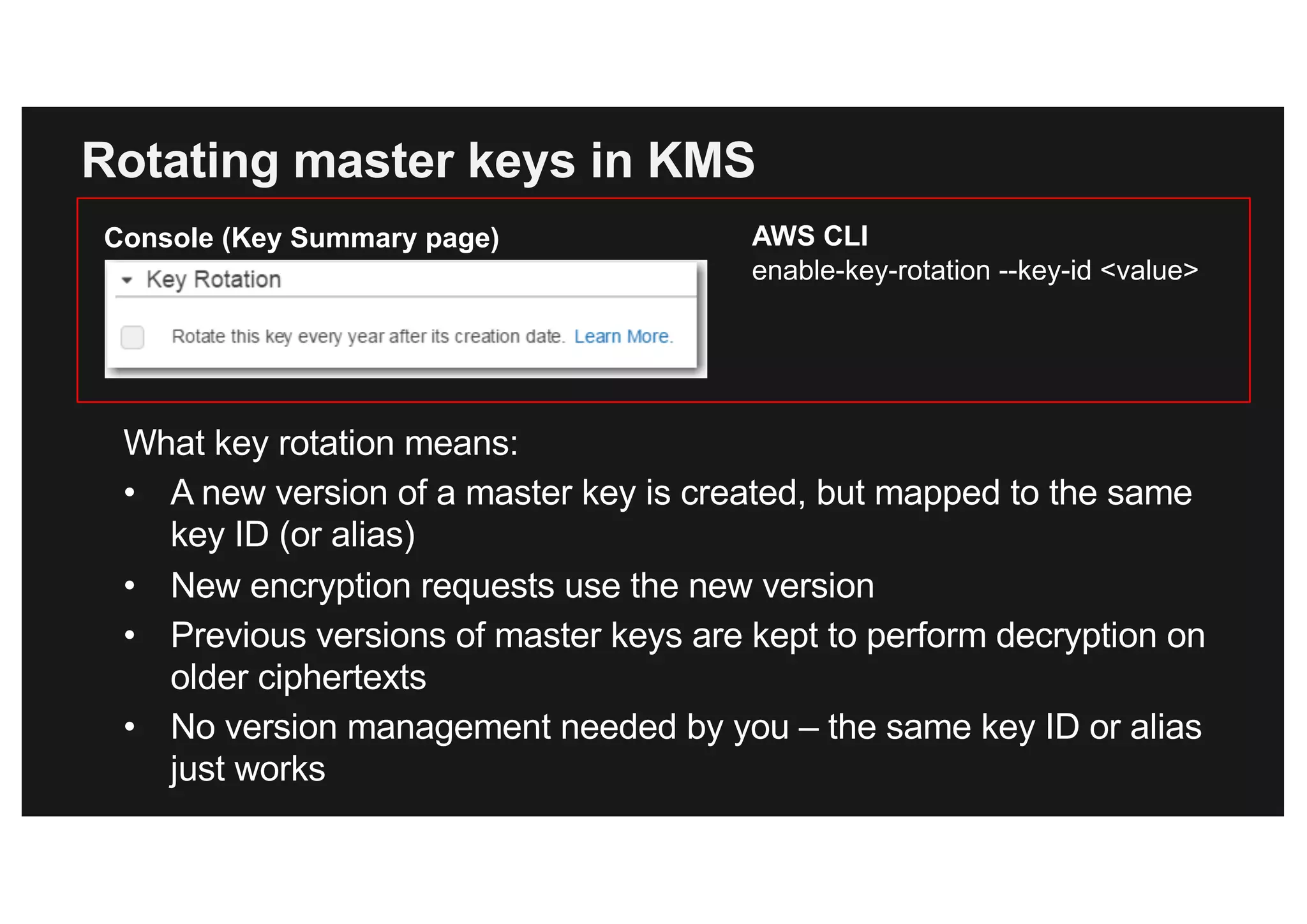
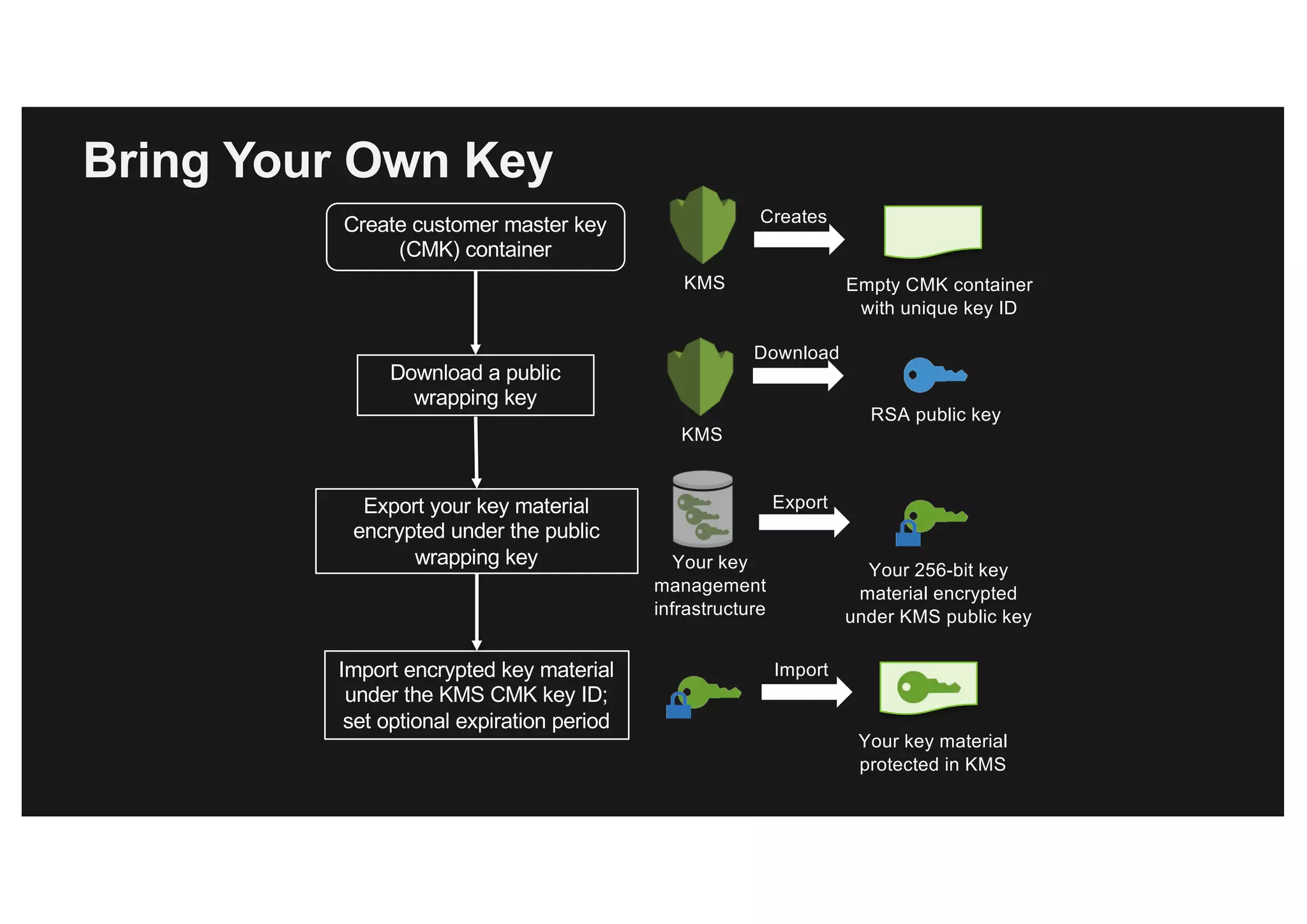
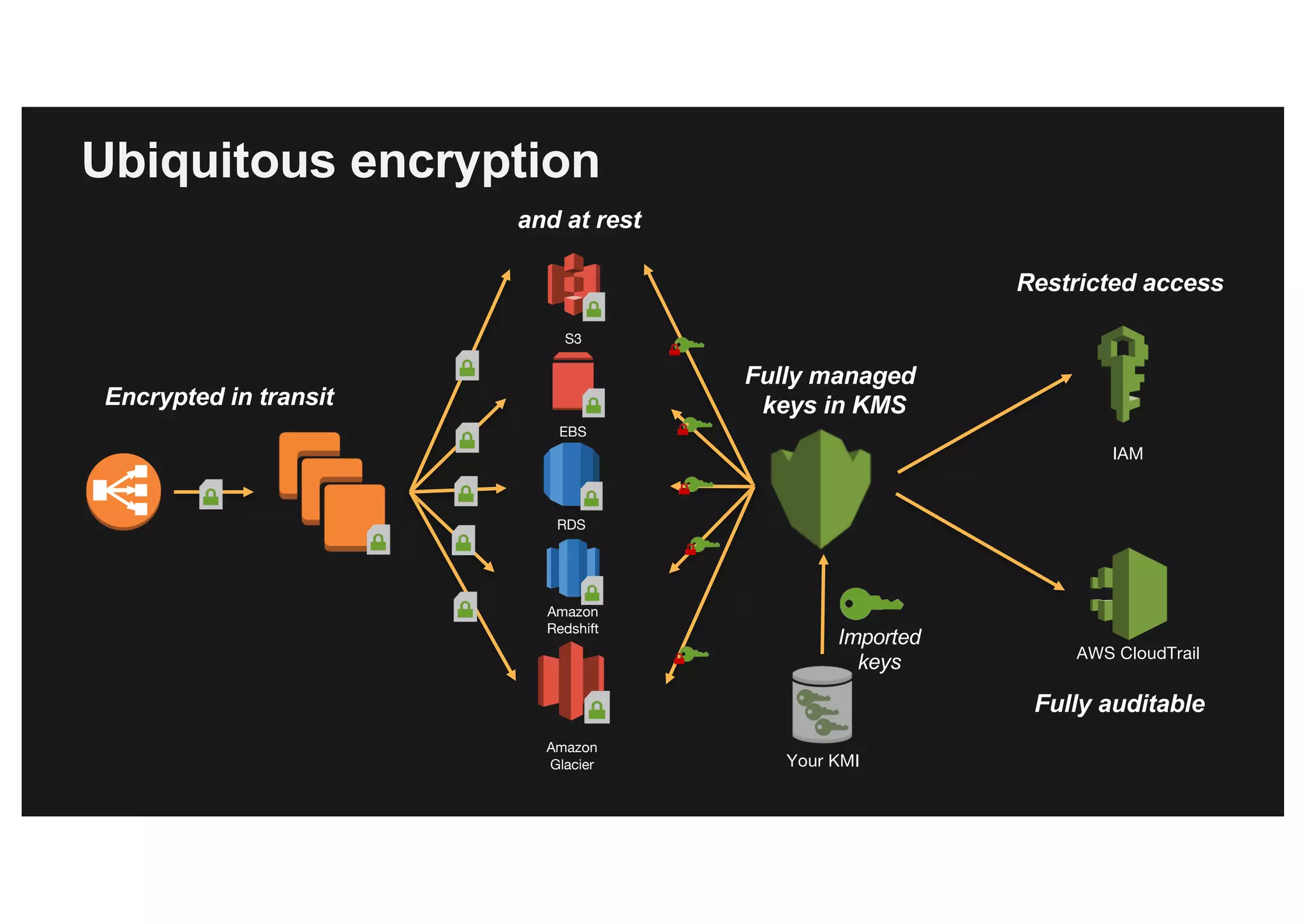
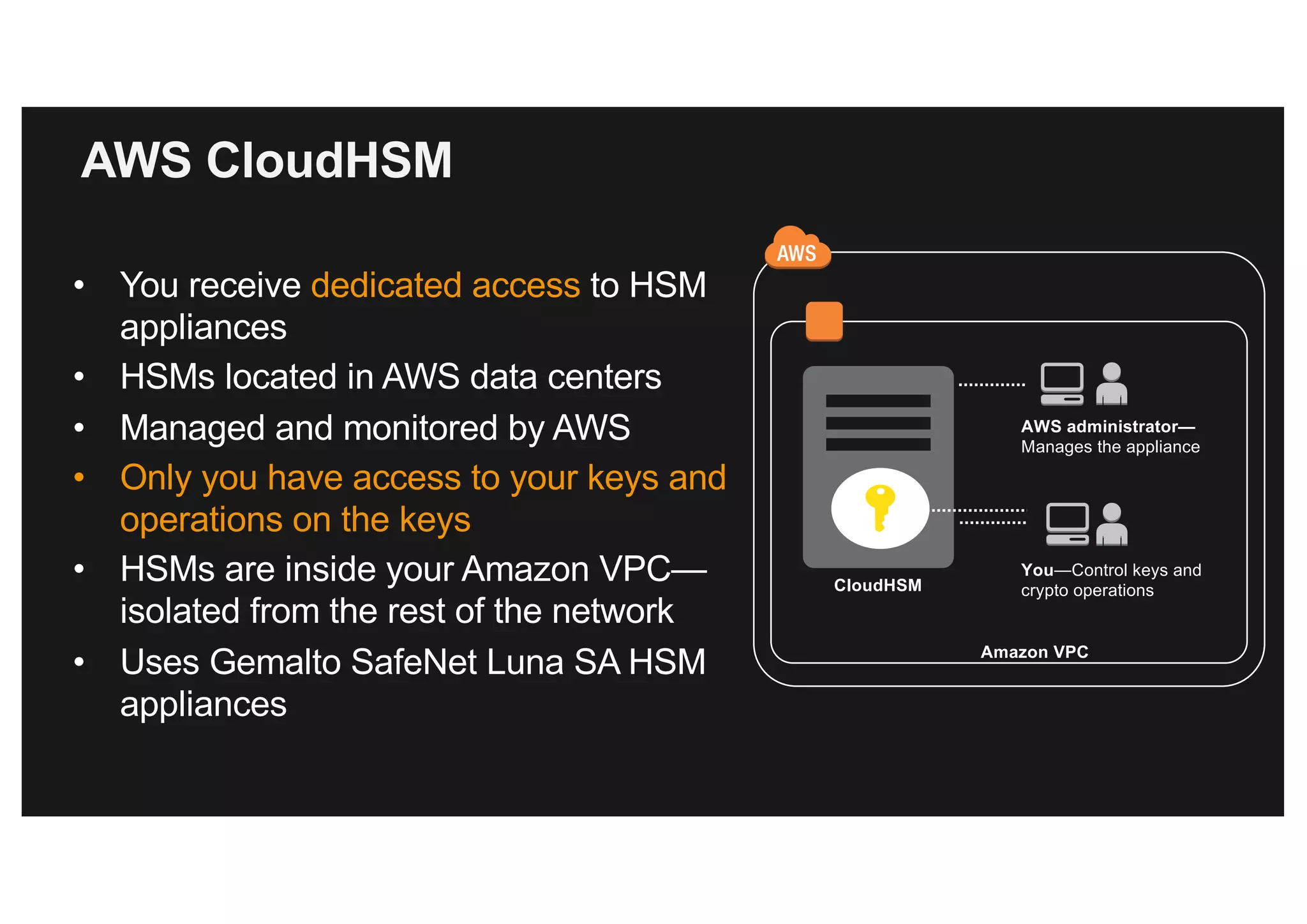
