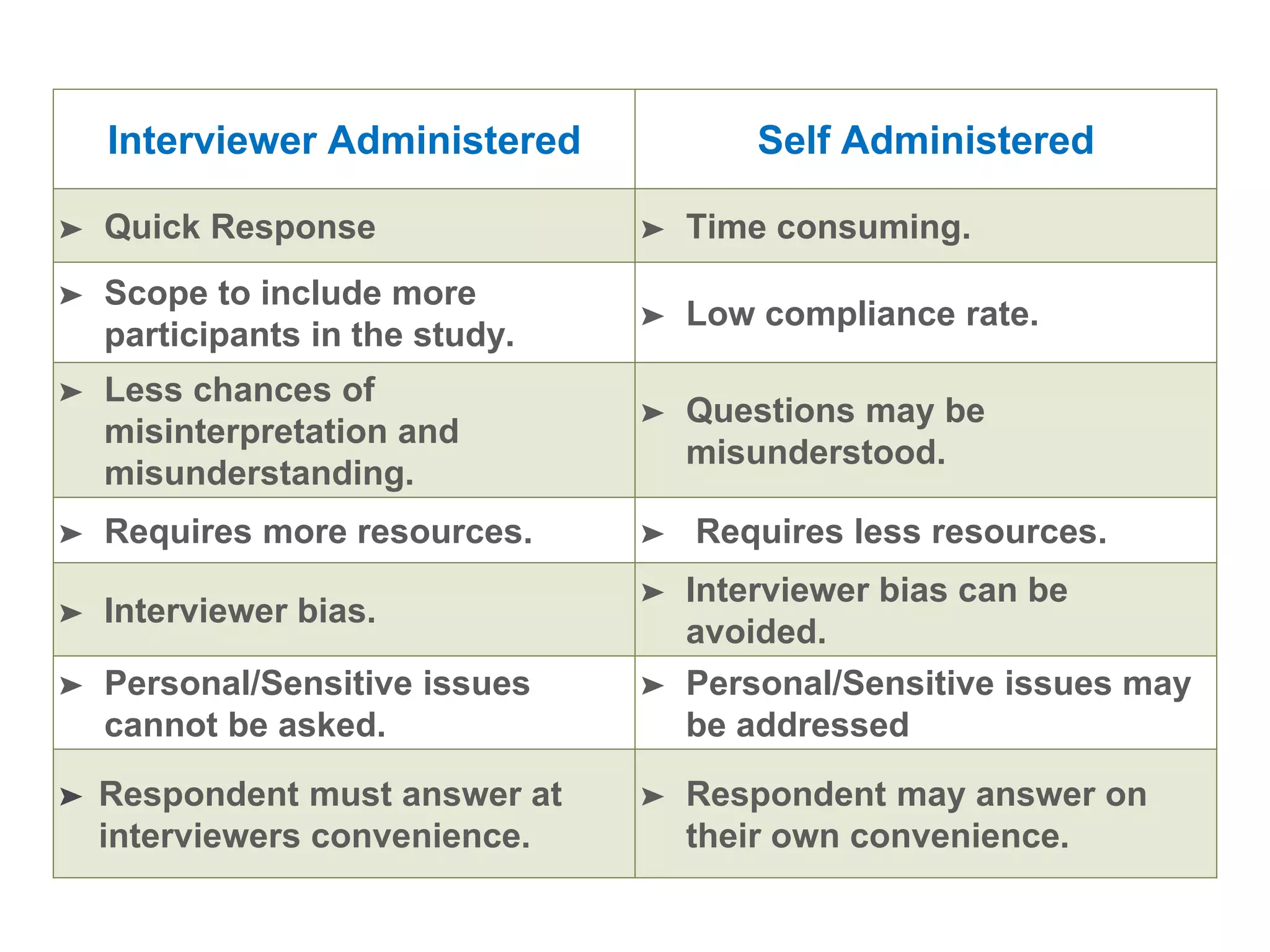
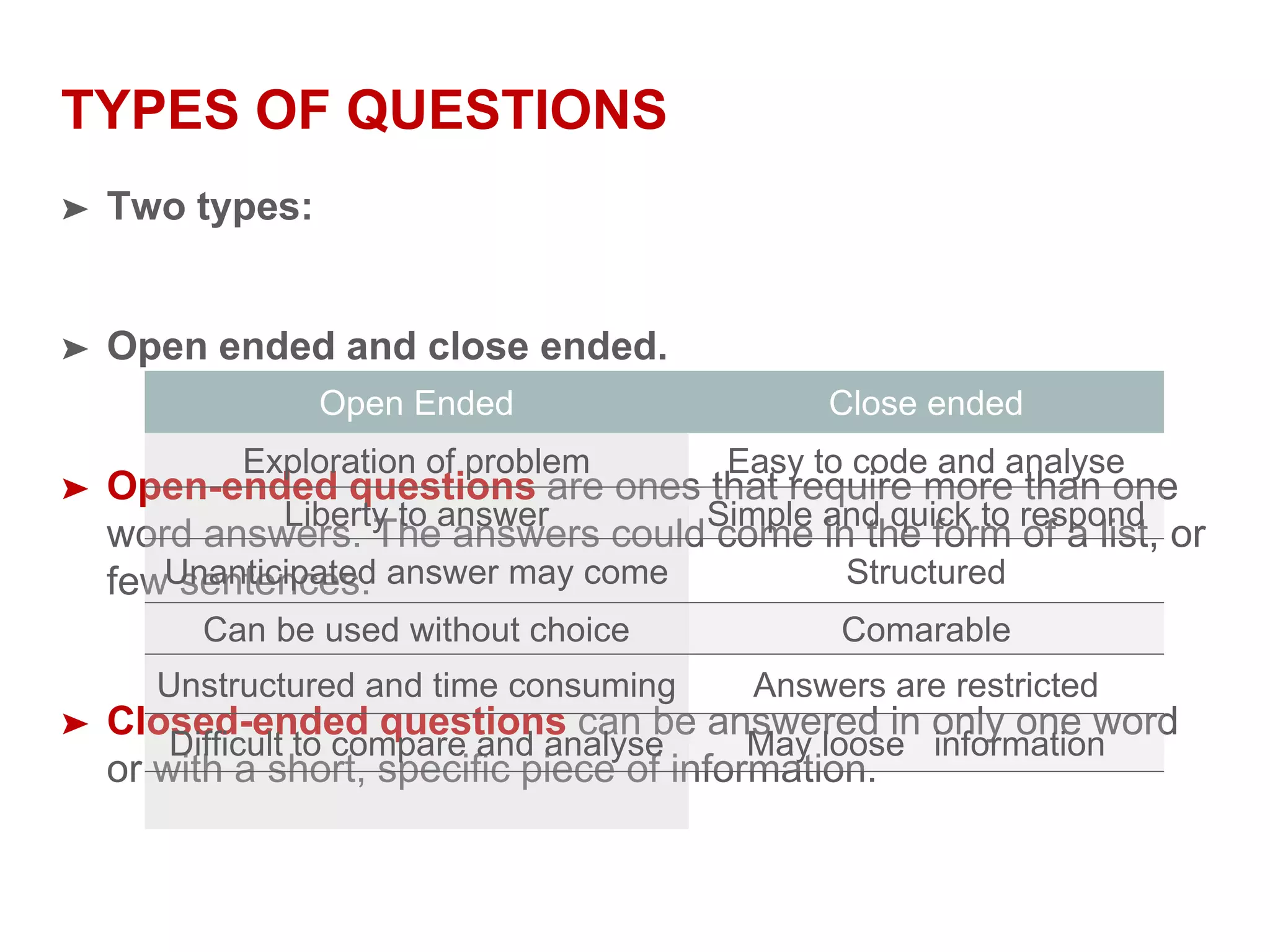
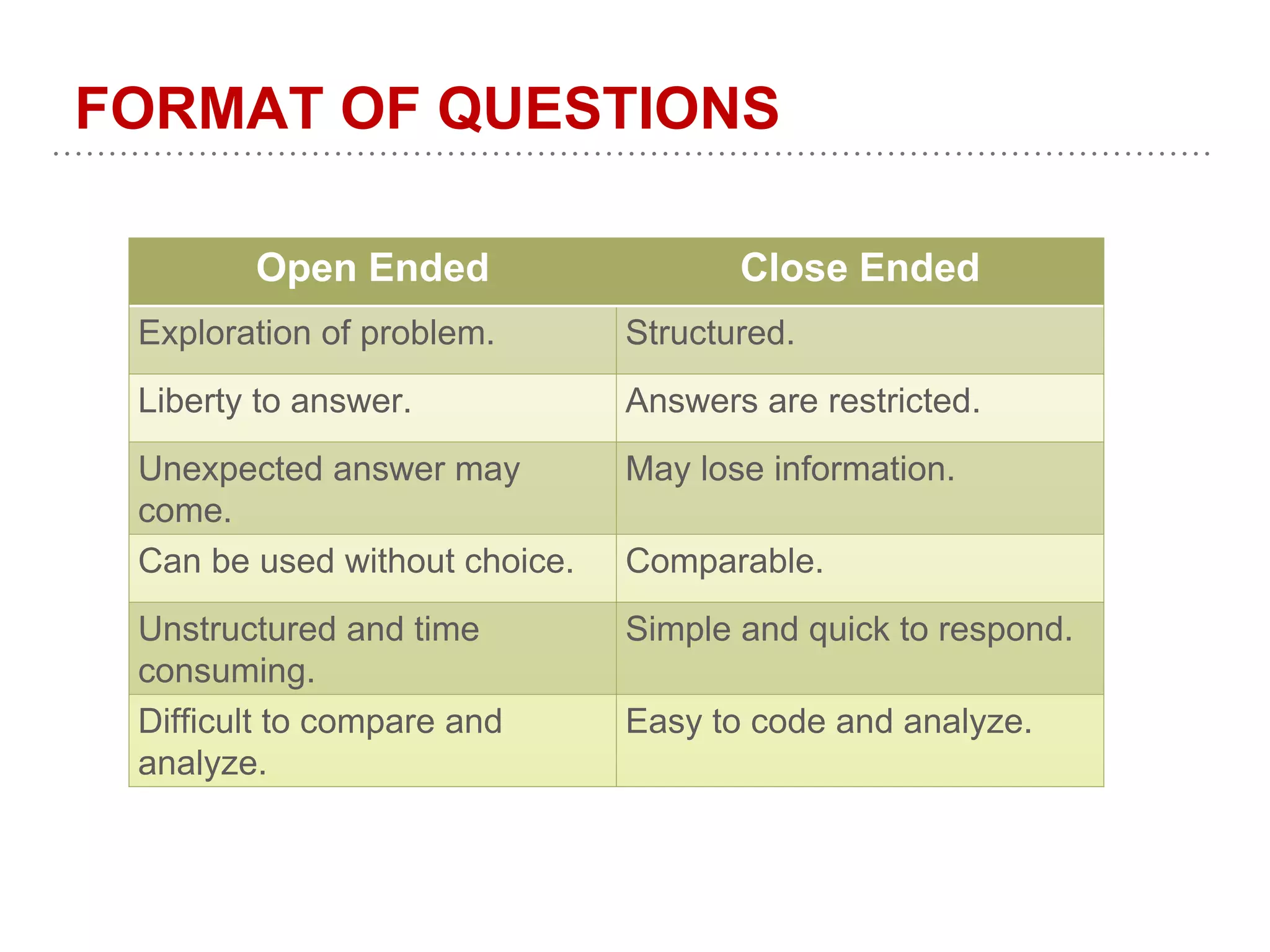
This document provides guidance on designing questionnaires for research studies. It discusses the structure of research studies, objectives of questionnaires, definition and importance of questionnaires, qualities of a good questionnaire, questionnaire development process, types of questions, order and format of questions, things to avoid, formalities before interviews, and validation. Well-designed questionnaires can efficiently collect accurate and relevant information to answer research questions. They should be concise, use simple language, and avoid biases and errors.