This document provides guidelines for formatting and structuring a project report, including:
- Reports should be typed, bound with a front and back cover, and follow proper formatting standards.
- The report should include sections like an introduction, problem definition, design, user manual, and conclusion.
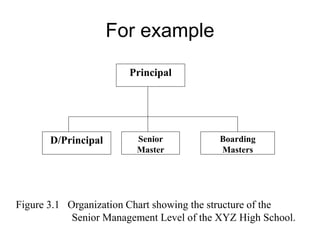
- Specific formatting requirements are provided for page layout, headings, figures, references, and bibliographies.
- Examples are given for formatting book and chapter references.












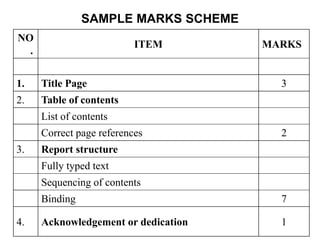
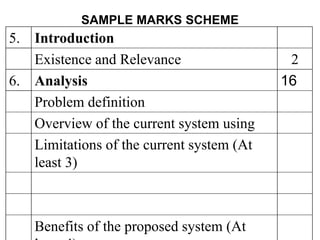
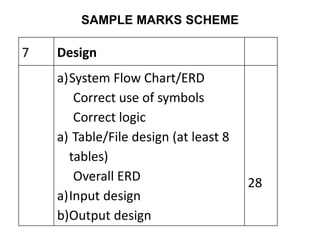
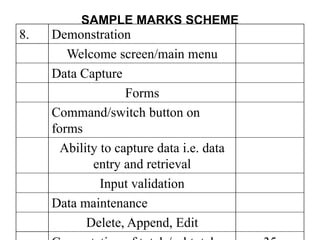
![Structure of the Project Report
• Title Page
• Preface/Acknowledgement
• Table of Contents
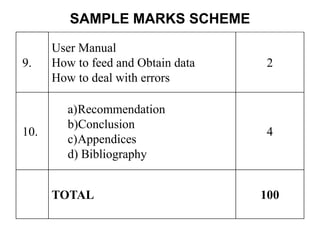
–[List of table]
–[List of Figures]
• Body of Report (Chapter 1-n)
• Bibliography
• Appendices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectreportguide-new-230814152128-e1315766/85/PROJECT-REPORT-GUIDE-new-ppt-15-320.jpg)