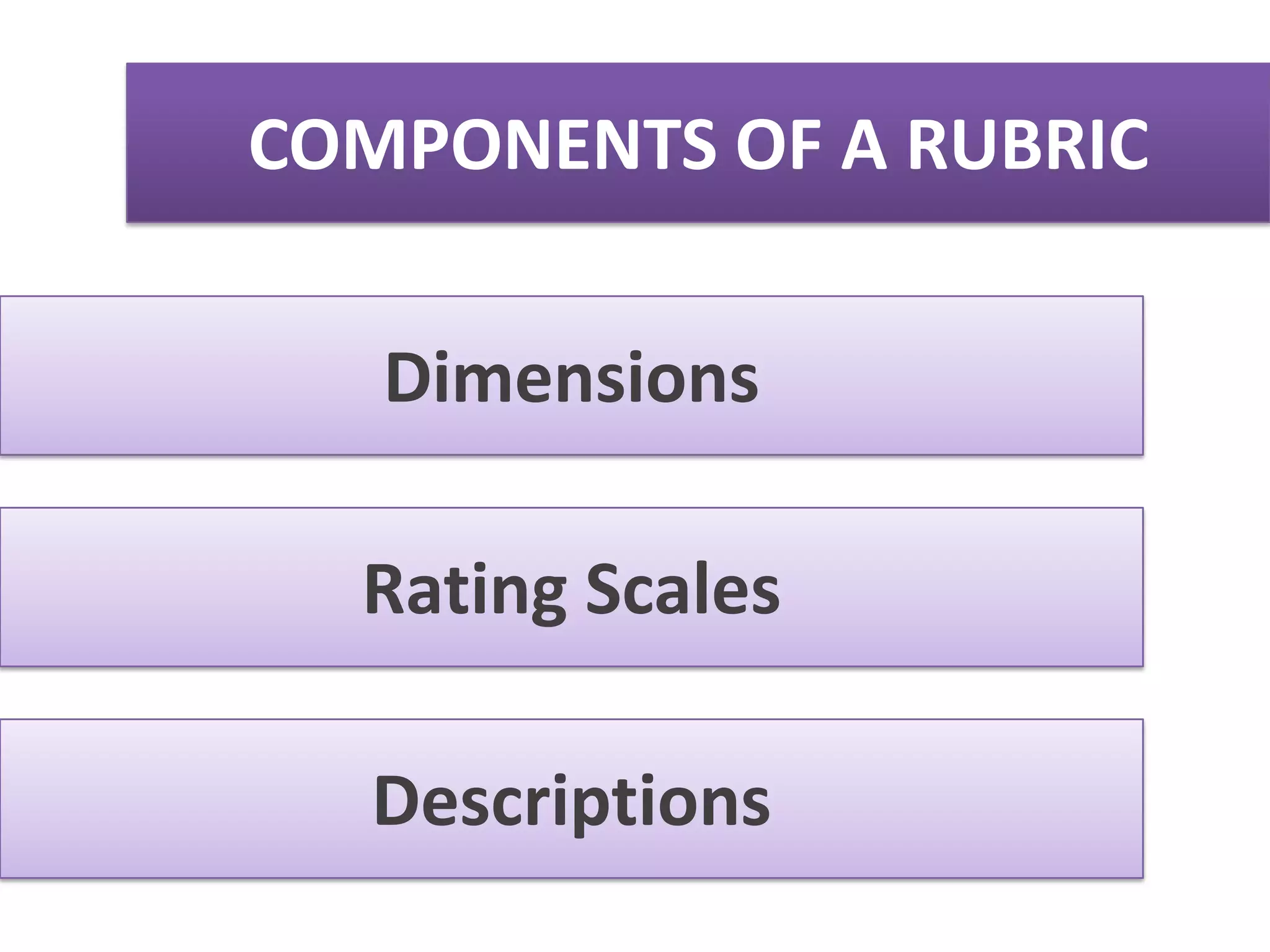
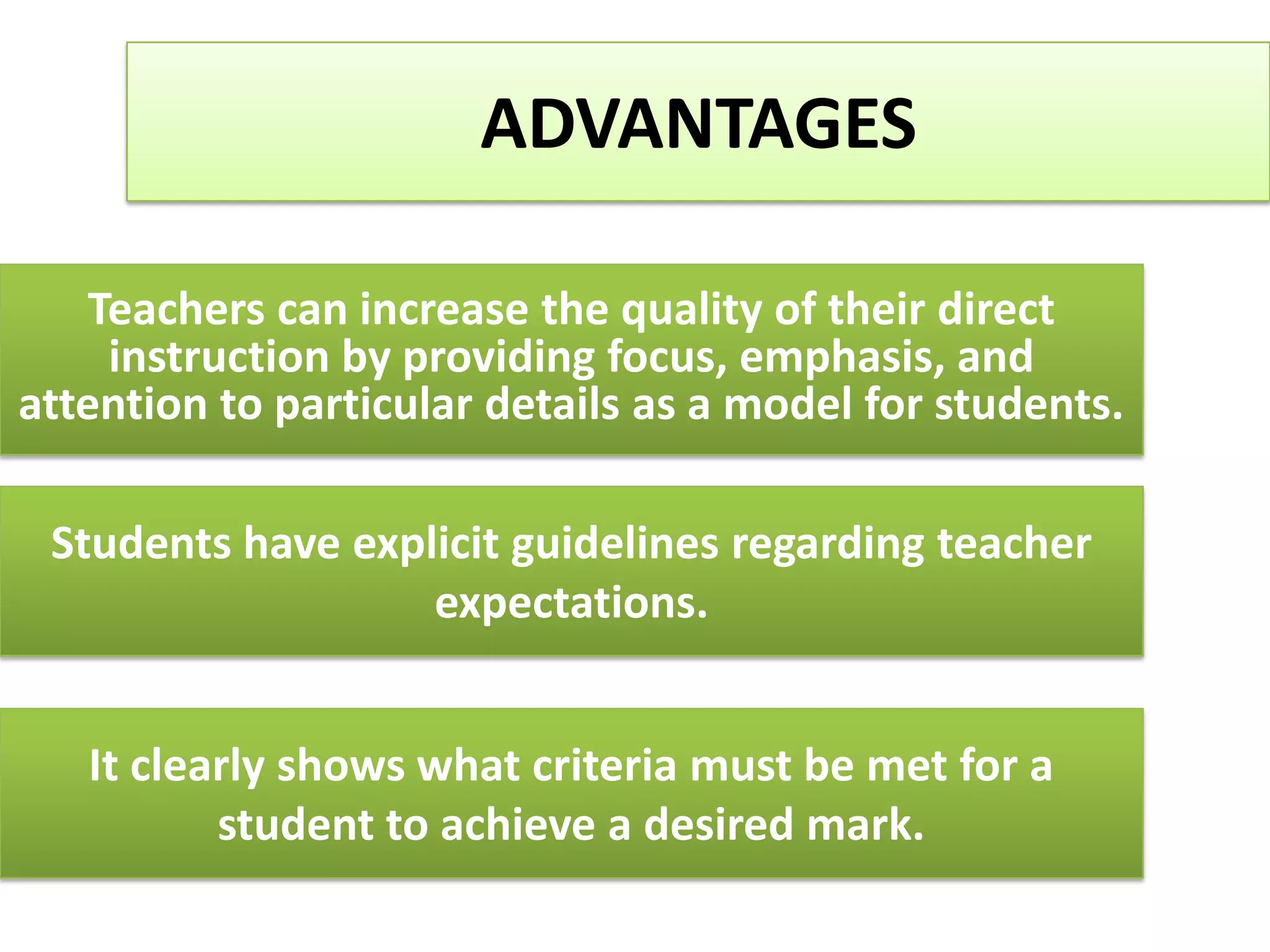
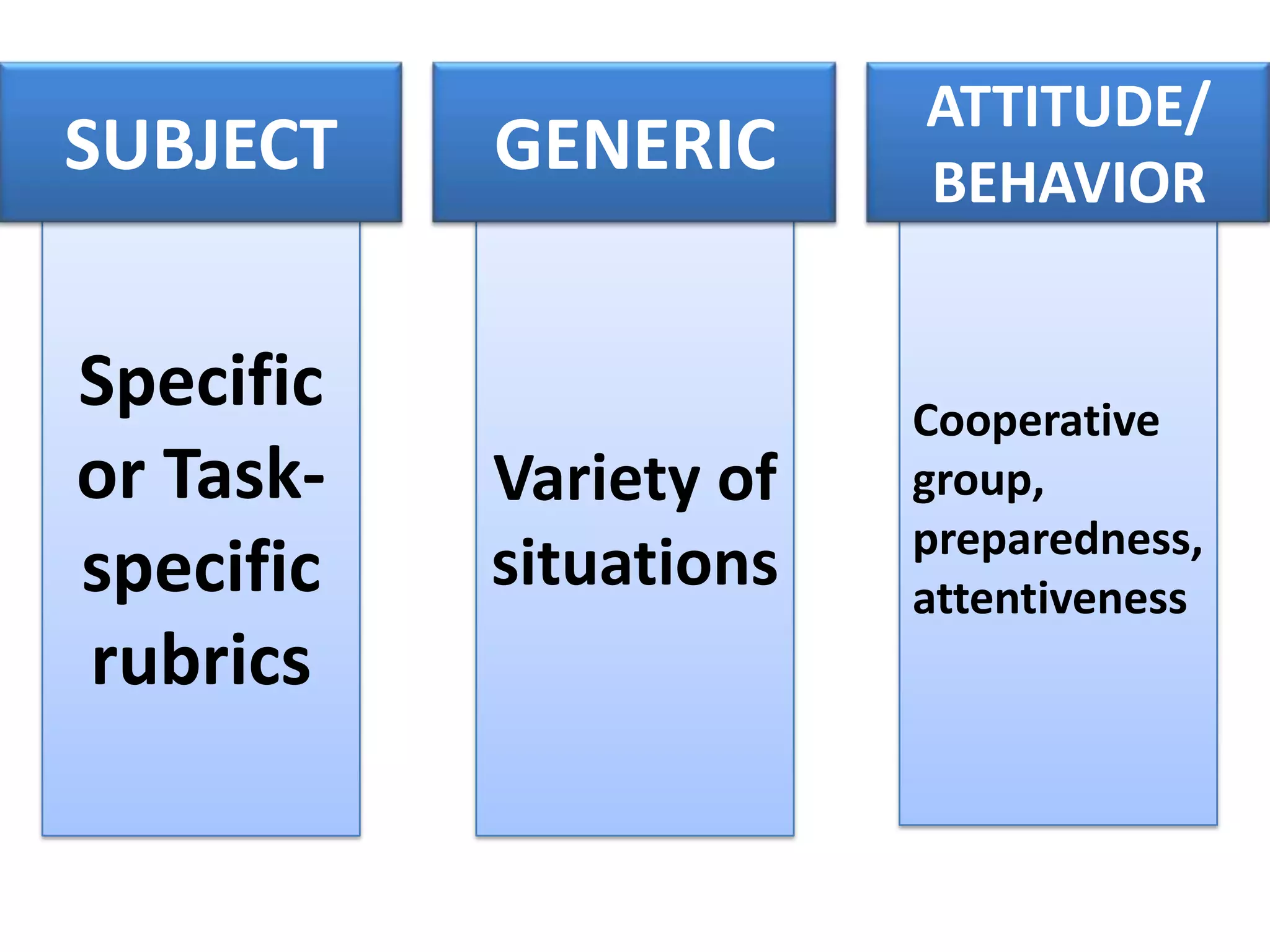