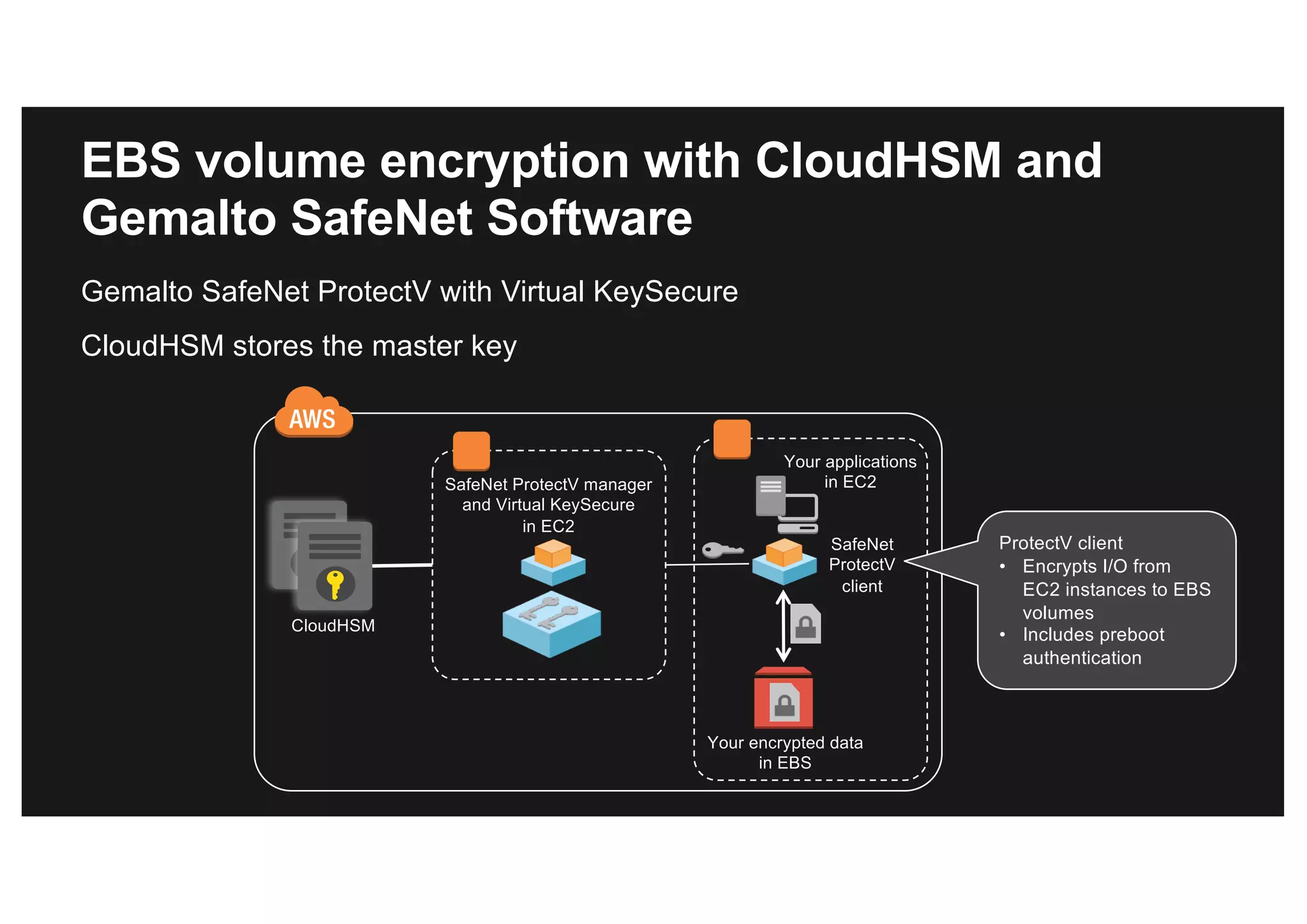
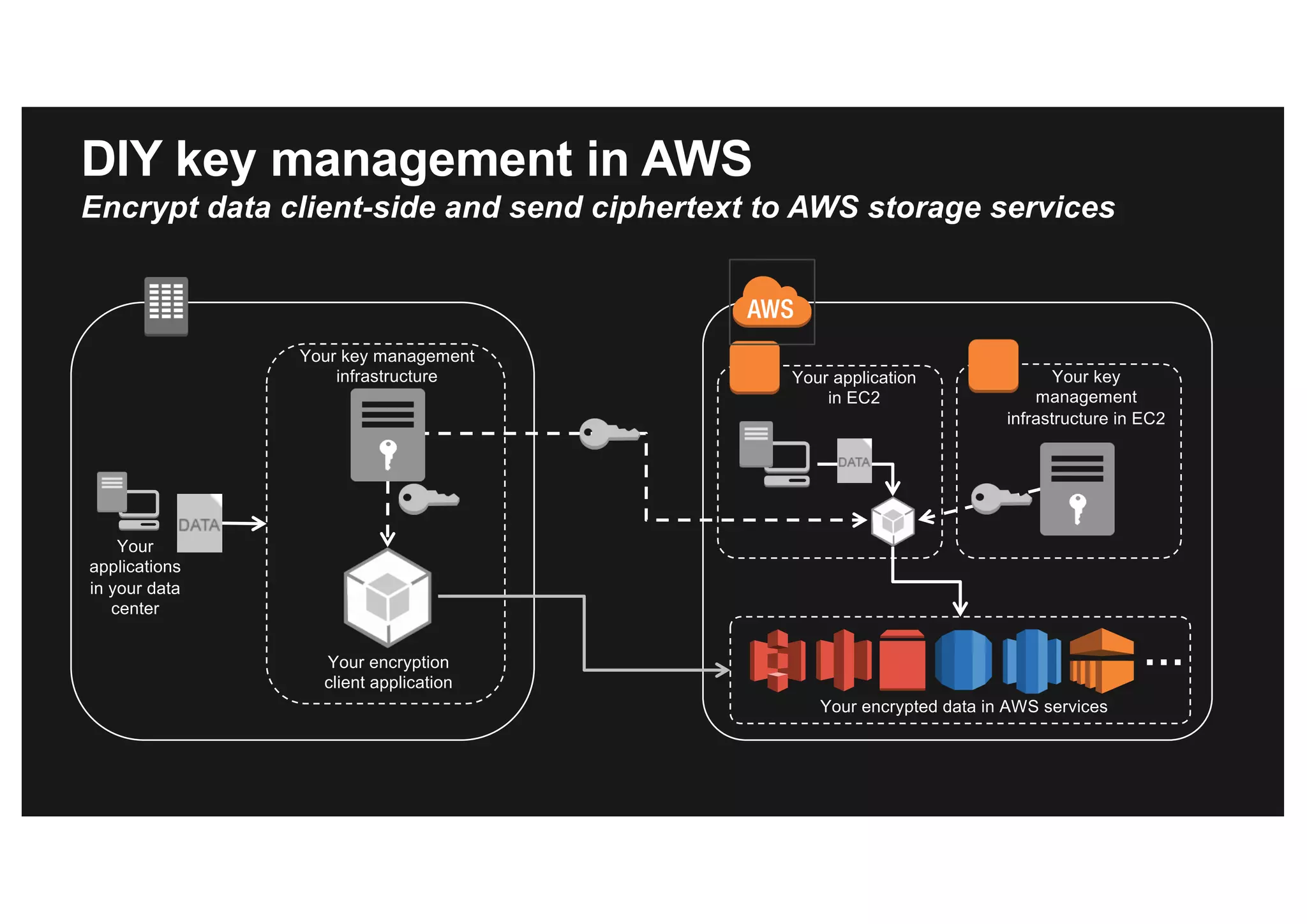
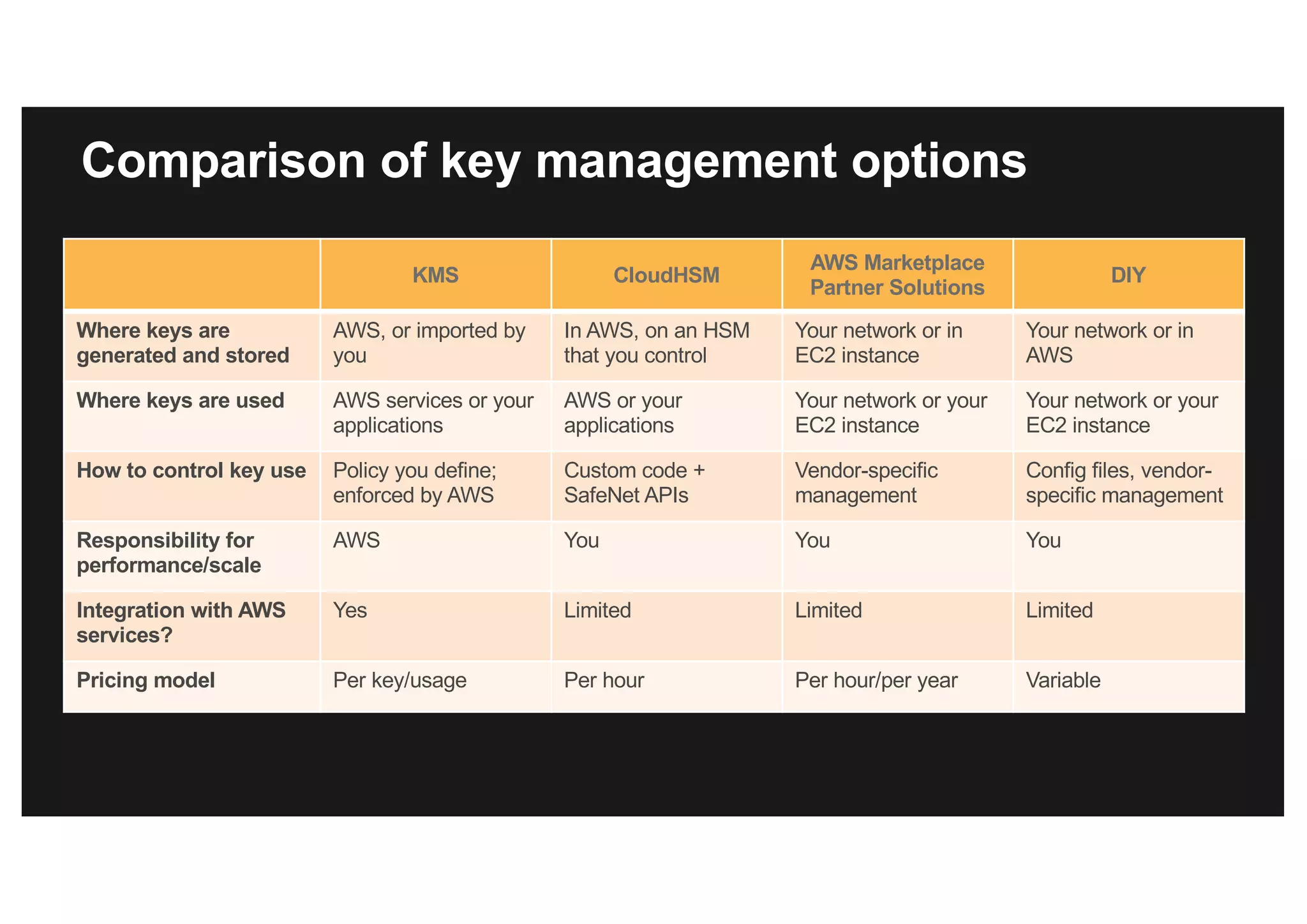
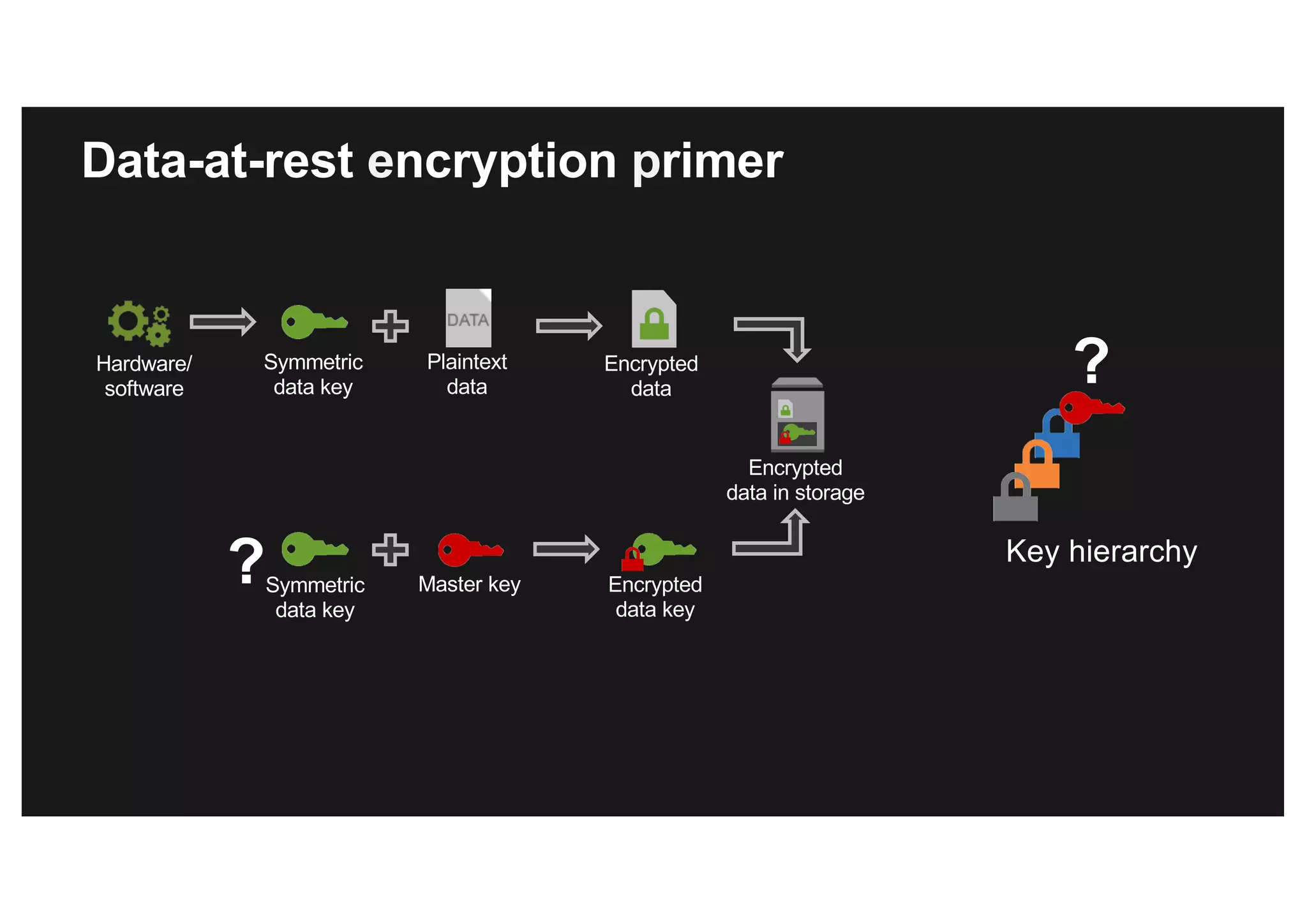
