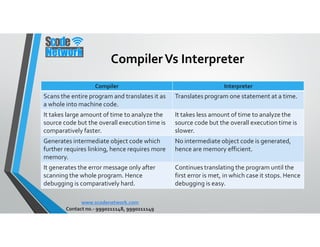
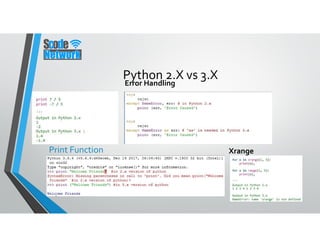
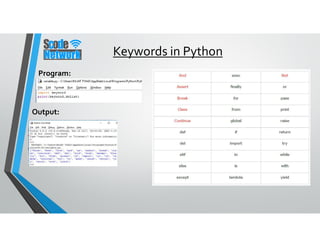
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language that supports various programming paradigms including object-oriented, imperative, and functional styles. It was developed by Guido van Rossum in 1989 and has evolved through various versions, with Python 3.0 released in 2008 to address fundamental flaws. Python's features include its ease of learning, cross-platform compatibility, and extensive libraries, making it suitable for a wide range of applications from web development to scientific computing.