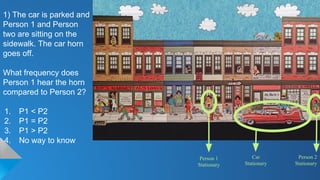
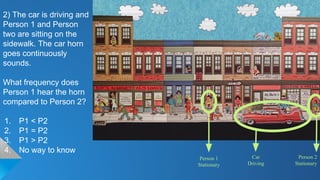
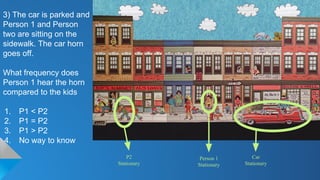
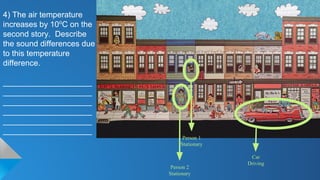
The document describes the doppler-ganger game, where players analyze visual scenarios involving sound frequency perception due to the Doppler effect. It presents various situations with stationary and moving cars, detailing how frequency is perceived by different observers. Explanations clarify the impact of motion and temperature on sound waves and frequency perception.