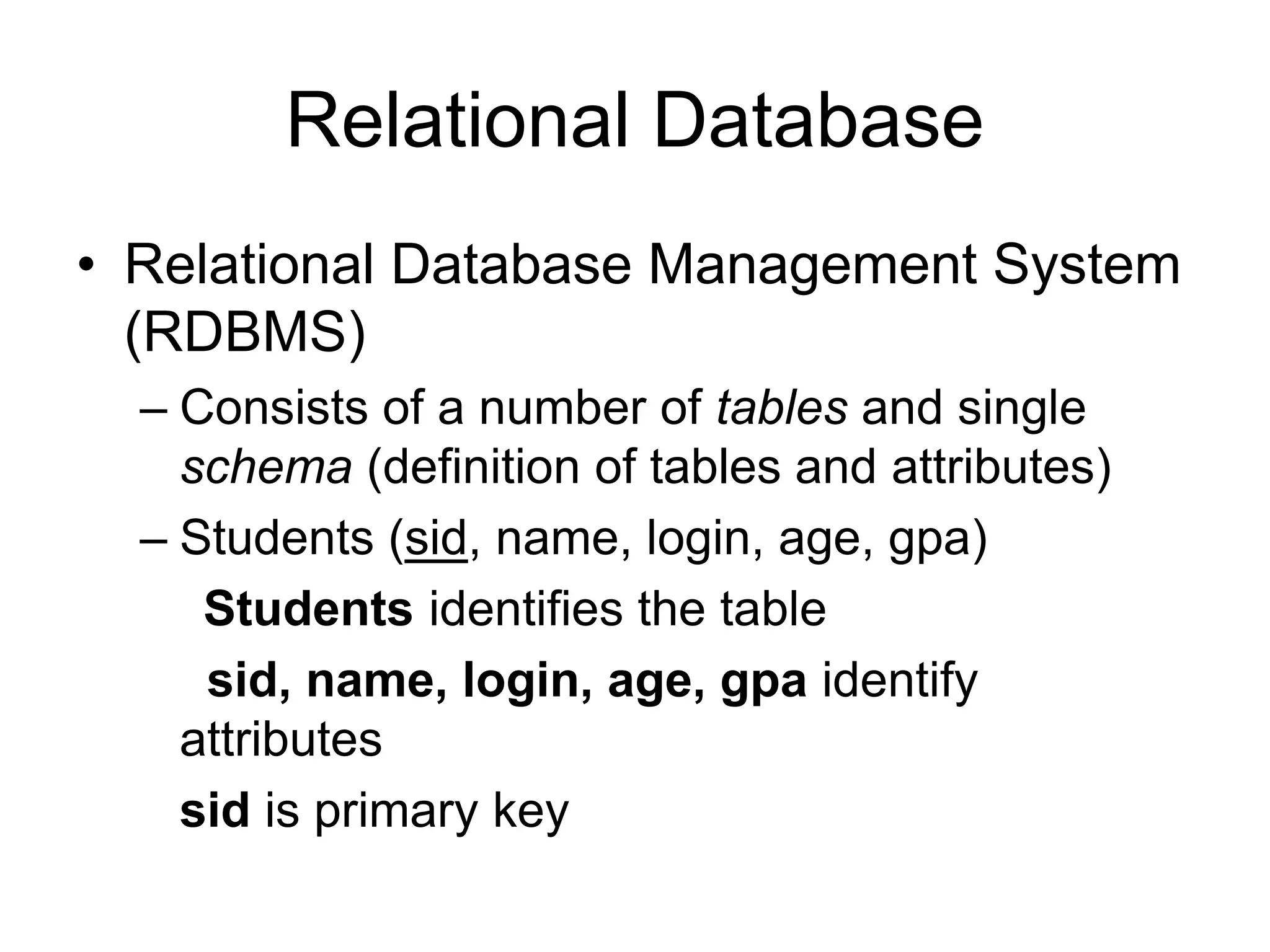
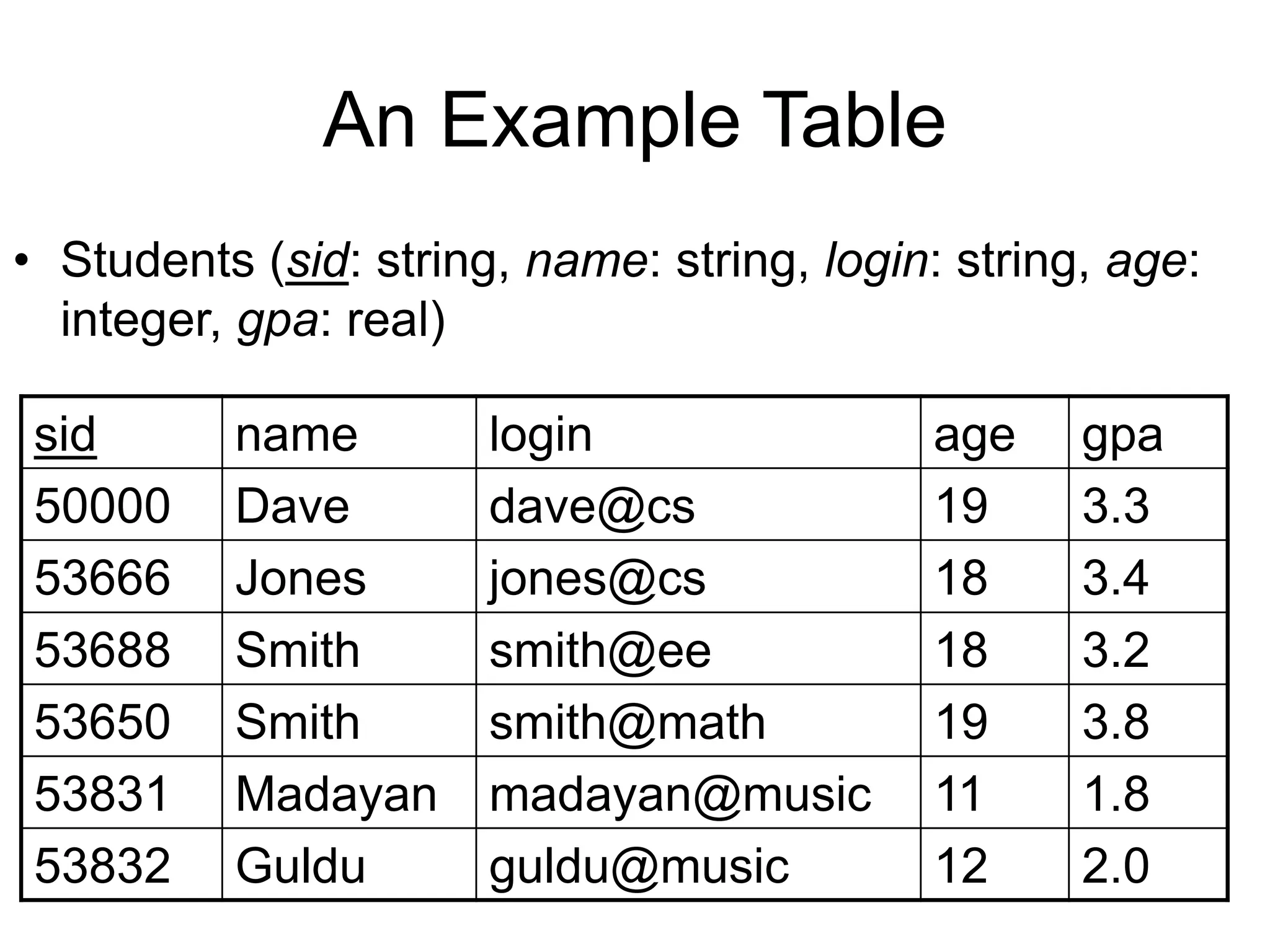
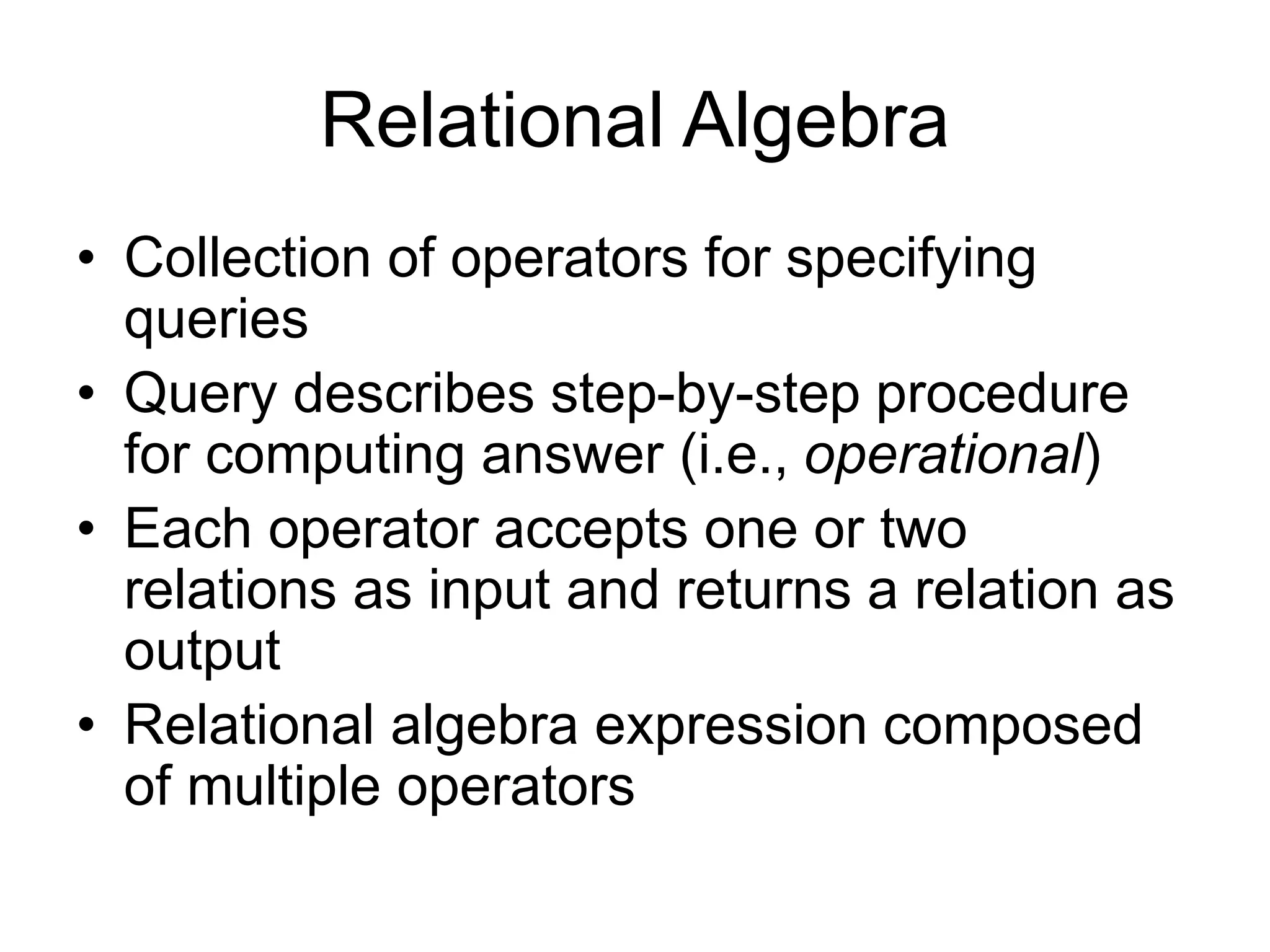
An RDBMS consists of tables and a schema. Tables contain attributes and tuples. A primary key uniquely identifies each tuple. Foreign keys connect tables by referencing attributes in other tables. Many-to-many relationships require a join table. Relational algebra uses operators like selection, projection, union, and cross product to specify queries that compute results by performing operations on tables.