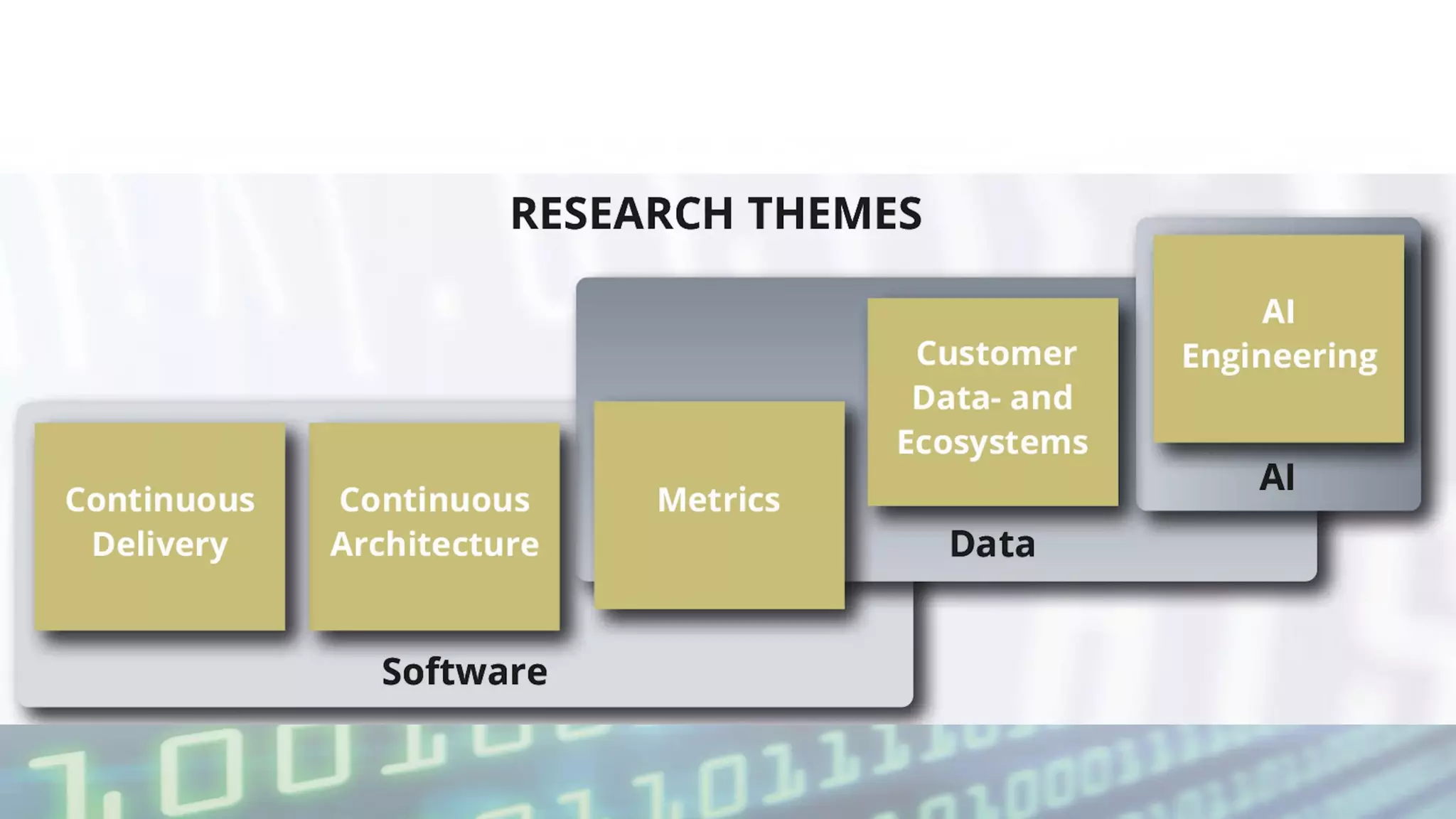
