This document provides an overview of key concepts related to quality including:
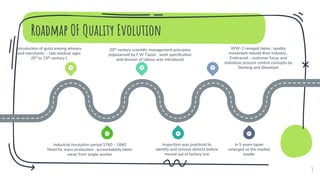
- The evolution of quality concepts from medieval guilds to modern quality gurus like Deming and Juran.
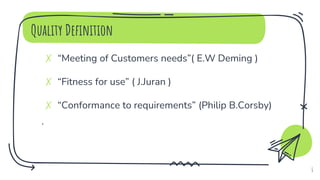
- Definitions of quality focusing on meeting customer needs, fitness for use, and conforming to requirements.
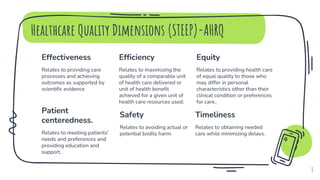
- Dimensions of healthcare quality including effectiveness, efficiency, equity, patient-centeredness, safety, and timeliness.
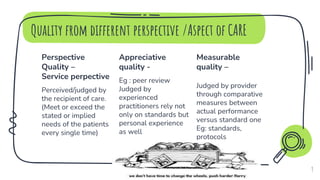
- Different perspectives for evaluating quality from the service, peer review, and measurable standards perspectives.
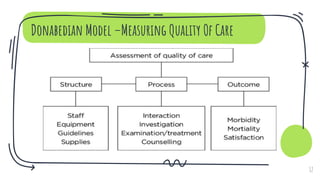
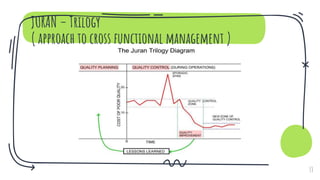
- Models for quality including the phases of quality, continuous quality improvement (CQI), the Donabedian model for measuring care quality, and Juran's trilogy for quality management.