The document provides detailed instructions for two programming homework assignments related to Python. The first assignment involves creating a dictionary to manage an inventory of items categorized by price, and implementing functions to retrieve information about these items. The second assignment focuses on building a web indexing and search engine with a ranking system based on word frequency and requires implementing several functions for indexing, searching, and sorting web pages.

![Quick Reference
D = { } – creates an empty dictionary
D = {key1:value1, …} – creates a non-empty dictionary
D[key] – returns the value that’s mapped to by key. (What if there’s no such key?)
D[key] = newvalue – maps newvalue to key. Overwrites any previous value. del D[key]
– deletes the mapping with that key from D.
len(D) – returns the number of entries (mappings) in D. x in D, x not in D – checks
whether the key x is in the dictionary D.
D.items( ) – returns the entries as a list of (key, value) tuples. for k in D – iterates over
all of the keys in D.
Problem 1 – Inventory Finder
Download the inventory.py file. The file shows eight different items, each having a
name, a price and a count, like so:
HAMMER = “hammer”
HAMMER_PRICE = 10
HAMMER_COUNT = 100
Problems
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-2-320.jpg)


![In order to rank each site by the frequency of search terms in it, we’ll have to store the
information in our index.
To begin, you can copy your functions’ code from webindexer1.py into webindexer2.py,
but you don’t have to.
Task 1 – Implement the index_site function. What information will each site in the index
need to store with it? What’s the best way to store this information? If we have more than
one choice, which choice is mutable, and which one is immutable? While we’re building
the index, we’ll be repeatedly making changes, so which choice is better?
Hints: If you’re stuck, think very logically. When I’m searching, I have a word. I want to be
able to look up this word and get what information? The information needs to be enough
for me to sort it.
Now that we’ve taken care of indexing, we can again move on to searching. And again, we’ll
tackle one word first before multiple words. This should be very similar to your previous
function, but we have to do one additional thing: sort the results based on frequency.
Task 2 – Implement the search_single_word function. We have to return a list of (site,
frequency) tuples. If we have a list L of these tuples, to sort them, do this:
L.sort(key = lambda pair: pair[1], reverse = True)
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-5-320.jpg)
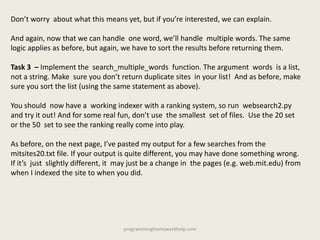


![inventory = { # key1 : value1, note how I can continue on the next line,
# key2 : value2, I don't need a backslash or anything.
# key3 : value3
}
def get_items(cheapness):
""" Return a list of (item, (price, count) tuples that are the given
cheapness. Note that the second element of the tuple is another tuple. """
# your code here
return [] # delete this
# Testing
cheap = get_items(CHEAP)
print type(cheap) is list
print len(cheap) == 5
print (HAMMER, (HAMMER_PRICE, HAMMER_COUNT)) in cheap
print (NAIL, (NAIL_PRICE, NAIL_COUNT)) in cheap
print (SCREW, (SCREW_PRICE, SCREW_COUNT)) in cheap
print (SCREWDRIVER, (SCREWDRIVER_PRICE, SCREWDRIVER_COUNT)) in cheap
print (HANDSAW, (HANDSAW_PRICE, HANDSAW_COUNT)) in cheap
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-9-320.jpg)

![index = {}
def get_sites():
""" Return all the sites that are in FILENAME. """
sites_file = open(FILENAME)
sites = []
for site in sites_file:
sites.append("http://" + site.strip())
return sites
def read_site(site):
""" Attempt to read the given site. Return the text of the site if
successful, otherwise returns False. """
try:
connection = urlopen(site)
html = connection.read()
connection.close()
except:
return False
parser = HtmlTextParser()
parser.parse(html)
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-11-320.jpg)




![inventory = {
CHEAP : {
HAMMER : (HAMMER_PRICE, HAMMER_COUNT),
NAIL : (NAIL_PRICE, NAIL_COUNT),
SCREW : (SCREW_PRICE, SCREW_COUNT),
SCREWDRIVER : (SCREWDRIVER_PRICE, SCREWDRIVER_COUNT),
HANDSAW : (HANDSAW_PRICE, HANDSAW_COUNT)
},
MODERATE : {
DRILL : (DRILL_PRICE, DRILL_COUNT),
CHAINSAW : (CHAINSAW_PRICE, CHAINSAW_COUNT)
},
EXPENSIVE : {
WORKBENCH : (WORKBENCH_PRICE, WORKBENCH_COUNT)
}
}
def get_items(cheapness):
""" Return a list of (item, (price, count)) tuples that are the given
cheapness. Note that the second element of the tuple is another tuple. """
return inventory[cheapness].items()
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-16-320.jpg)

![# webindexer2.py
# Stub file for lab 10, problem 2
#
# 6.189 - Intro to Python
# IAP 2008 - Class 8
from urllib import urlopen
from htmltext import HtmlTextParser
FILENAME = "smallsites.txt"
index = {}
def get_sites():
""" Return all the sites that are in FILENAME. """
sites_file = open(FILENAME)
sites = []
for site in sites_file:
sites.append("http://" + site.strip())
return sites
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-18-320.jpg)
![def read_site(site):
""" Attempt to read the given site. Return the text of the site if
successful, otherwise returns False. """
try:
connection = urlopen(site)
html = connection.read()
connection.close()
except:
return False
parser = HtmlTextParser()
parser.parse(html)
return parser.get_text()
def index_site(site, text):
""" Index the given site with the given text. """
words = text.lower().split()
for word in words:
if word not in index: # case 1: haven't seen word anywhere
index[word] = {site:1} # make a new entry for the word
elif site not in index[word]: # case 2: haven't seen word on
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-19-320.jpg)
![this site
index[word][site] = 1 # make a new entry for this site
else: # case 3: seen this word on this site
index[word][site] += 1 # increment the frequency by 1
def search_single_word(word):
""" Return a list of (site, frequency) tuples for all sites containing the
given word, sorted by decreasing frequency. """
if word not in index:
return []
L = index[word].items()
L.sort(key = lambda pair: pair[1], reverse = True)
return L
def search_multiple_words(words):
""" Return a list of (site, frequency) tuples for all sites containing any
of the given words, sorted by decreasing frequency. """
all_sites = {}
for word in words:
for site, freq in search_single_word(word):
if site not in all_sites: # case 1: haven't included this site
all_sites[site] = freq # make a new entry for site, freq
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-20-320.jpg)
![else: # case 2: have included this site
all_sites[site] += freq # add the frequencies
L = all_sites.items()
L.sort(key = lambda pair: pair[1], reverse = True)
return L
def build_index():
""" Build the index by reading and indexing each site. """
for site in get_sites():
text = read_site(site)
while text == False:
text = read_site(site) # keep attempting to read until successful
index_site(site, text)
programminghomeworkhelp.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminghomeworkhelp-211204050844/85/Python-Homework-Help-21-320.jpg)