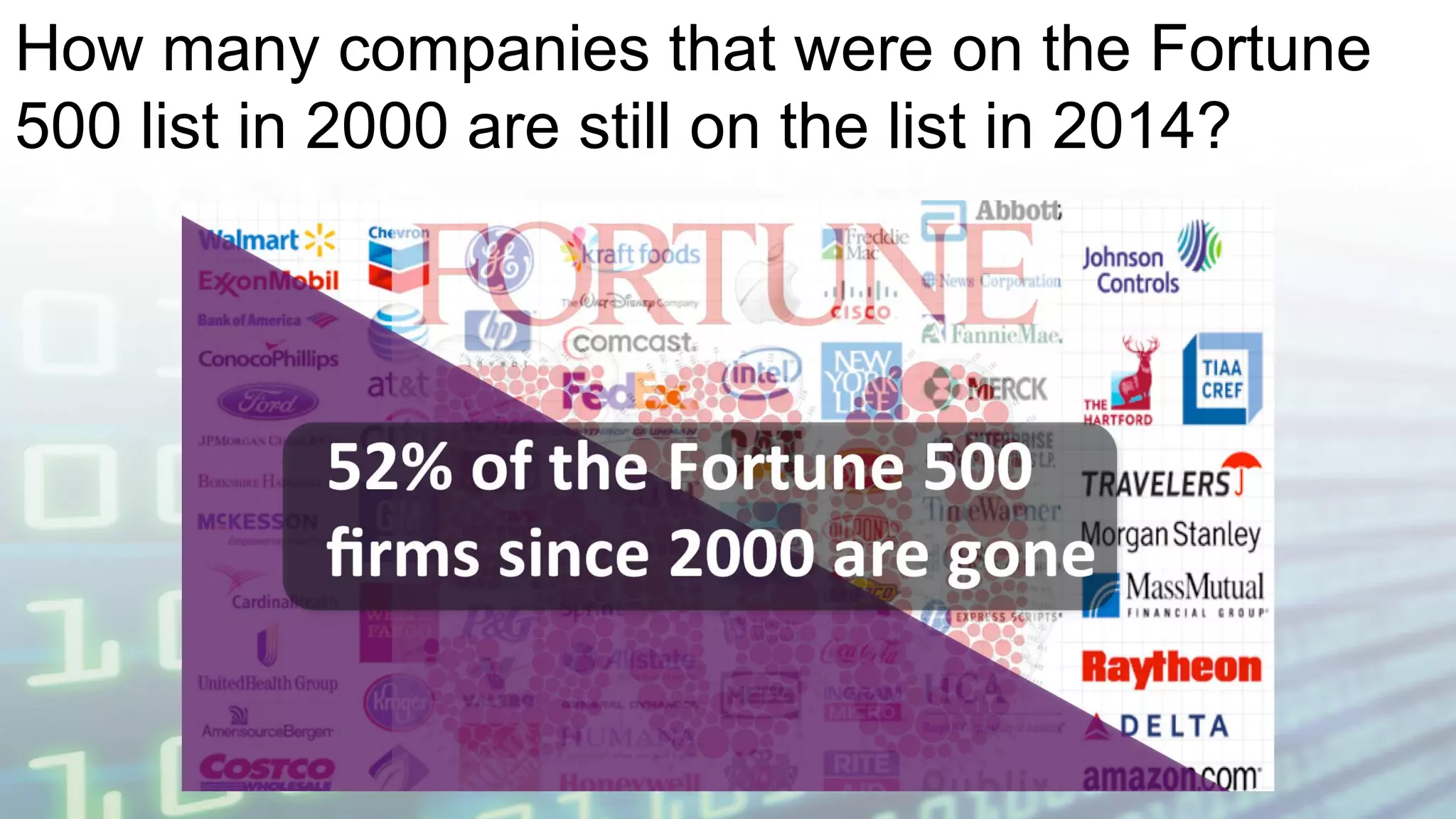
