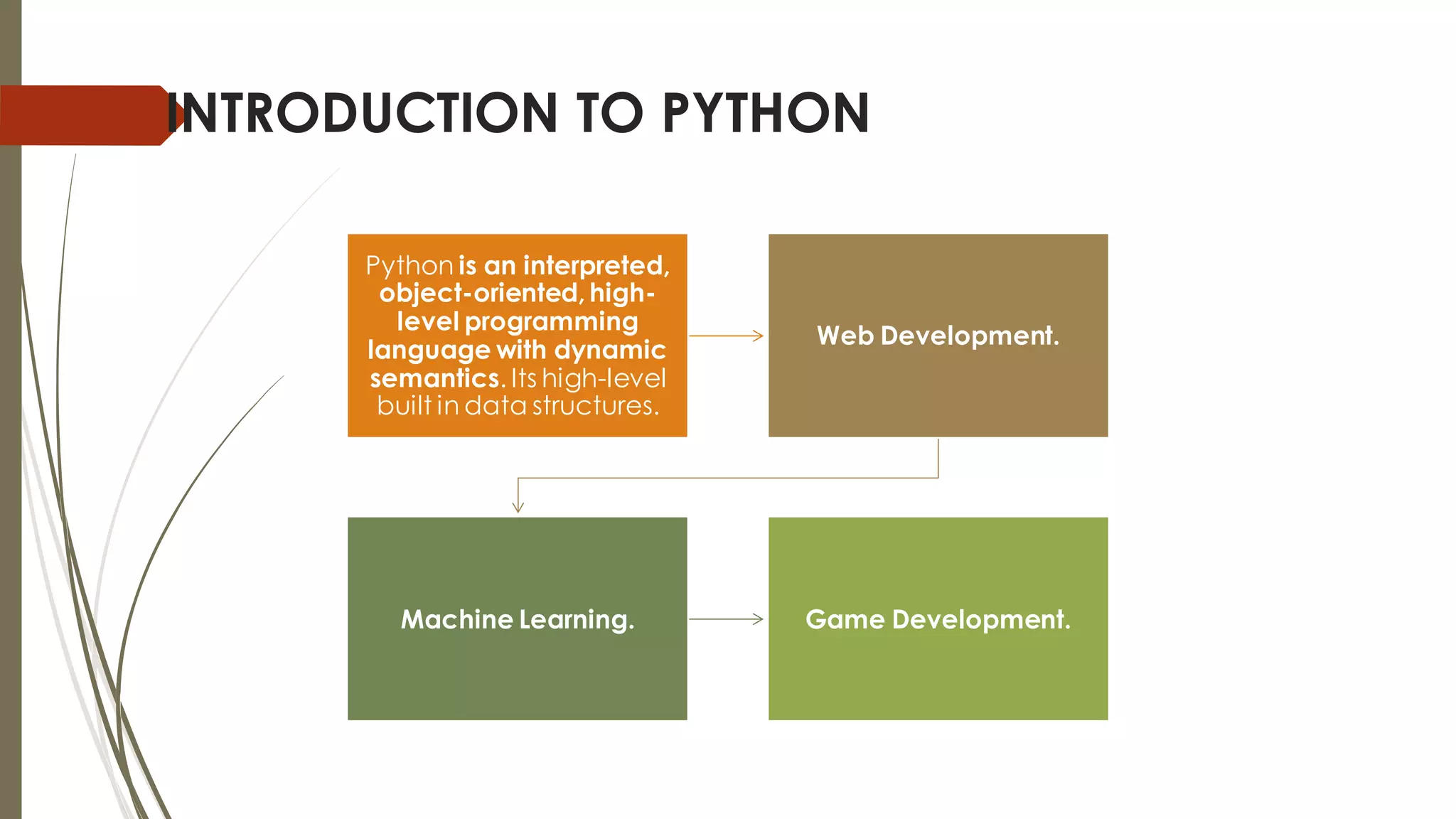
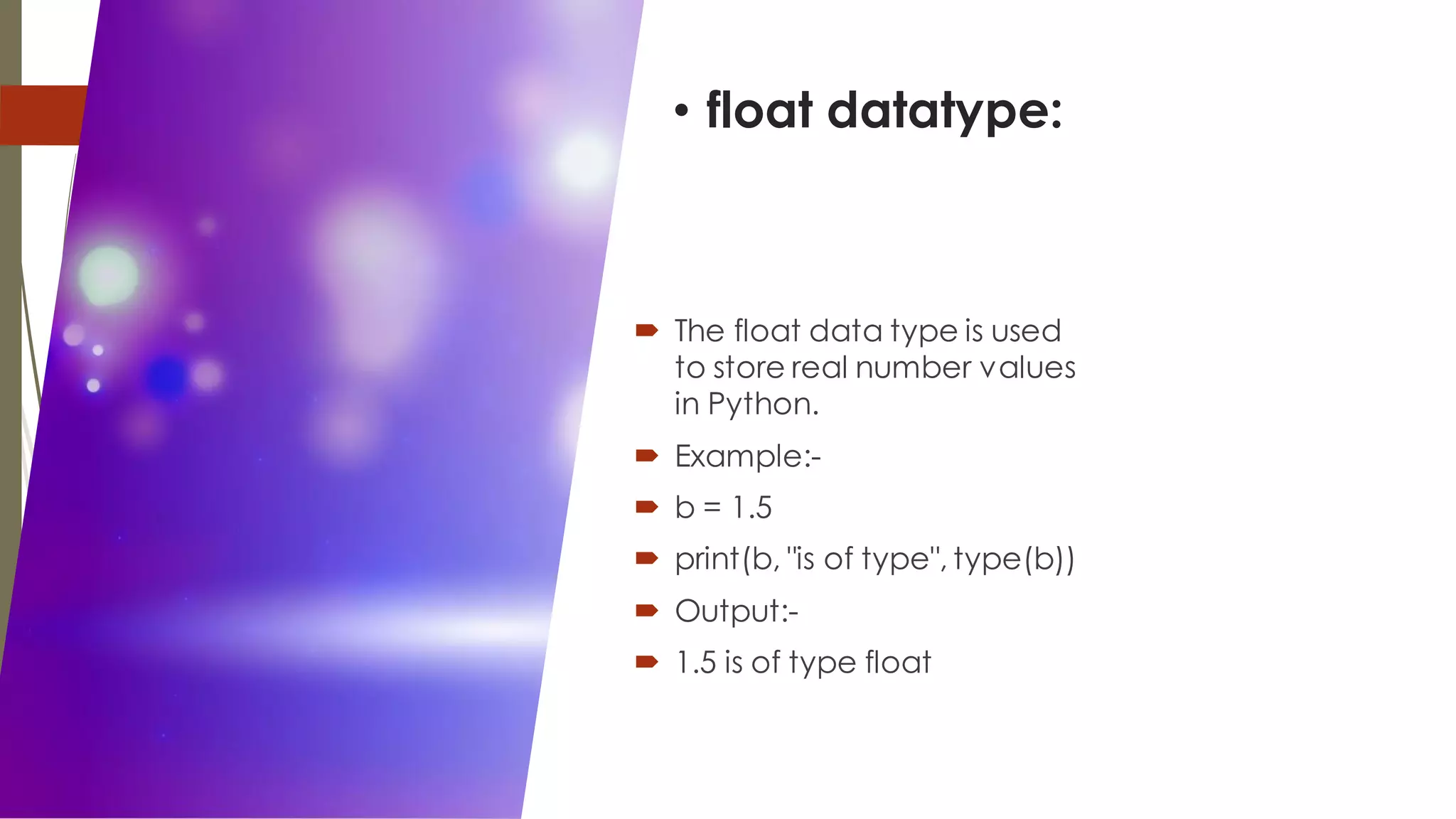
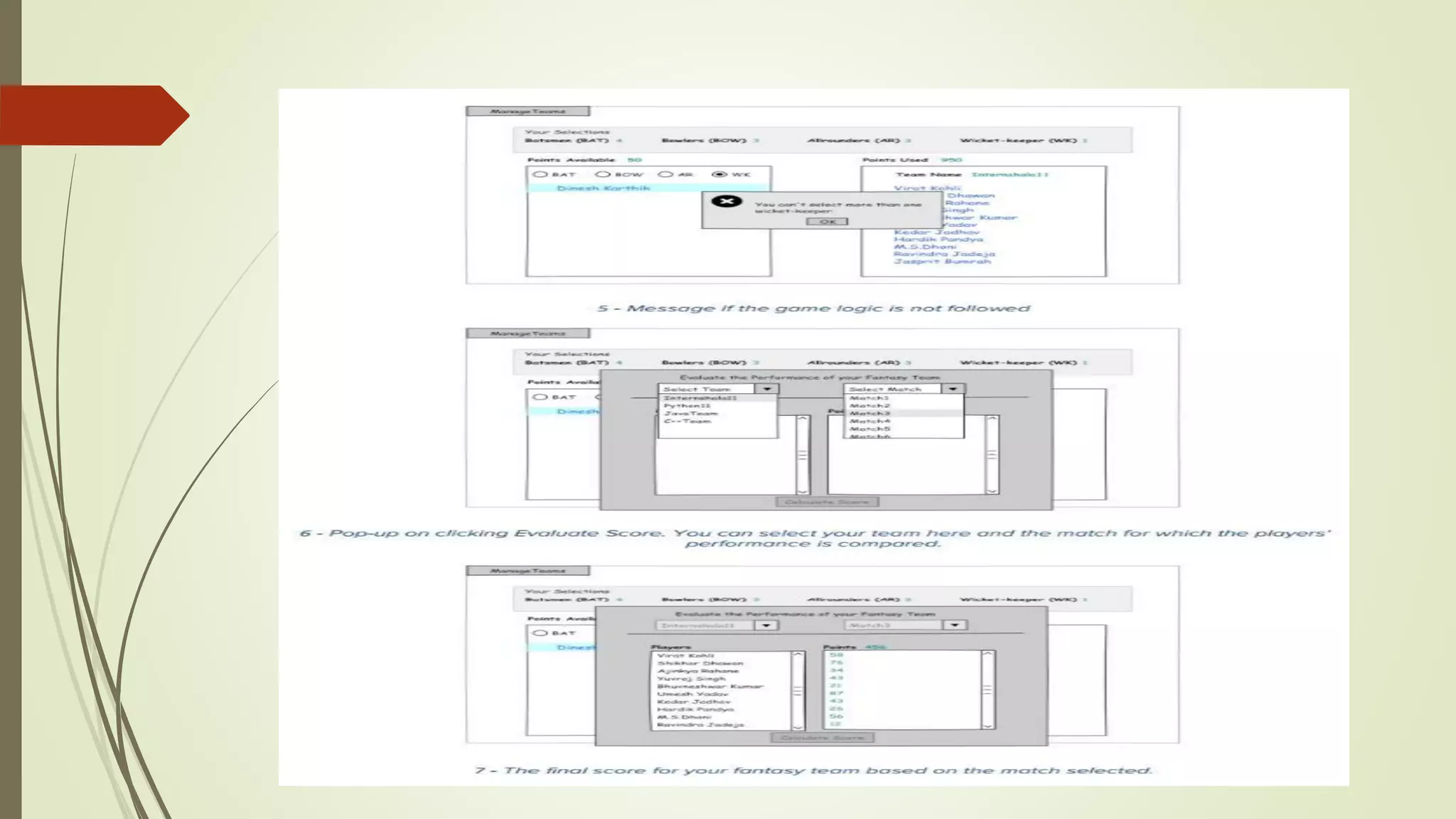
