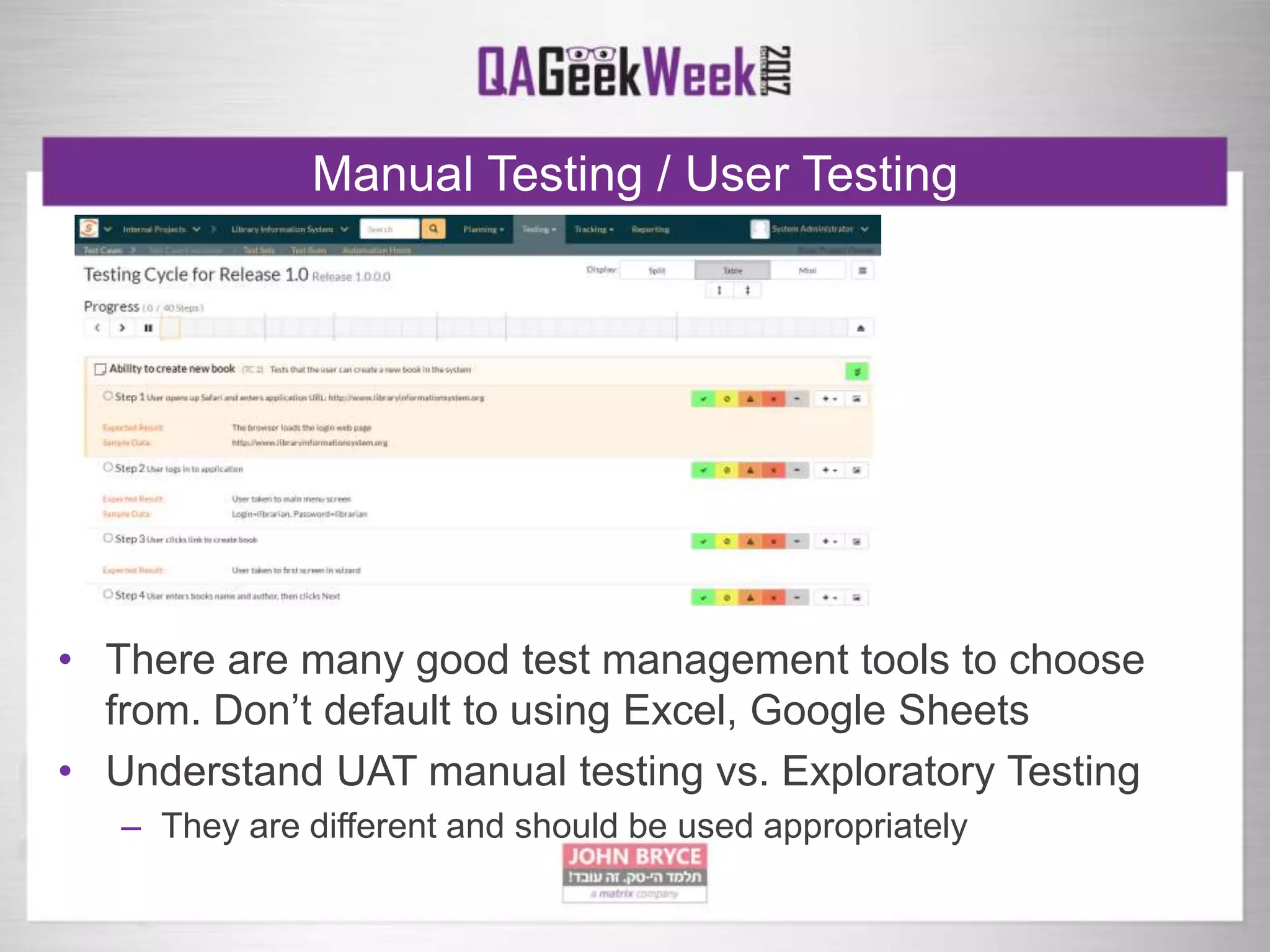
The document discusses a comprehensive strategy for testing in a real-life test operations environment, covering various testing tiers, tools, and methodologies. It emphasizes the importance of defining requirements, developing a test strategy, and the appropriate use of manual versus automated testing. Additionally, it highlights the significance of continuous integration and the need for robust monitoring of testing activities and coverage metrics.