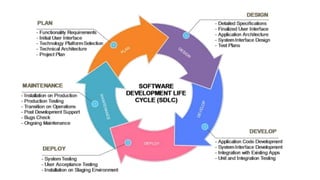
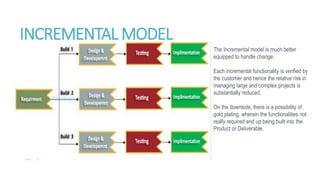
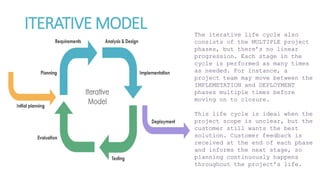
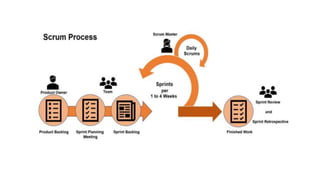
The document discusses various project life cycle models, emphasizing the importance of understanding these phases for effective project delivery. It highlights two specific models: the incremental model, which reduces risk by verifying each functionality with the customer but may lead to unnecessary features, and the iterative model, which allows for repeated phases and continuous planning based on customer feedback, particularly useful for unclear project scopes. Overall, these models cater to different project types and organizational needs.