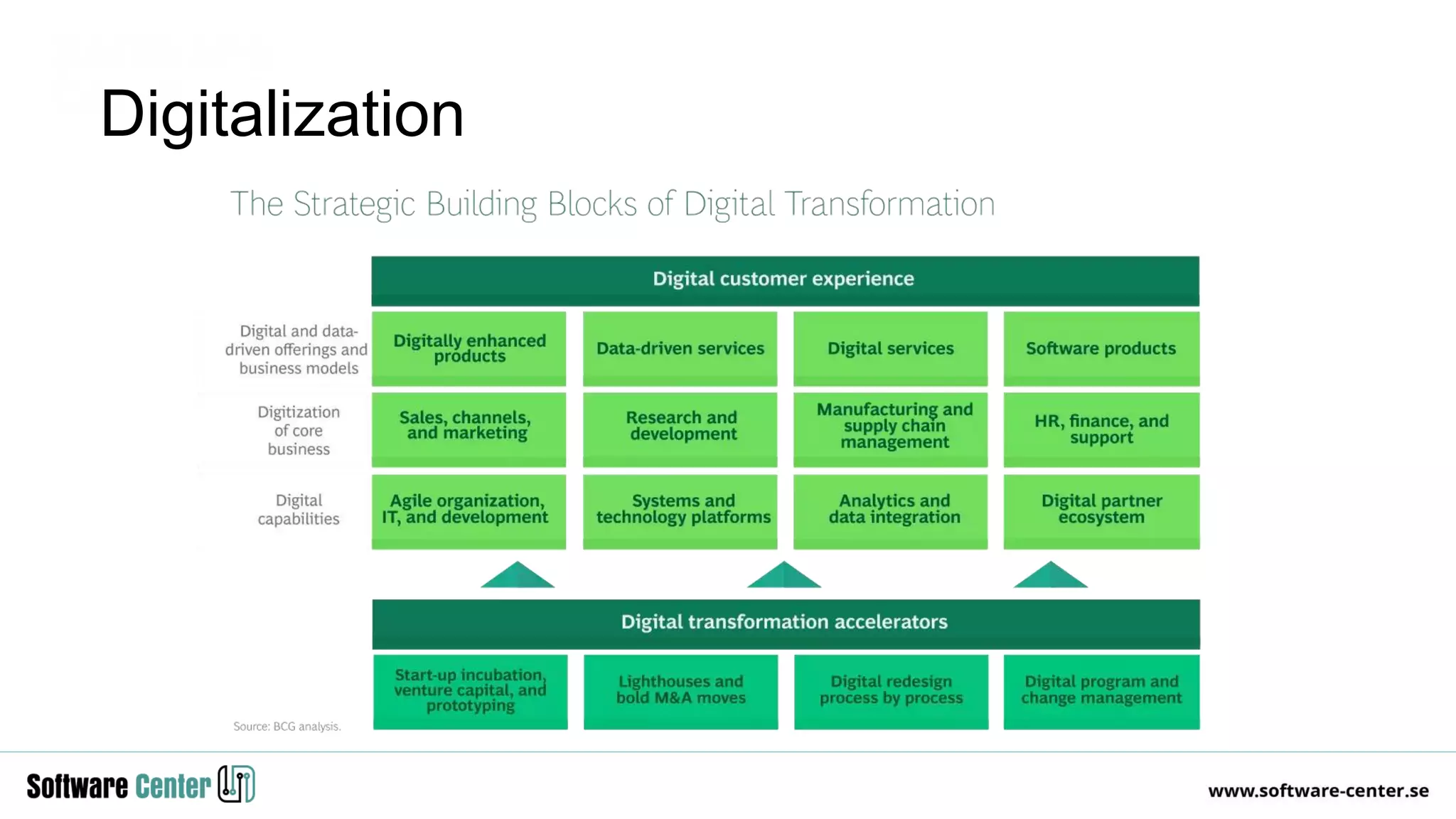
