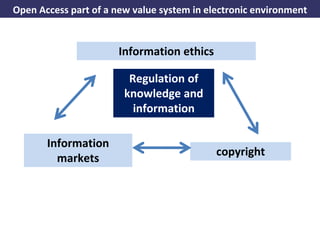
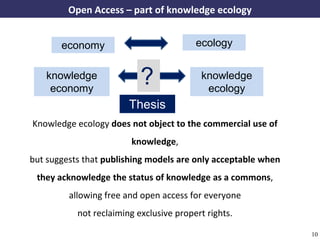
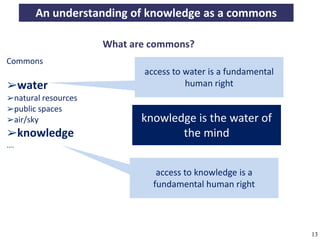
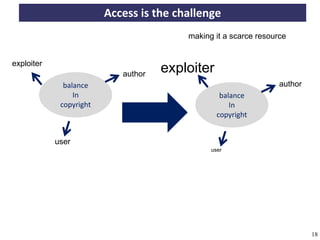
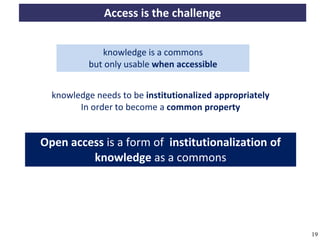
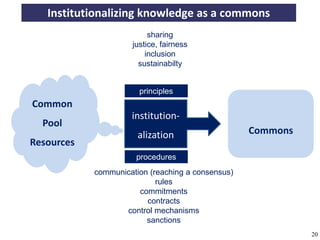
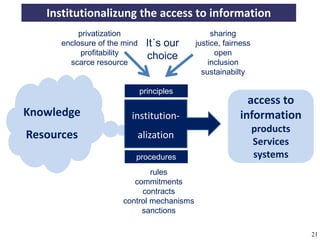
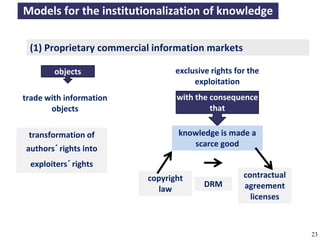
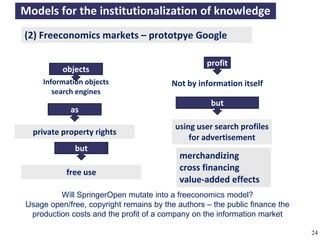
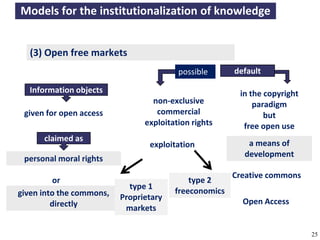
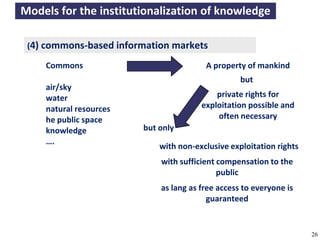
The document discusses the concept of open access as part of a new value system within digital environments, emphasizing the importance of knowledge as a commons and advocating for unrestricted access to knowledge for all. It critiques current commercial publishing models and copyright regulations, proposing more sustainable and inclusive frameworks for knowledge dissemination. The conclusion urges a transformation in understanding intellectual property rights and the institutionalization of knowledge to ensure it remains accessible and usable for everyone.