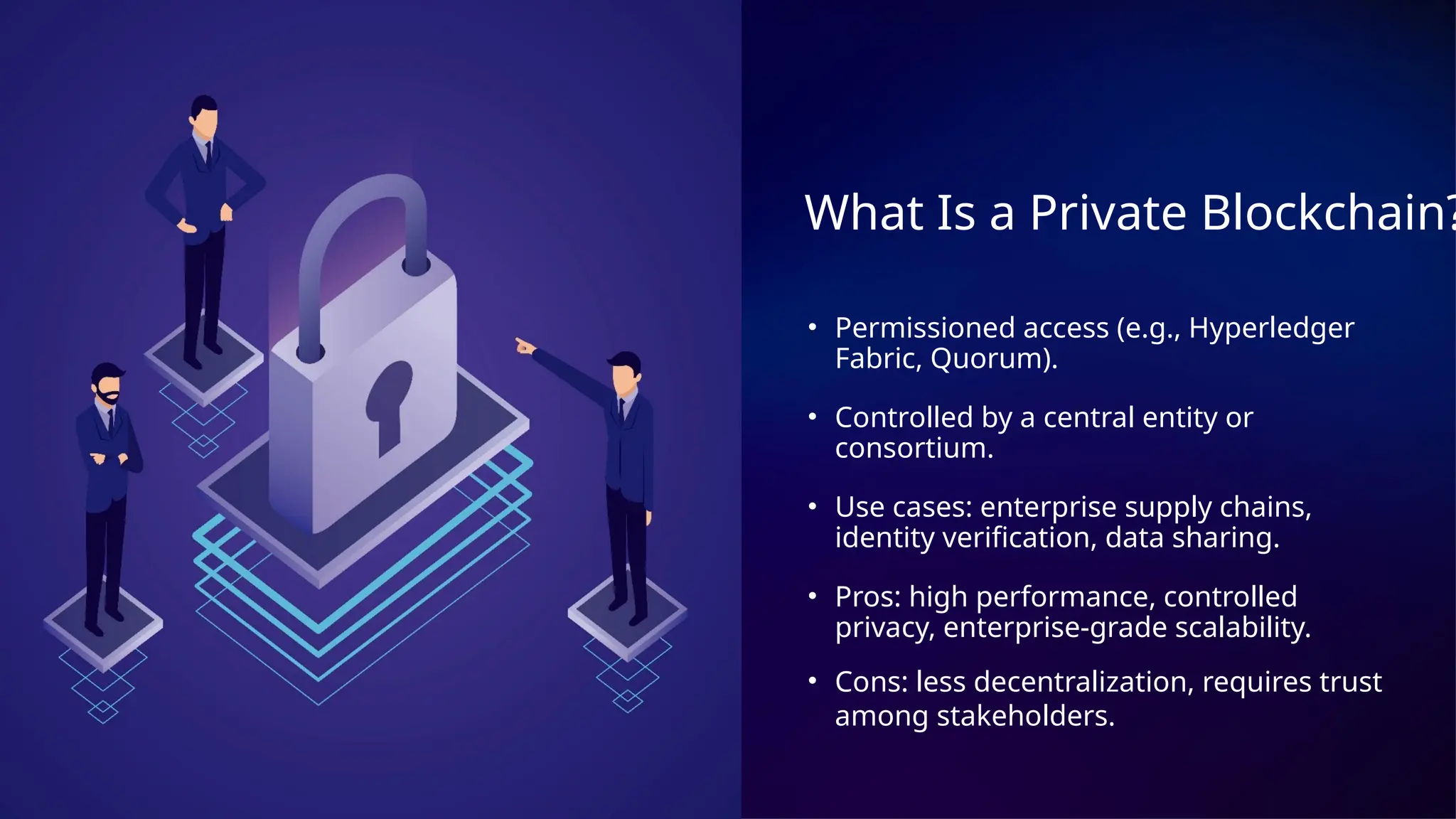
Deciding between public and private blockchains is more than a tech call—it’s a business-critical one. In this presentation, we walk through real use cases, from healthcare to logistics, and explore how enterprise blockchain solutions and smart contract development services help companies build secure, scalable systems. Whether you’re new to blockchain software development services or refining your strategy, this guide covers what matters most in 2025.