Embed presentation
Download to read offline




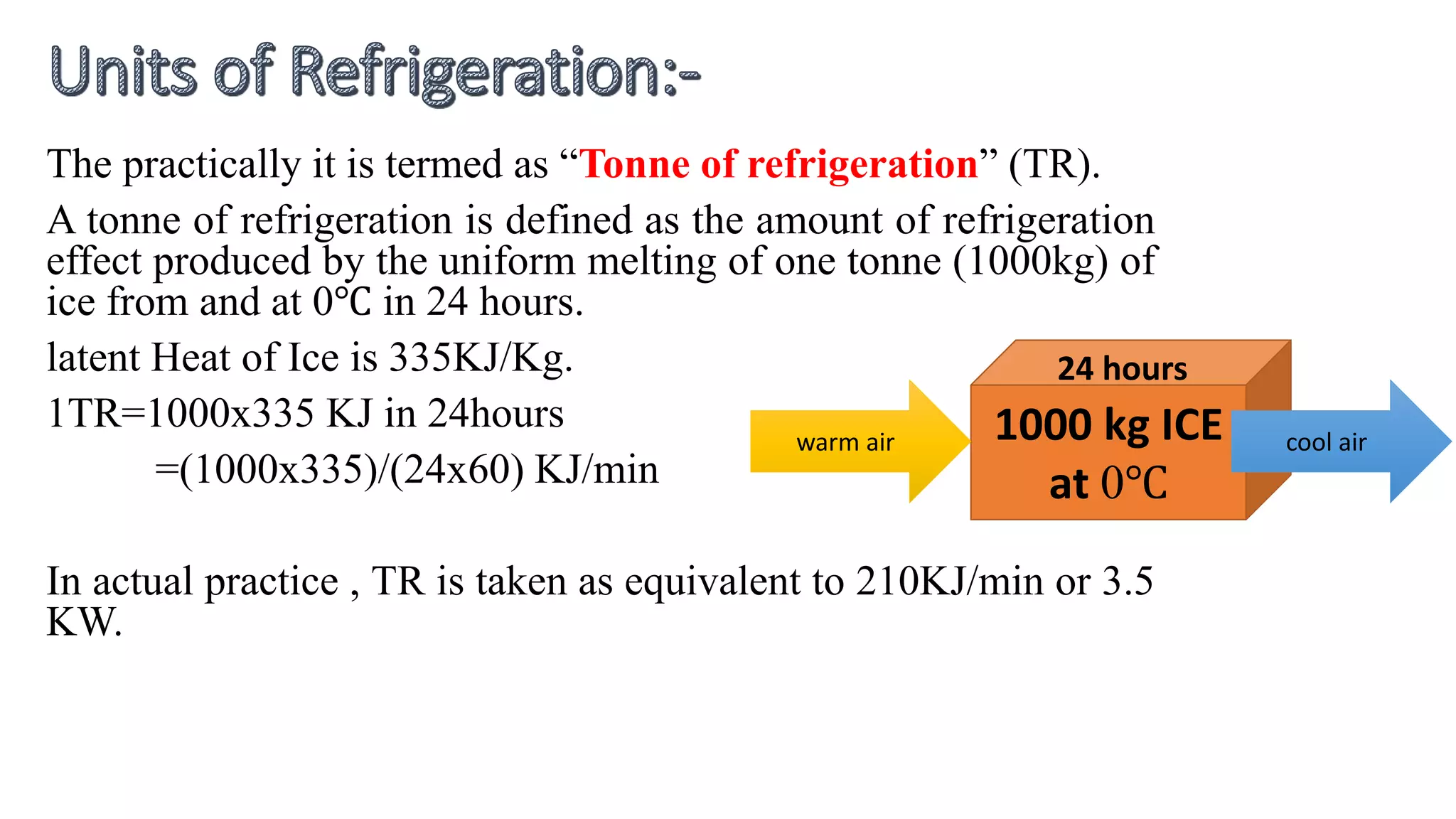

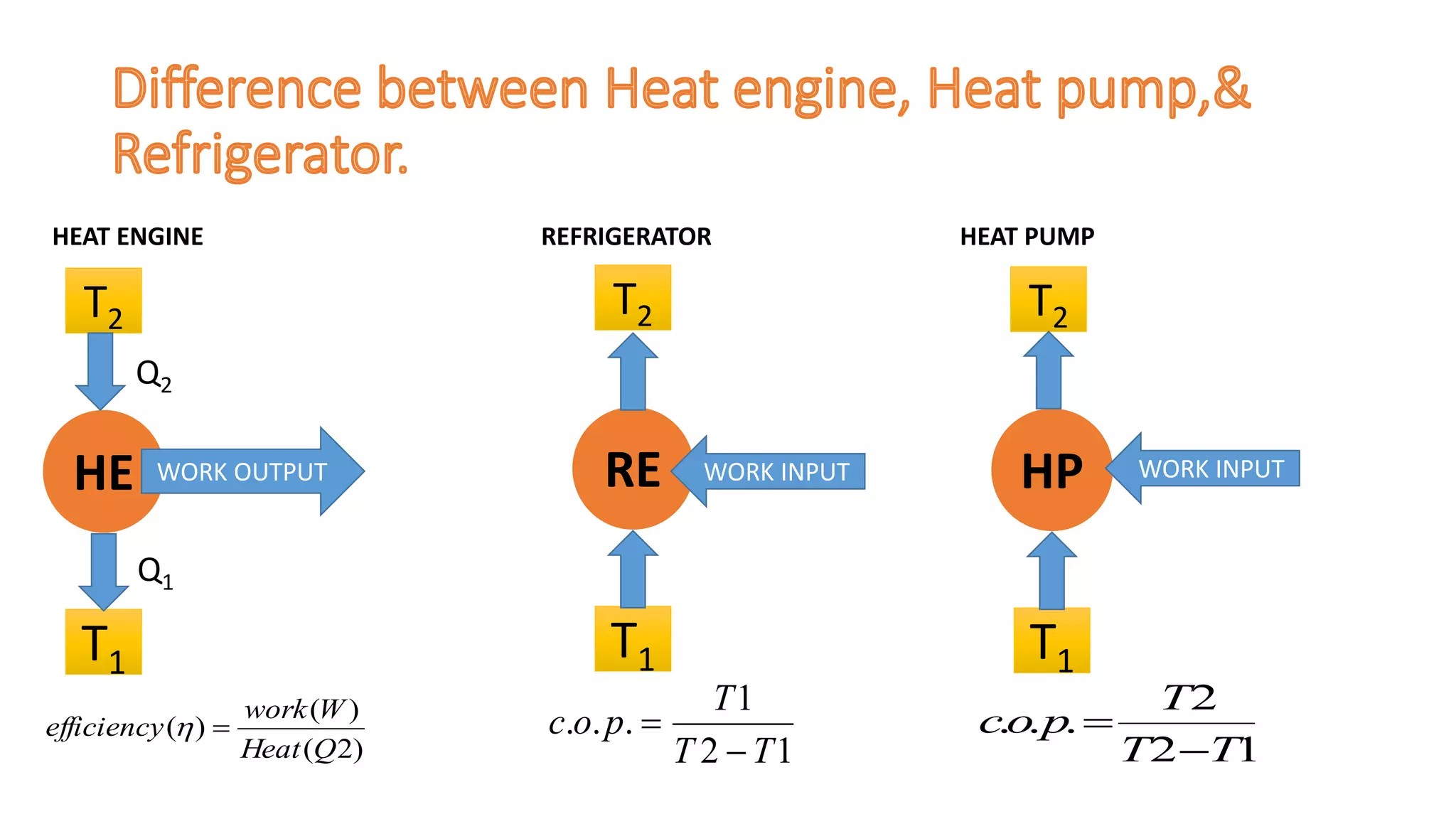

This document defines refrigeration and discusses air refrigeration cycles. It explains that refrigeration is the process of removing heat from a substance to lower its temperature below its surroundings. Air was historically used as a refrigerant since it is freely available, but has low heat carrying capacity and requires high power. The document also defines the unit of refrigeration as the melting of one tonne of ice at 0°C in 24 hours. Finally, it compares heat engines, heat pumps, and refrigerators, defining coefficient of performance as the ratio of heat removed or supplied to work input.







