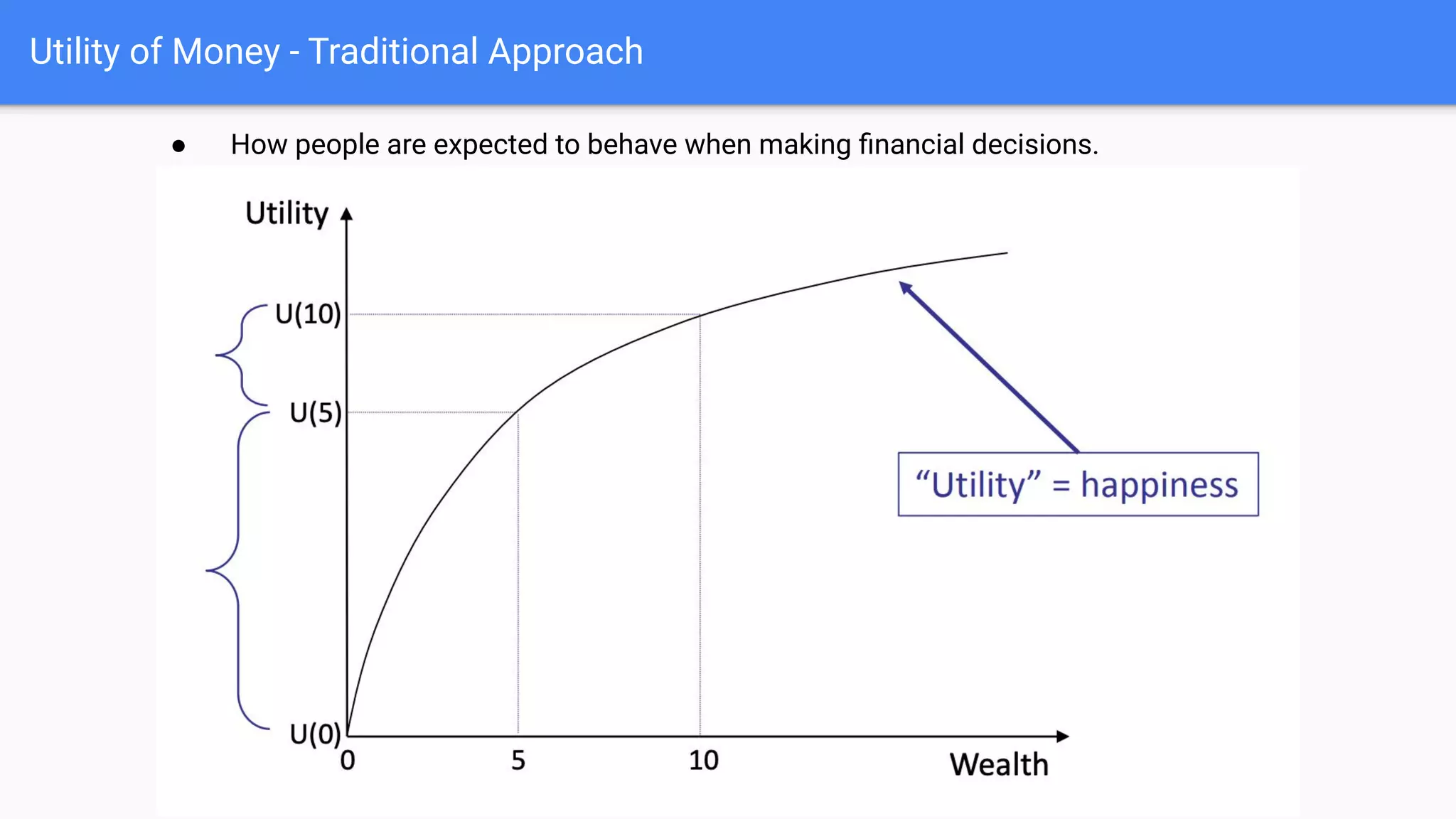
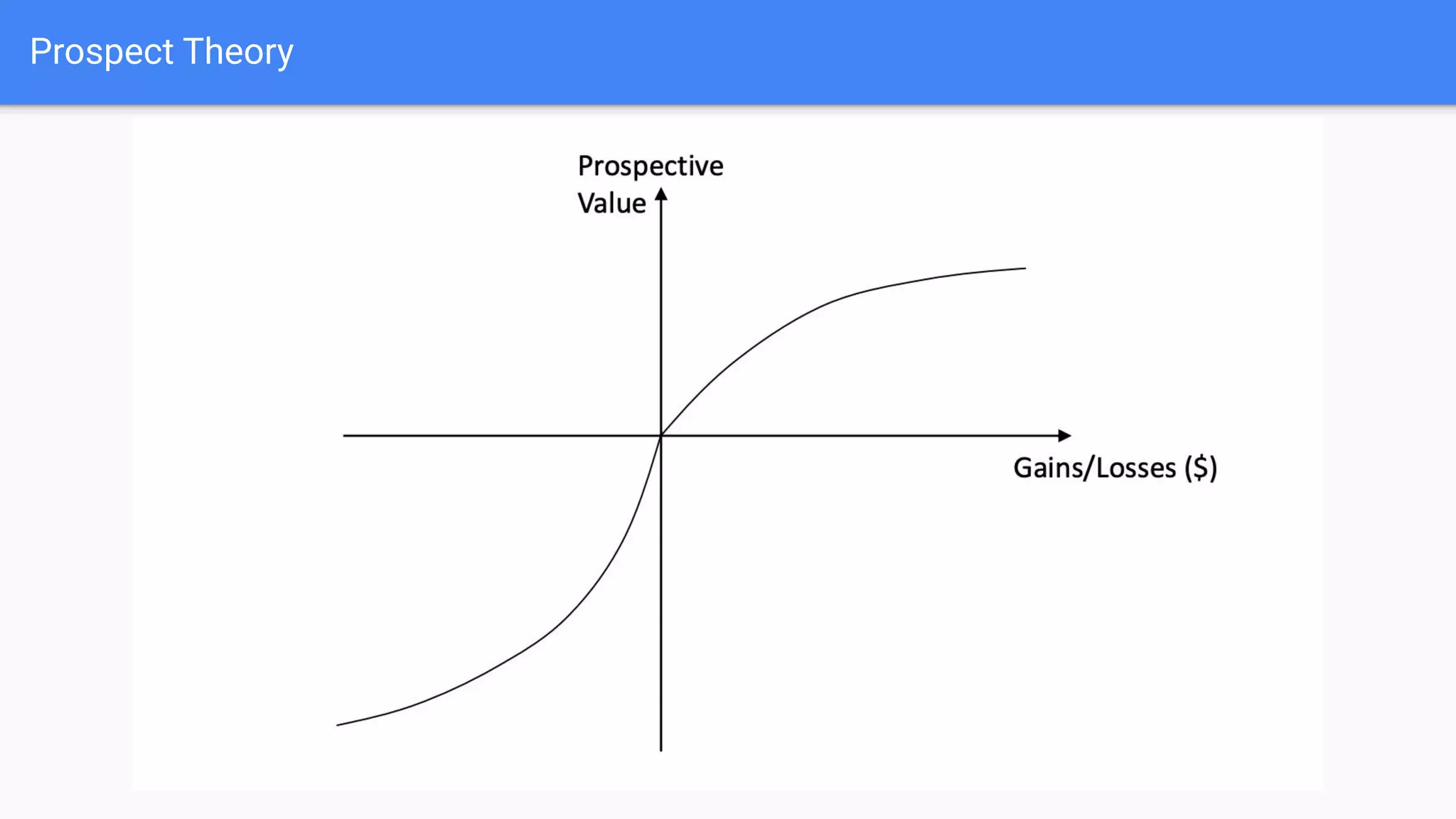
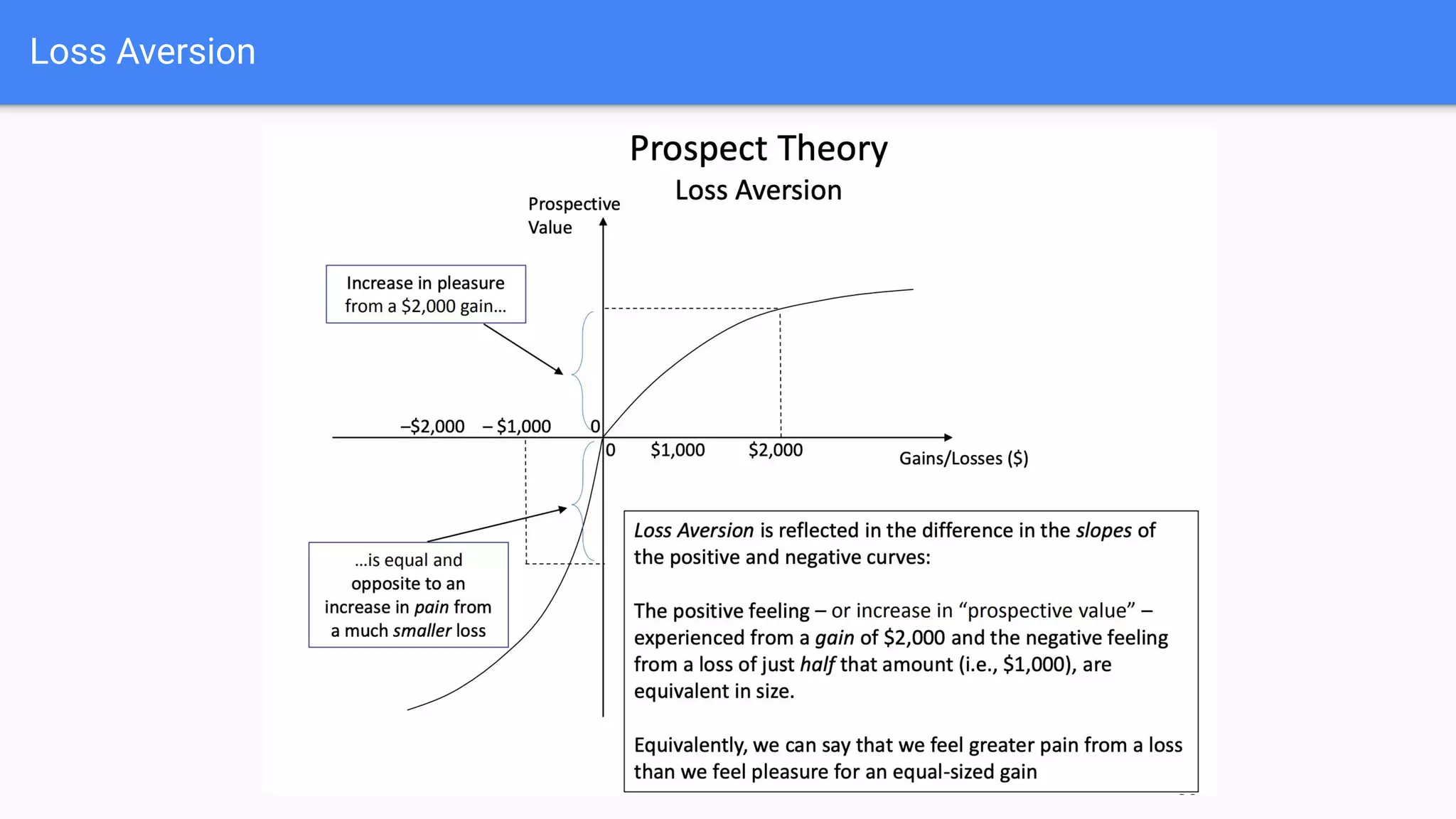
People do not make financial decisions solely based on expected value, but how outcomes are framed. Prospect theory shows people are loss averse - they prefer avoiding losses to acquiring equivalent gains. People also regret potential losses more than potential gains. This leads to risk aversion for gains but risk seeking for losses. Certainty effects also influence decisions - people overweight certainty and avoid uncertainty, preferring options described as 100% effective over 70% effective even with higher probabilities.