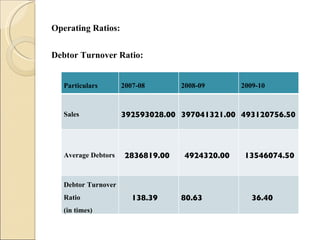
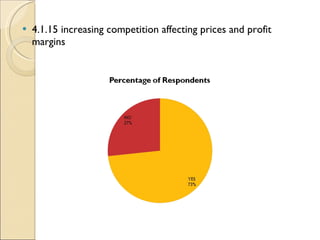
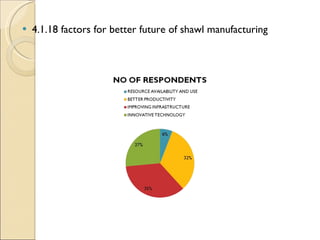
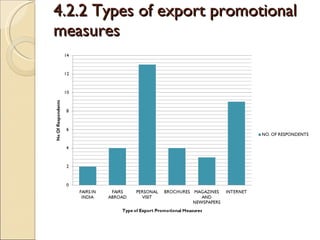
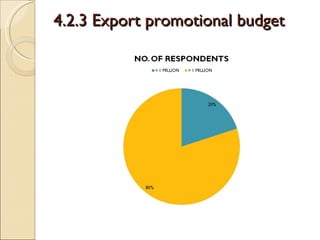
The document discusses the shawl manufacturing industry in Ludhiana, India. It provides background on the origin and current state of the Indian shawl industry. It then focuses on major shawl manufacturers and exporters in Ludhiana, describing one company's operations, vision, strengths, and opportunities. It also includes an analysis of the financials and sales trends of shawl manufacturers. Finally, it discusses the challenges faced by manufacturers and exporters, including issues with infrastructure, labor, imports, and the need for government support through subsidies, export promotion, and simplified export procedures.