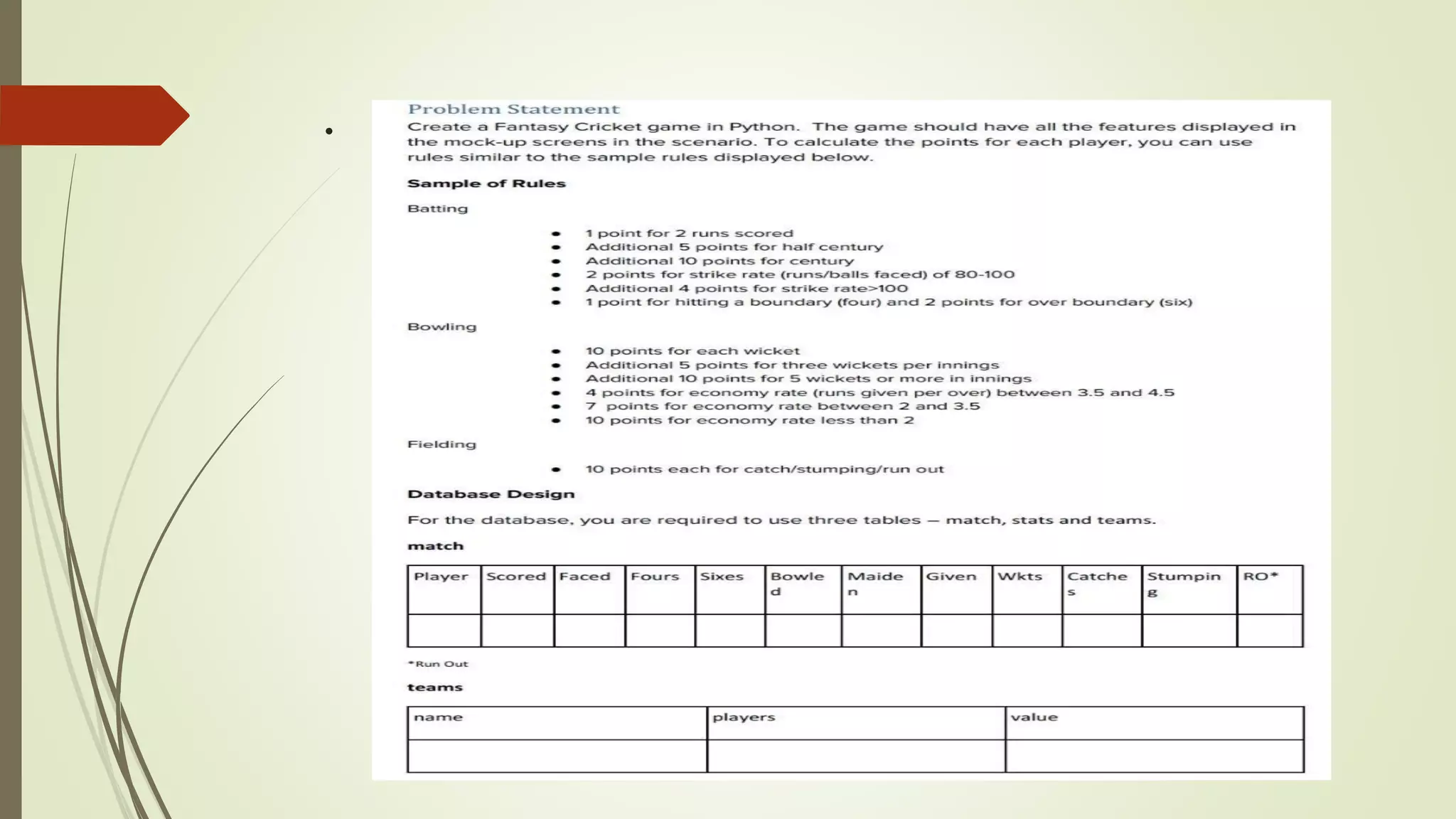
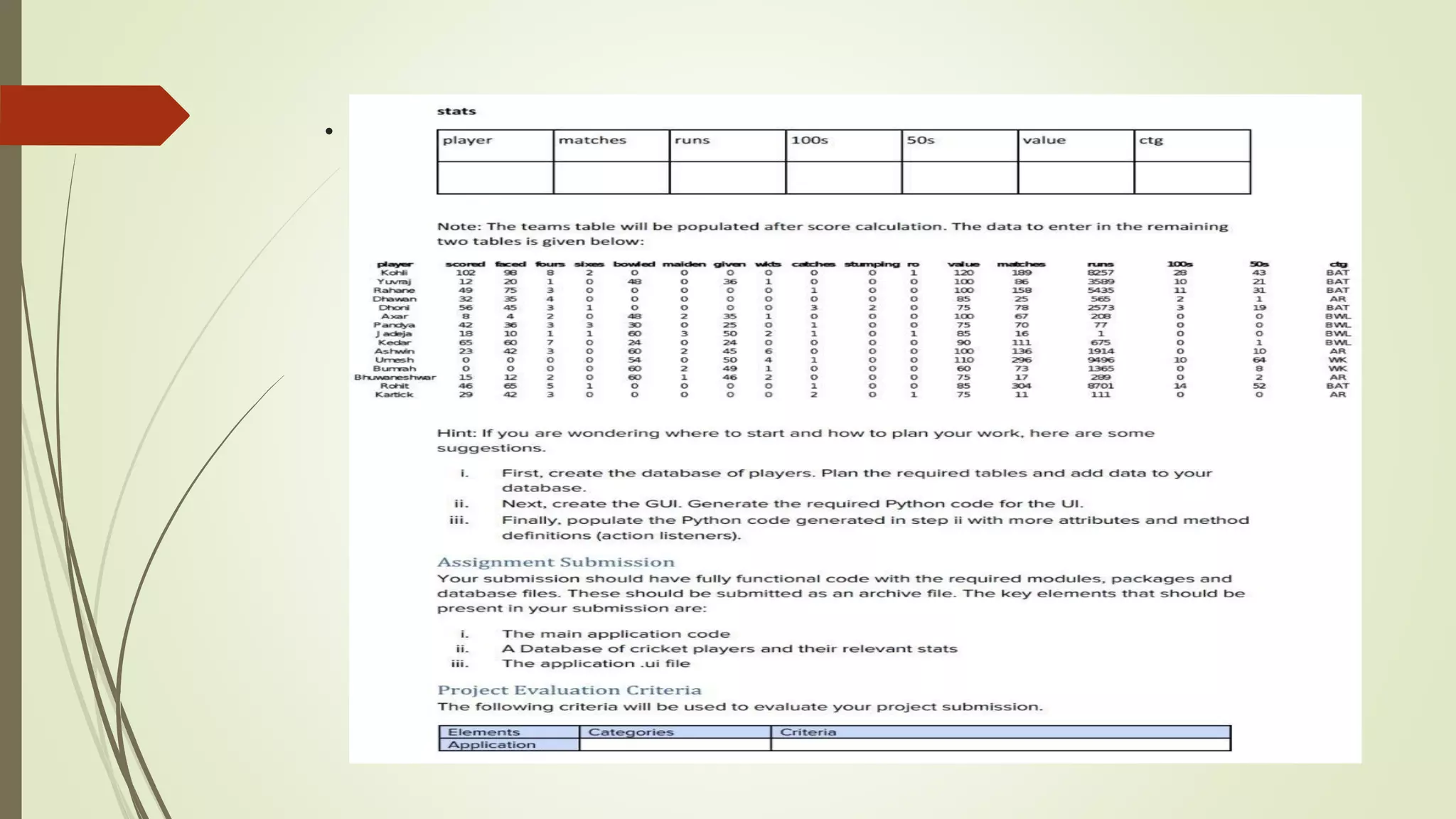
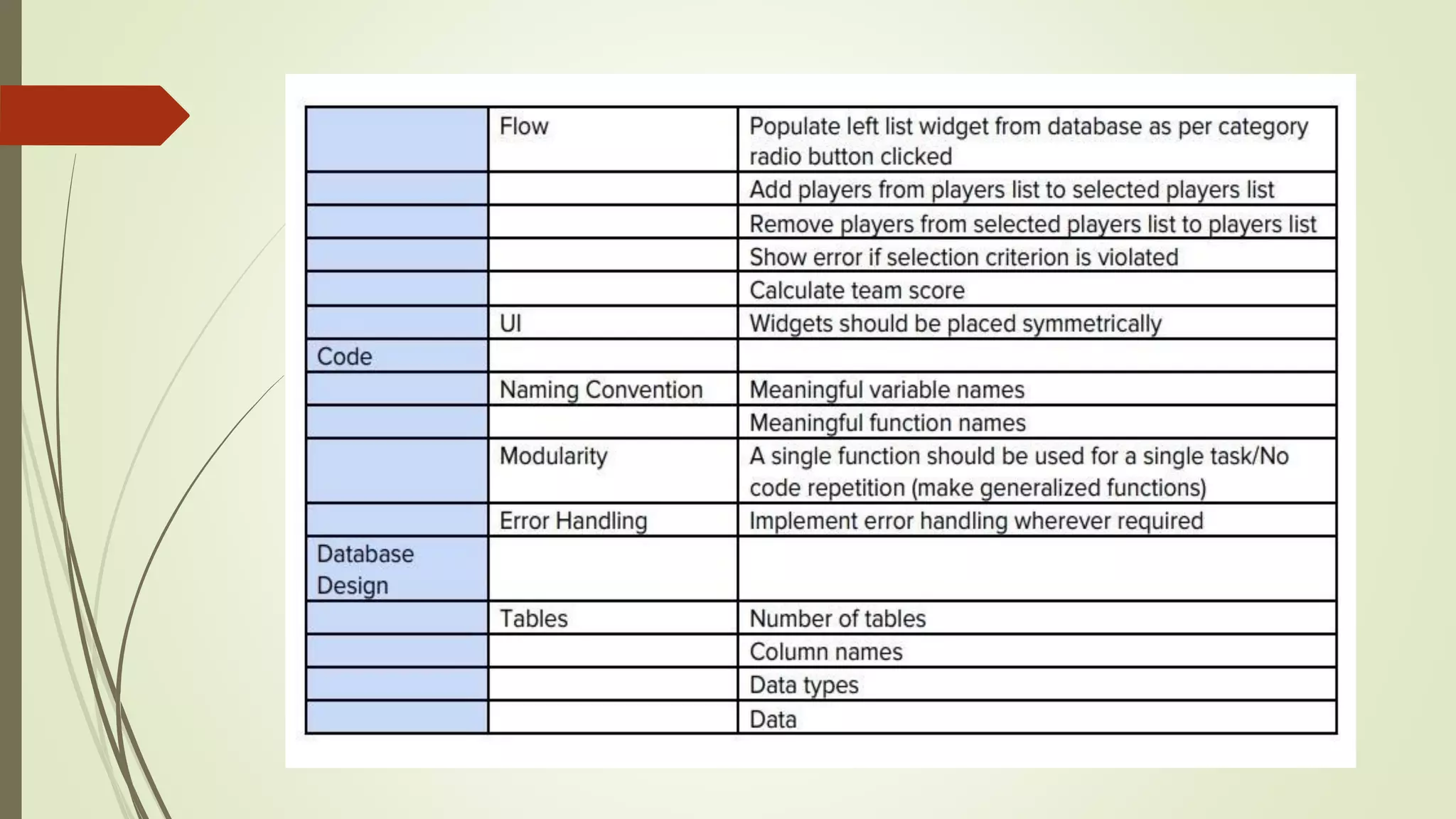
The document discusses an internship project report on Python. It introduces Python as an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language. It then describes some key features of Python like being free and open source, easy to code, and extensible. The document also covers basic data types in Python like integers, floats, booleans, strings, and complex numbers. It provides examples of how each data type is declared and used.