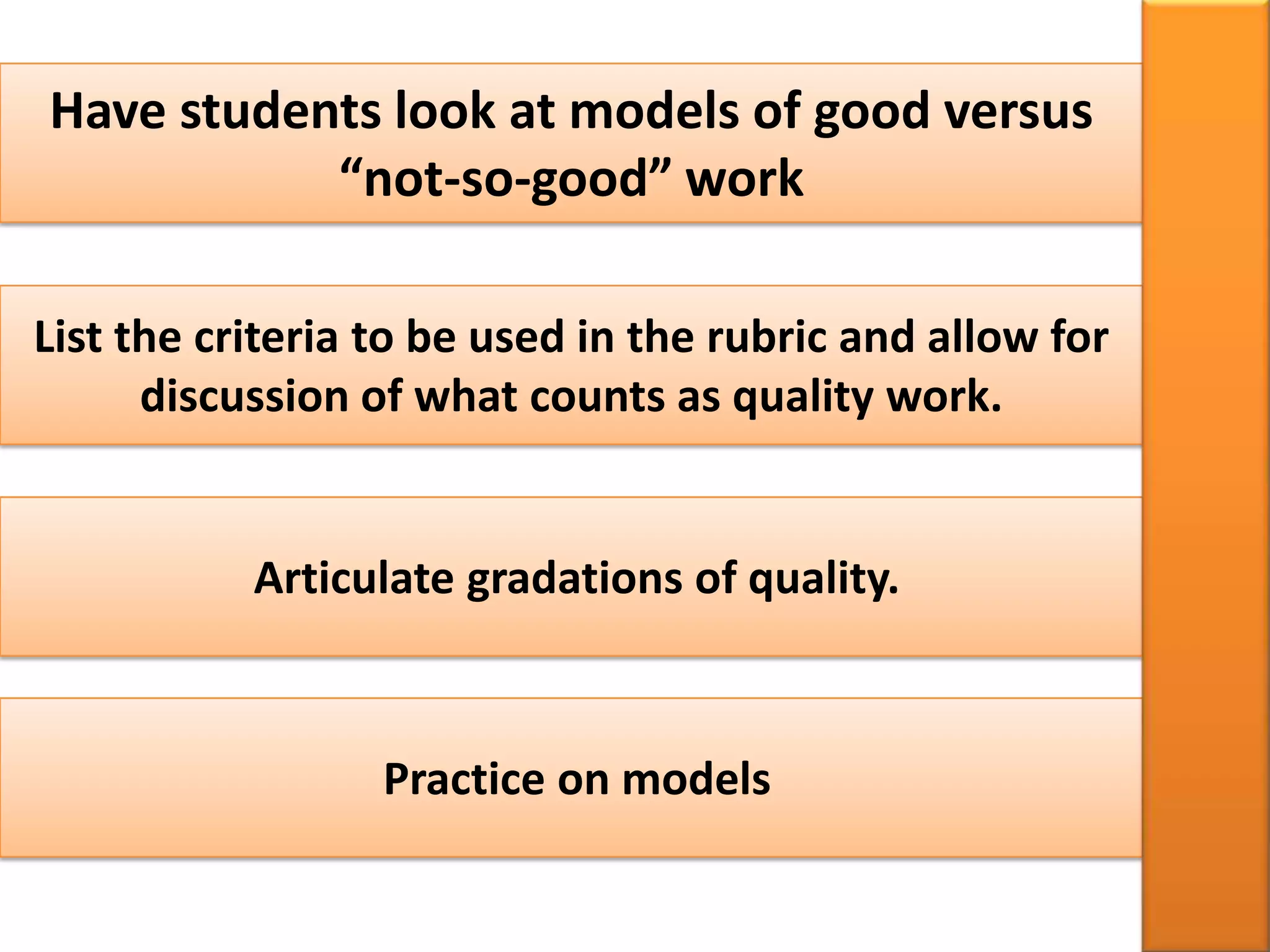
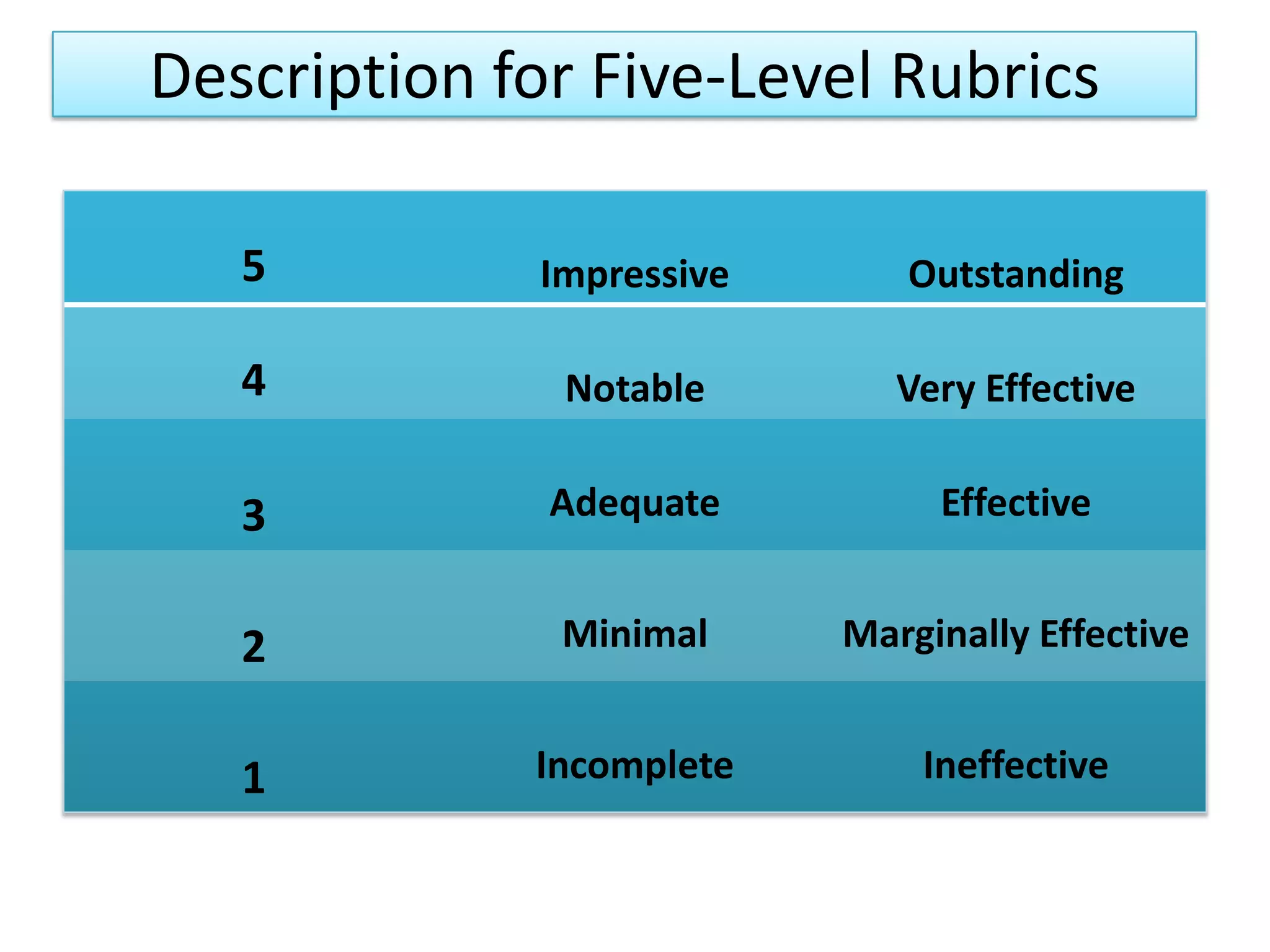
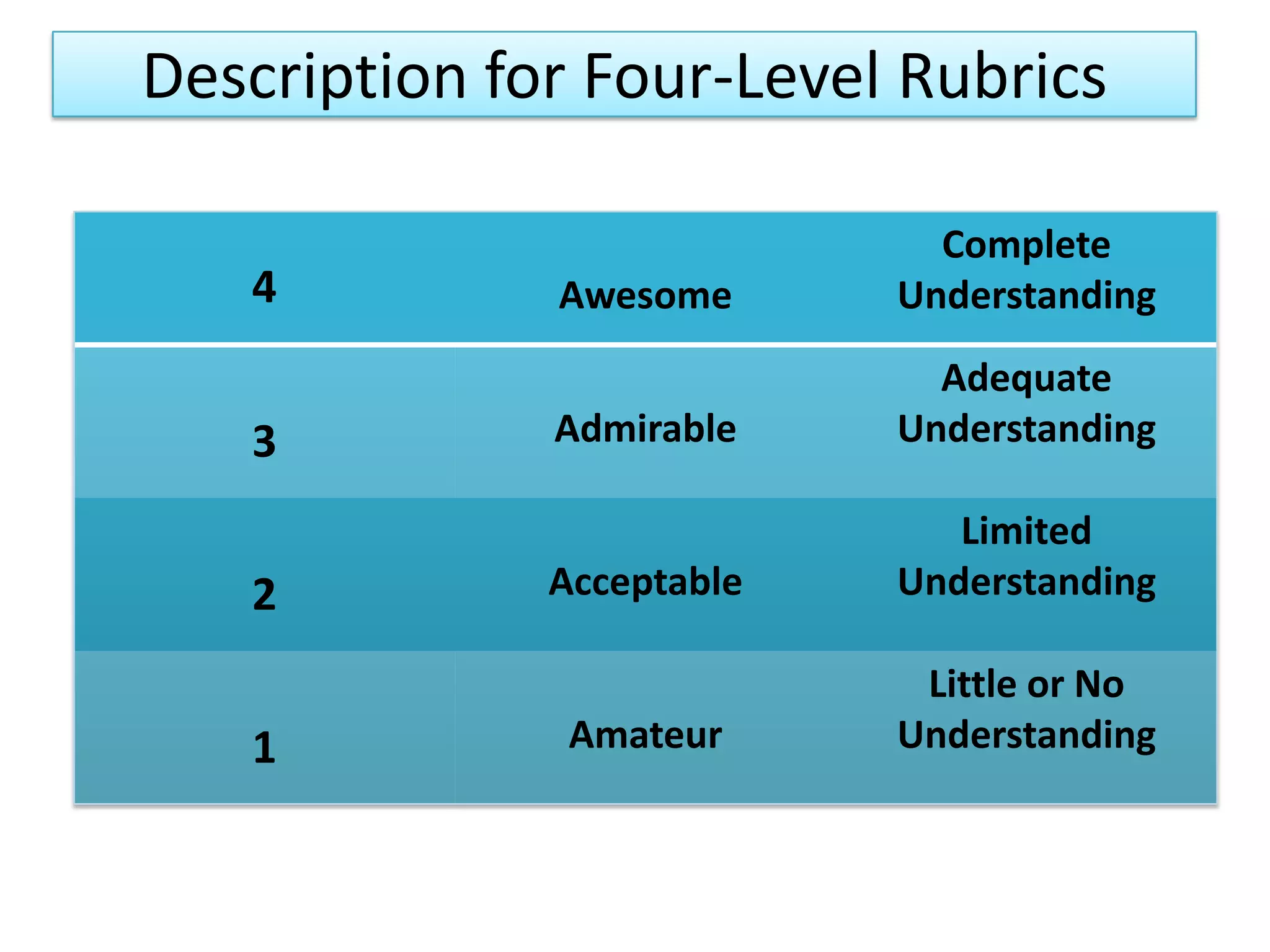
