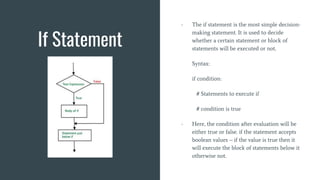
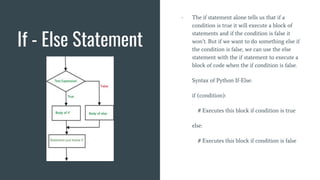
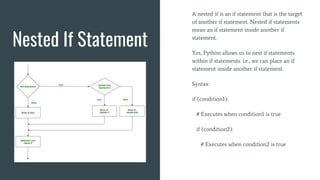
The workshop covered topics on Python programming including basics of Python, loops, conditionals, modules and importing libraries. It also covered the Matplotlib library, Linux commands, and building projects including a password manager and PDF password encrypter. Specific topics on loops included while and for loops. Conditionals covered if, if-else, and nested if statements. Modules allow organizing related code and accessing functions. Matplotlib is a data visualization library and Linux commands were demonstrated for file/folder management.