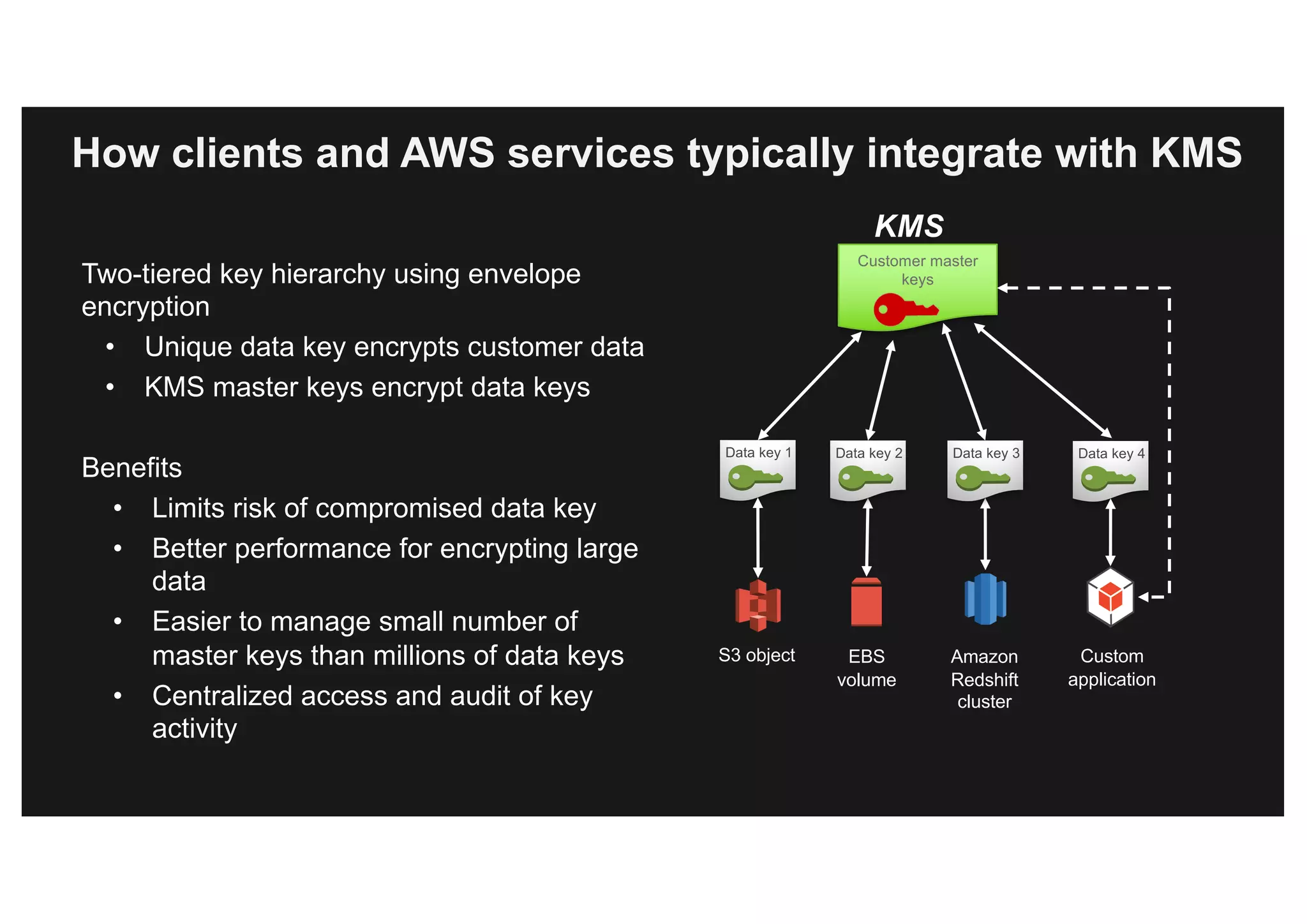
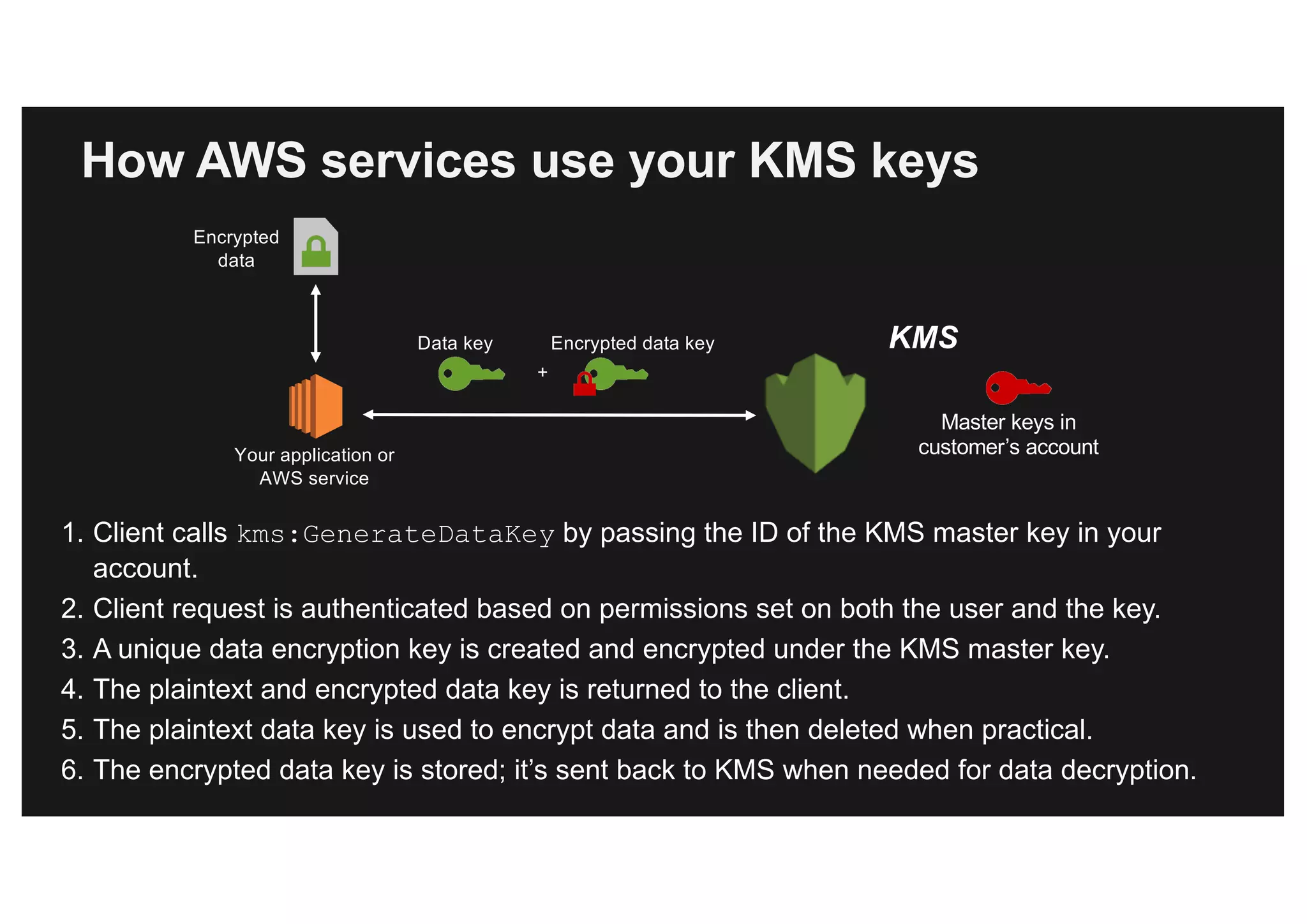
This document discusses various methods for protecting data in AWS, including transport layer security (TLS), server-side encryption, and key management options. It summarizes the AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) for provisioning SSL/TLS certificates, AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for centralized key management, and AWS CloudHSM for dedicated hardware security modules. It compares these services and provides alternatives like partner solutions and building your own key management. The key points covered are security best practices, available encryption options across AWS services, how clients and services integrate with KMS, Bring Your Own Key functionality in KMS, auditability through CloudTrail, and assurances around proper key handling.