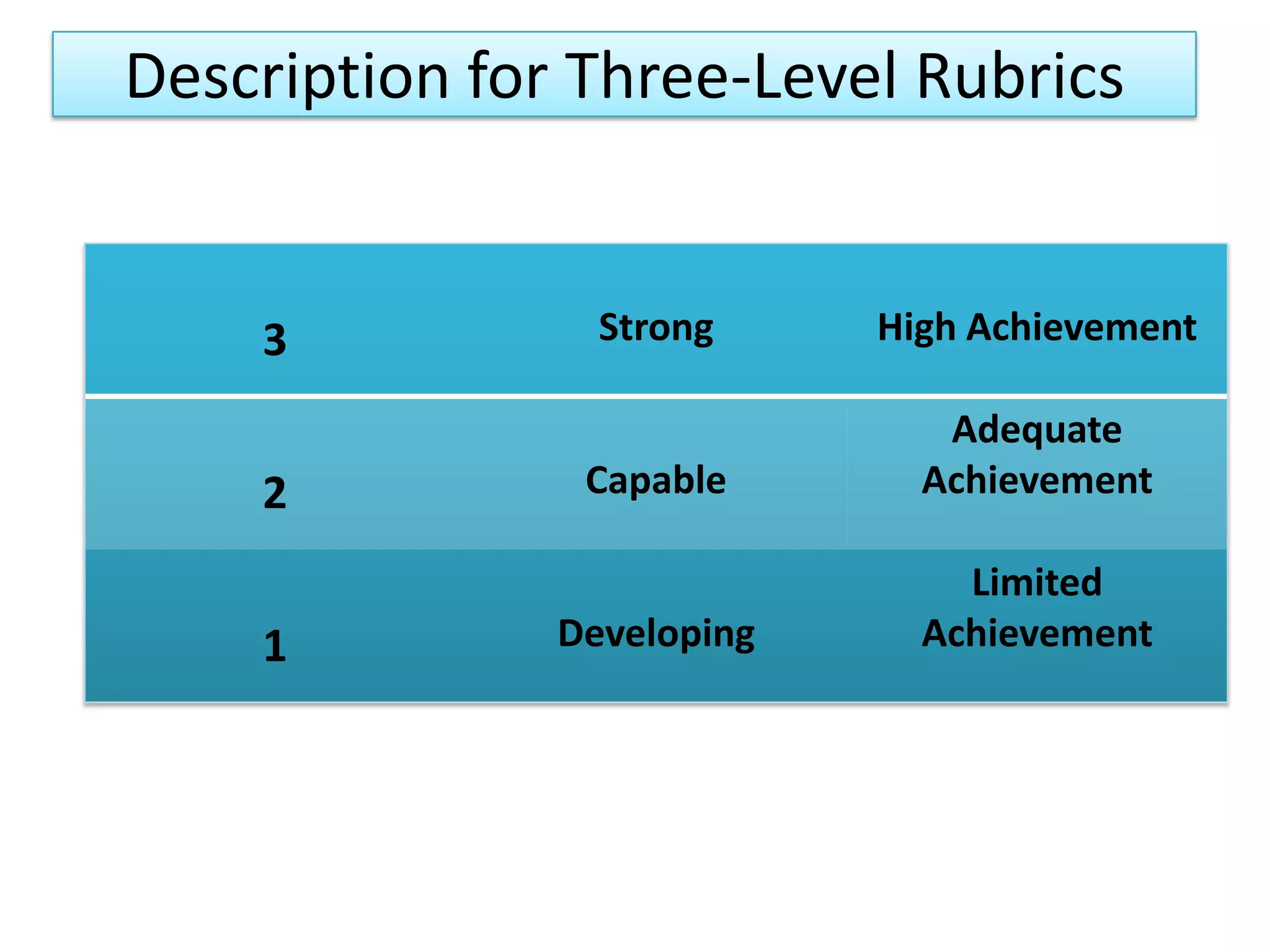
A rubric is a scoring tool that provides clear evaluation criteria in the form of levels of achievement. It allows for standardized assessment of student work like papers, projects, and essays according to learning objectives. Rubrics provide transparency by detailing what is required to receive a particular score. They benefit both students by communicating expectations, and teachers by facilitating grading. Rubrics can be tailored to different subject areas and can assess a variety of skills and competencies.