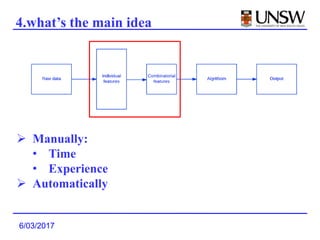
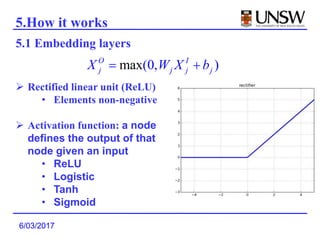
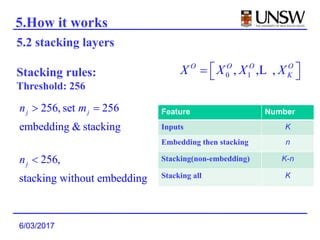
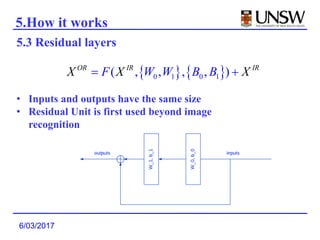
The document summarizes a research paper on Deep Crossing, a deep learning model that automatically combines features for web-scale modeling without manually crafted combinatorial features. The key points are:
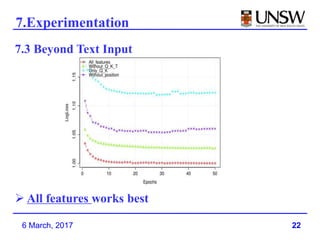
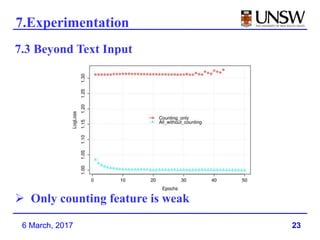
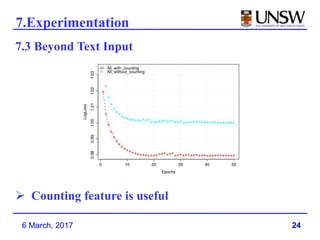
1. Deep Crossing uses a neural network to automatically learn combinatorial features from individual features, avoiding the manual feature engineering required by previous models.
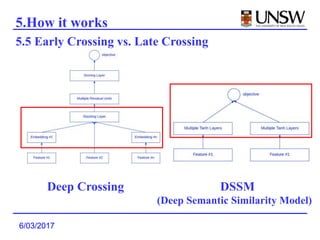
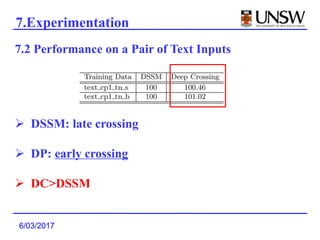
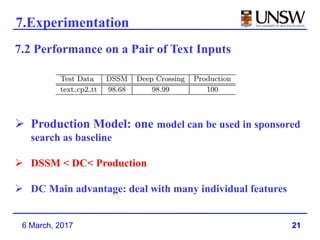
2. It was shown to outperform previous models like DSSM that used late feature crossing. Deep Crossing's early feature crossing was more effective.
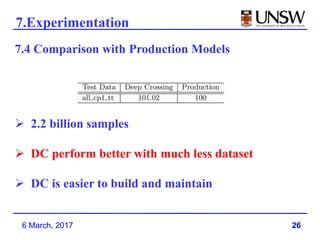
3. Deep Crossing was able to achieve better performance than production models using much less training data, and is easier to build and maintain than manually engineered models.