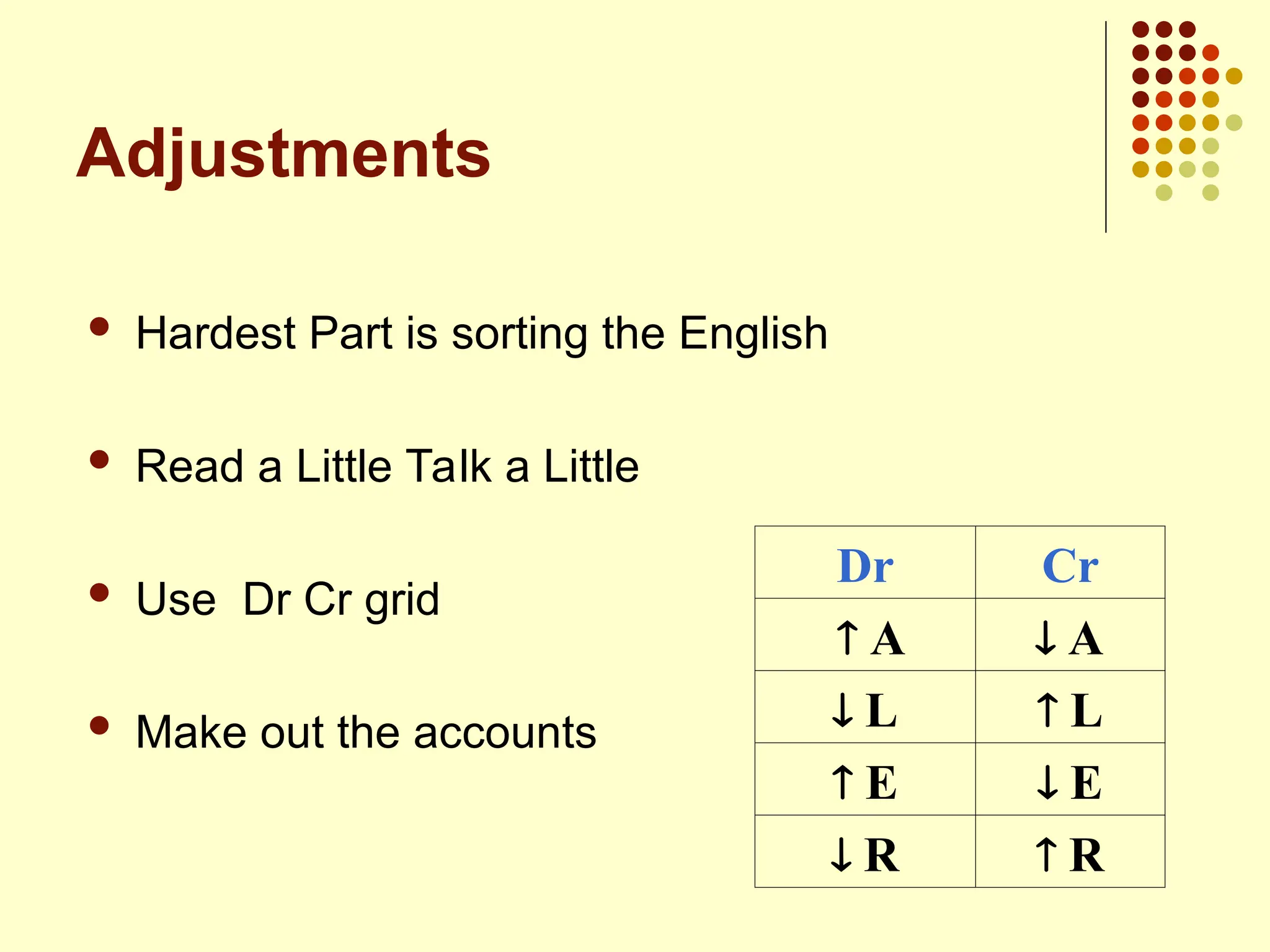
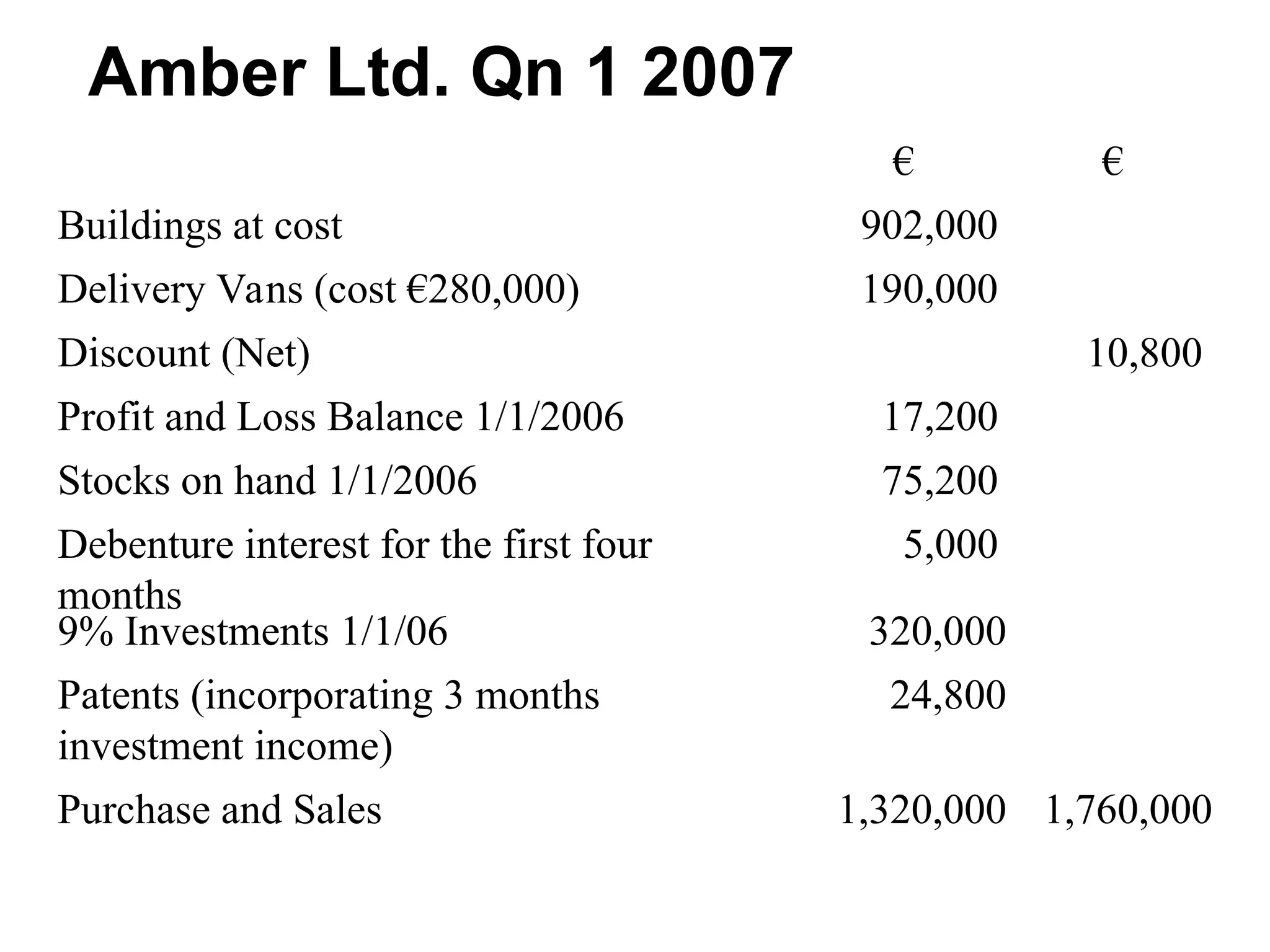
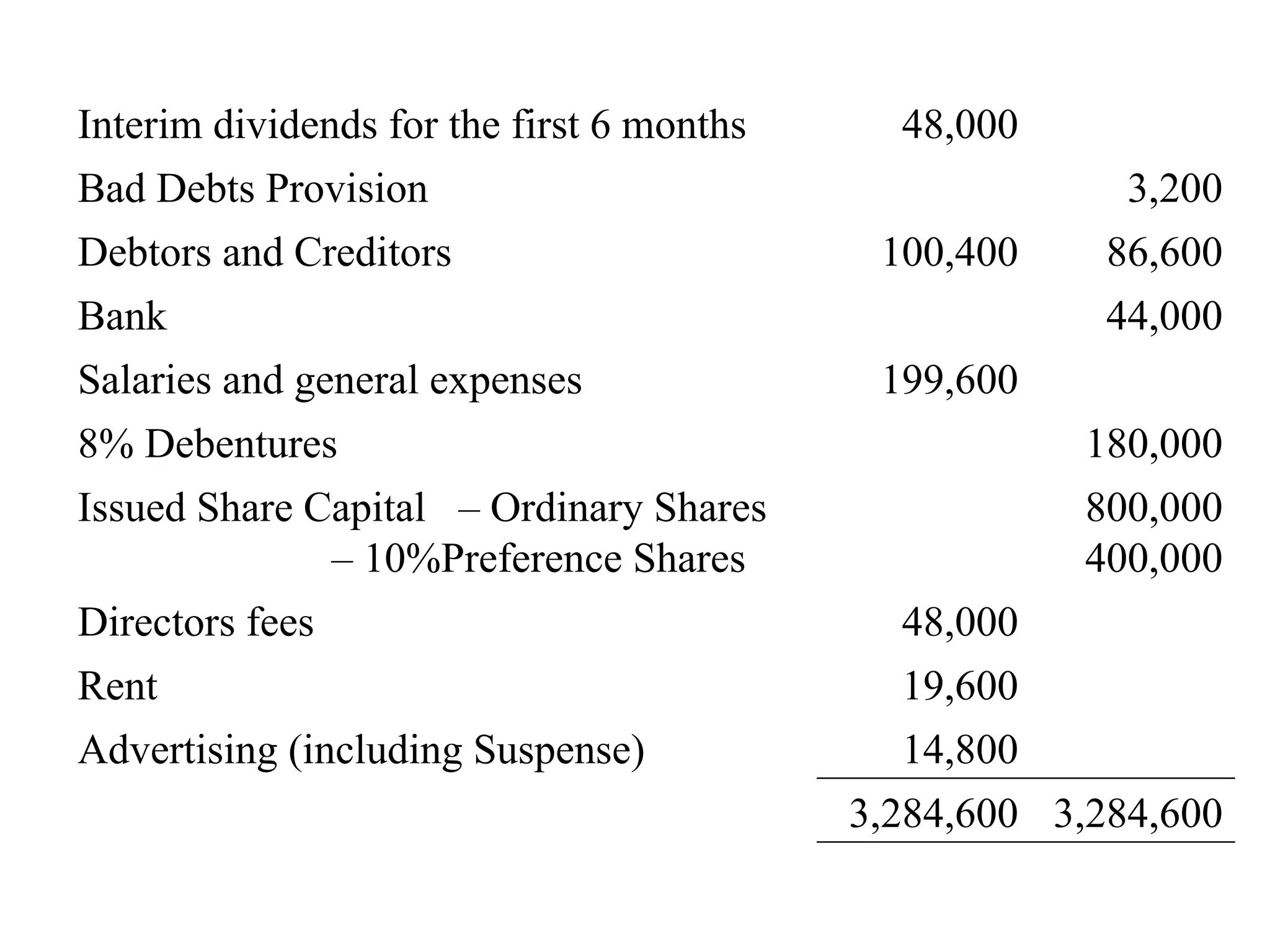
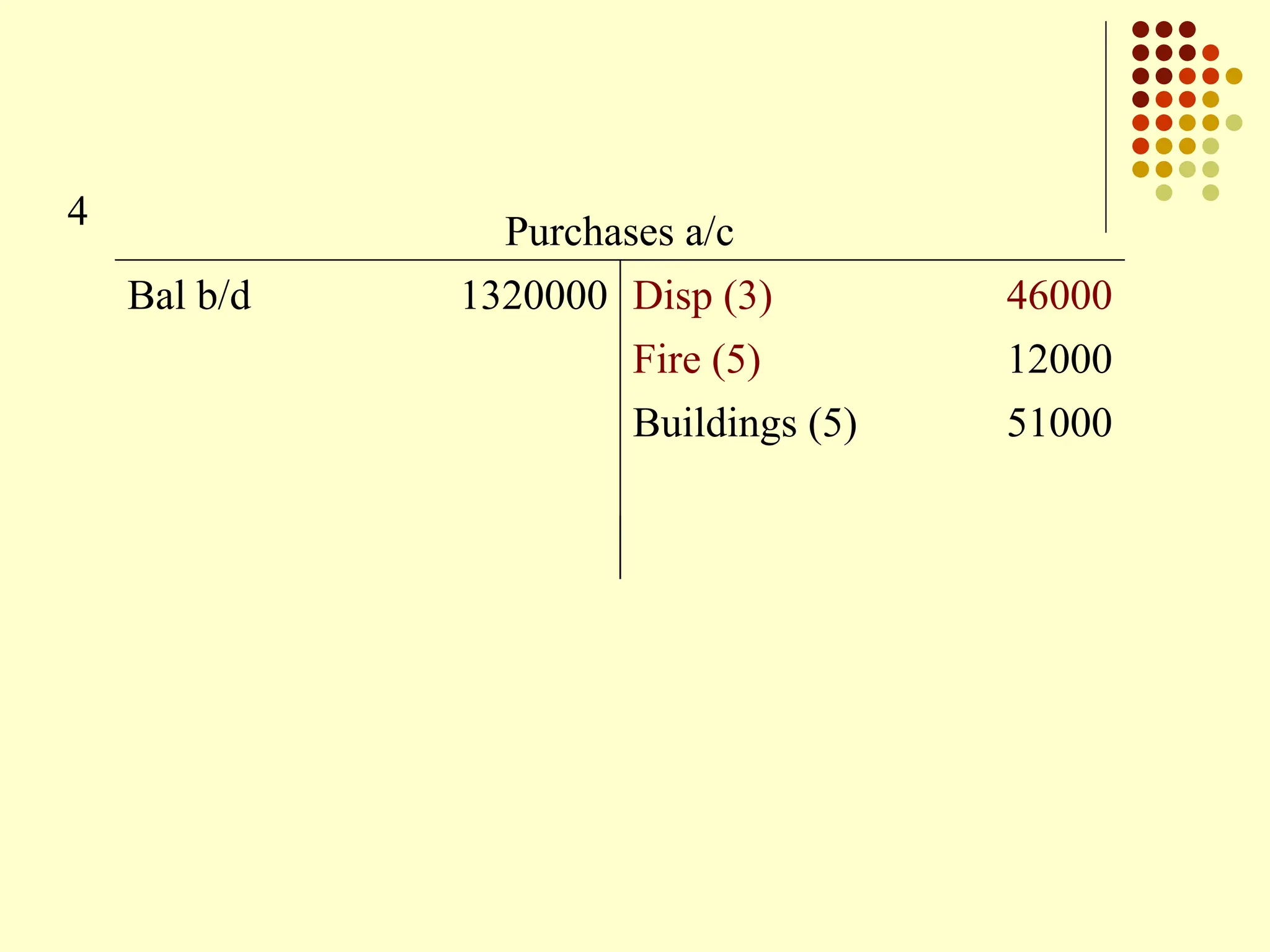
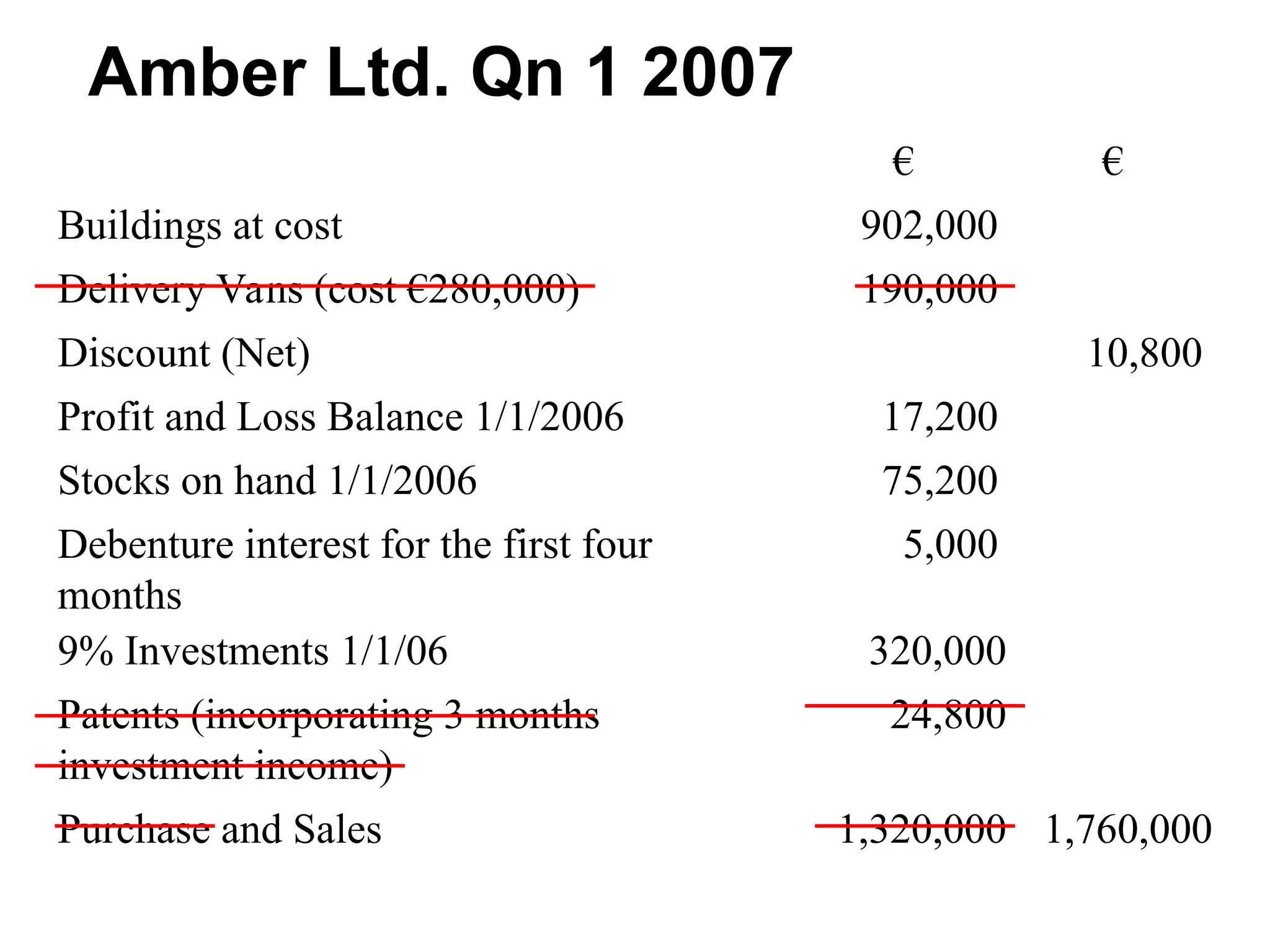
The document outlines the process of preparing final accounts using double entry accounting principles, highlighting key elements such as asset and liability management, matching transactions with appropriate accounts, and necessary adjustments for accuracy. It details how to record various financial transactions, prepare profit and loss accounts, and create a balance sheet to assess a firm's worth. Additionally, it offers guidance on handling specific adjustments and managing incomplete records while conducting a trial balance.















![Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4
Source Documents Subsidiary Books Ledger
Double Entry
Final Accounts
Balance Sheet
Invoices
[credit purchases and
sales]
Sales Book
Purchases Book Post these
transactions
using
Double Entry
Rules
Transfer
from the
Ledger to
ascertain
Profit for
the Year and
the Net
Worth of the
Company at
a point in
time
Credit Notes
Sales Returns Book
Purchases Returns
Book
Cheque Payments Cheque Payments Book
Receipts Cash Receipts Book
Anything Else General Journal
Recording Transactions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qn10-241113134730-0b074002/75/Qn-1_0-ppt-for-bba-mba-and-commerce-students-17-2048.jpg)