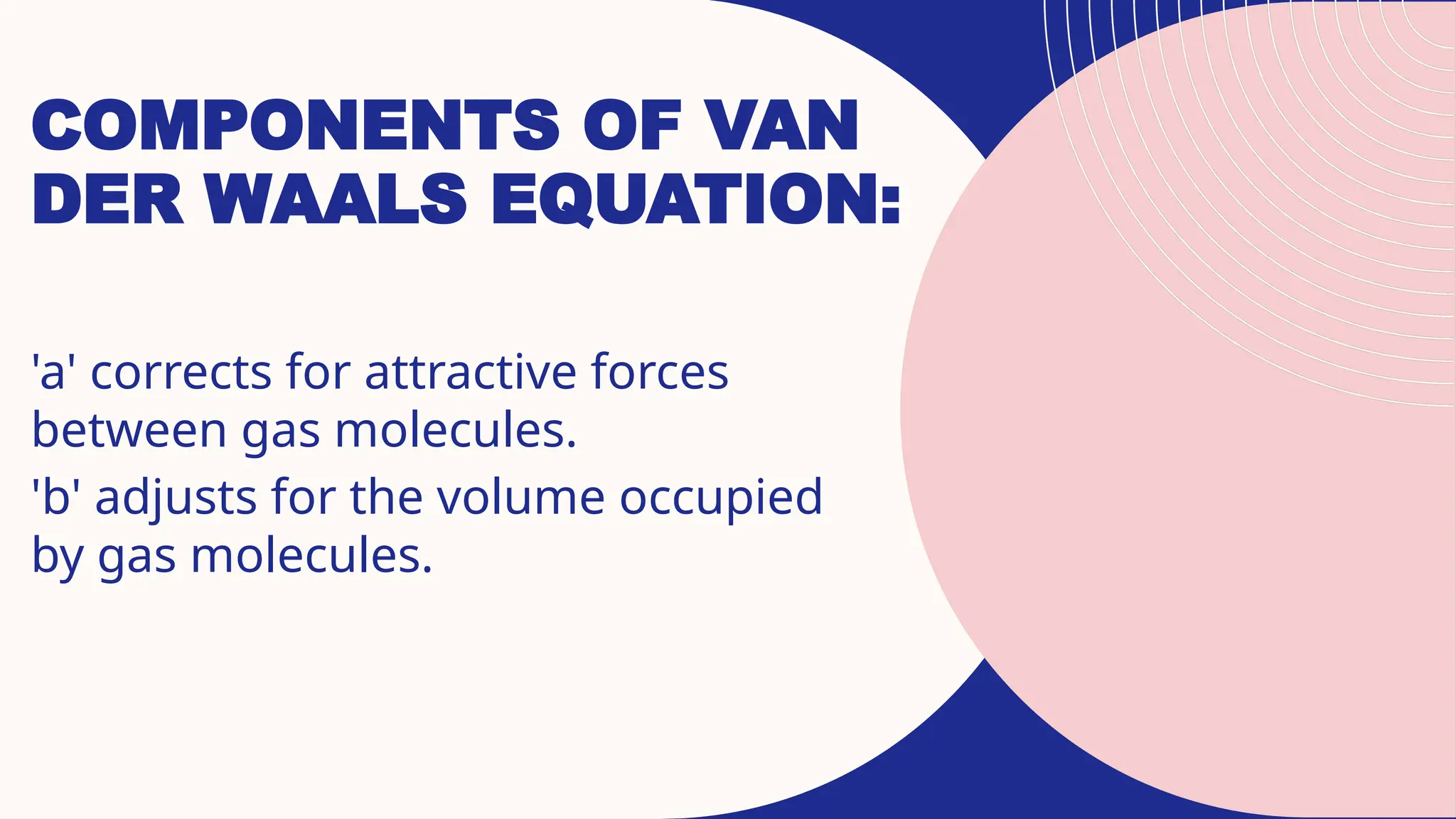
The document discusses the behavior of real gases and introduces the van der Waals equation, which modifies the ideal gas law to account for particle volume and intermolecular forces. It highlights the deviations from ideal gas behavior observed at high pressures and low temperatures, and the roles of the constants 'a' and 'b' in the equation. Lastly, while useful in predicting non-ideal gas behavior, the equation has limitations in extreme conditions.