![create-volume [--dry-run | --no-dry-run] [--size <value>] [--snapshot-id
<value>] --availability-zone <value> [--volume-type <value>] [--iops <value>]
[--encrypted | --no-encrypted] [--kms-key-id <value>] [--cli-input-json <value>]
[--generate-cli-skeleton]
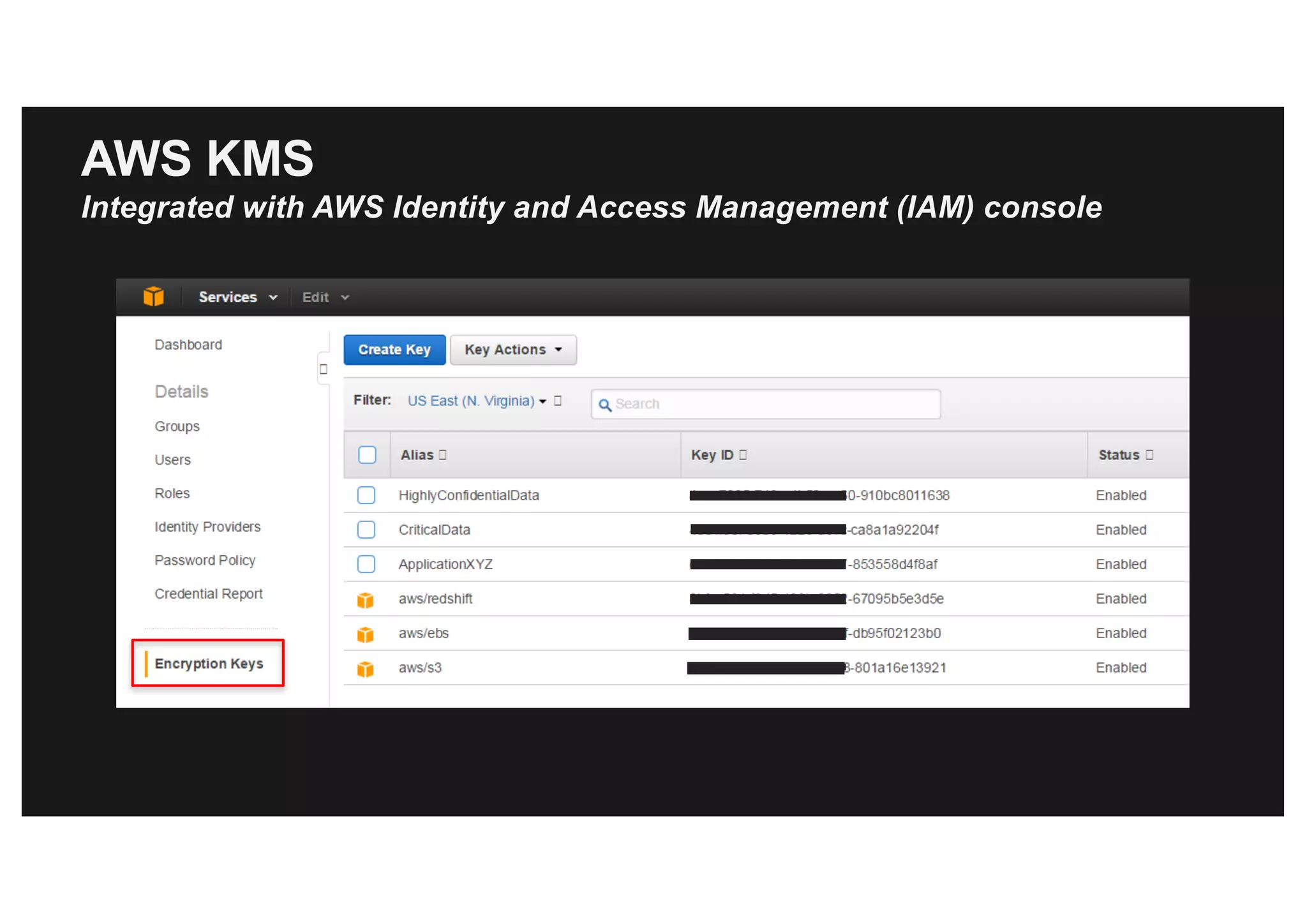
Console
AWS CLI/SDK
Interfaces to select KMS keys in AWS services](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protectingyourdatainawsdinah-170630173445/75/Protecting-your-data-in-AWS-18-2048.jpg)