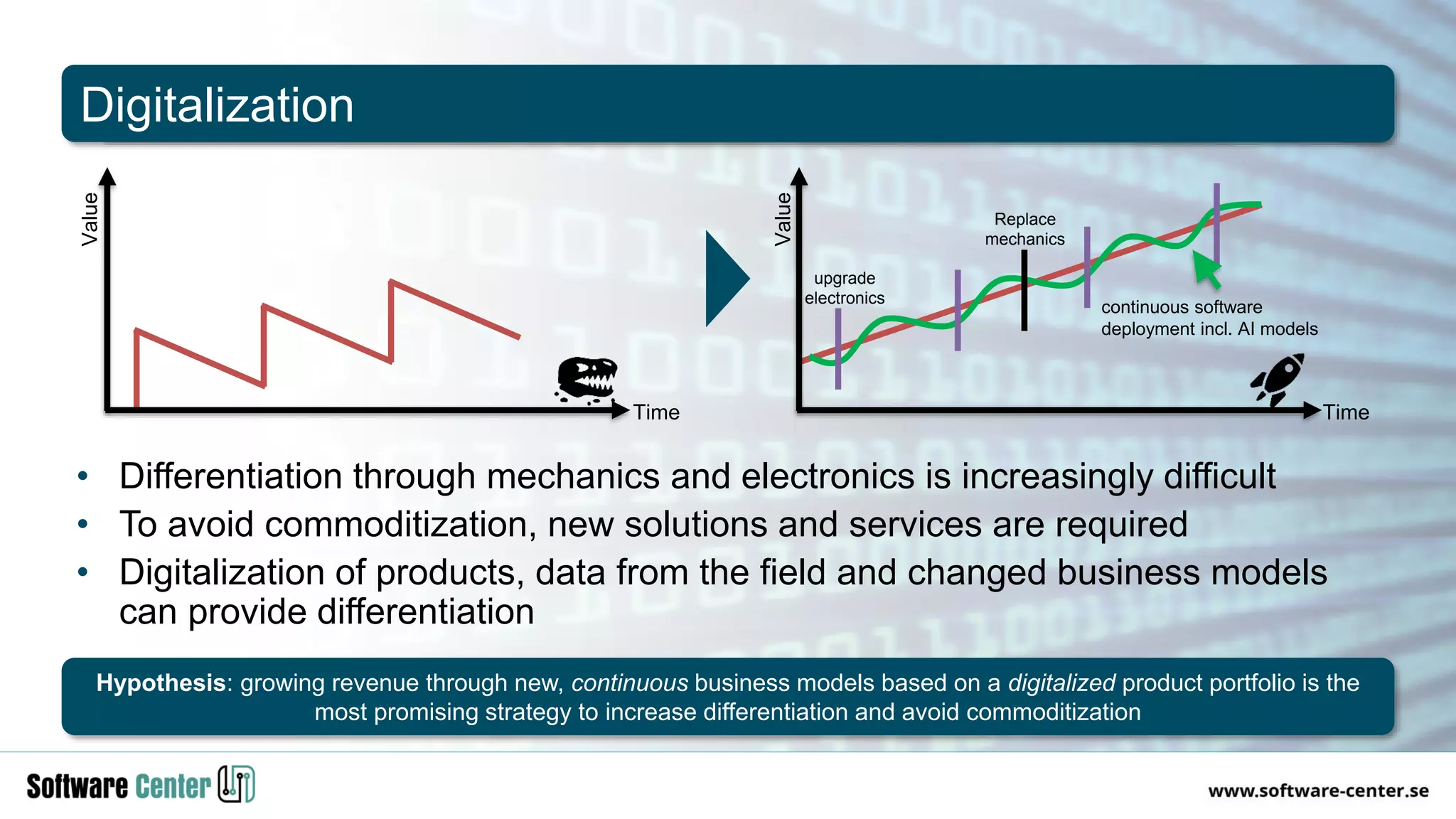
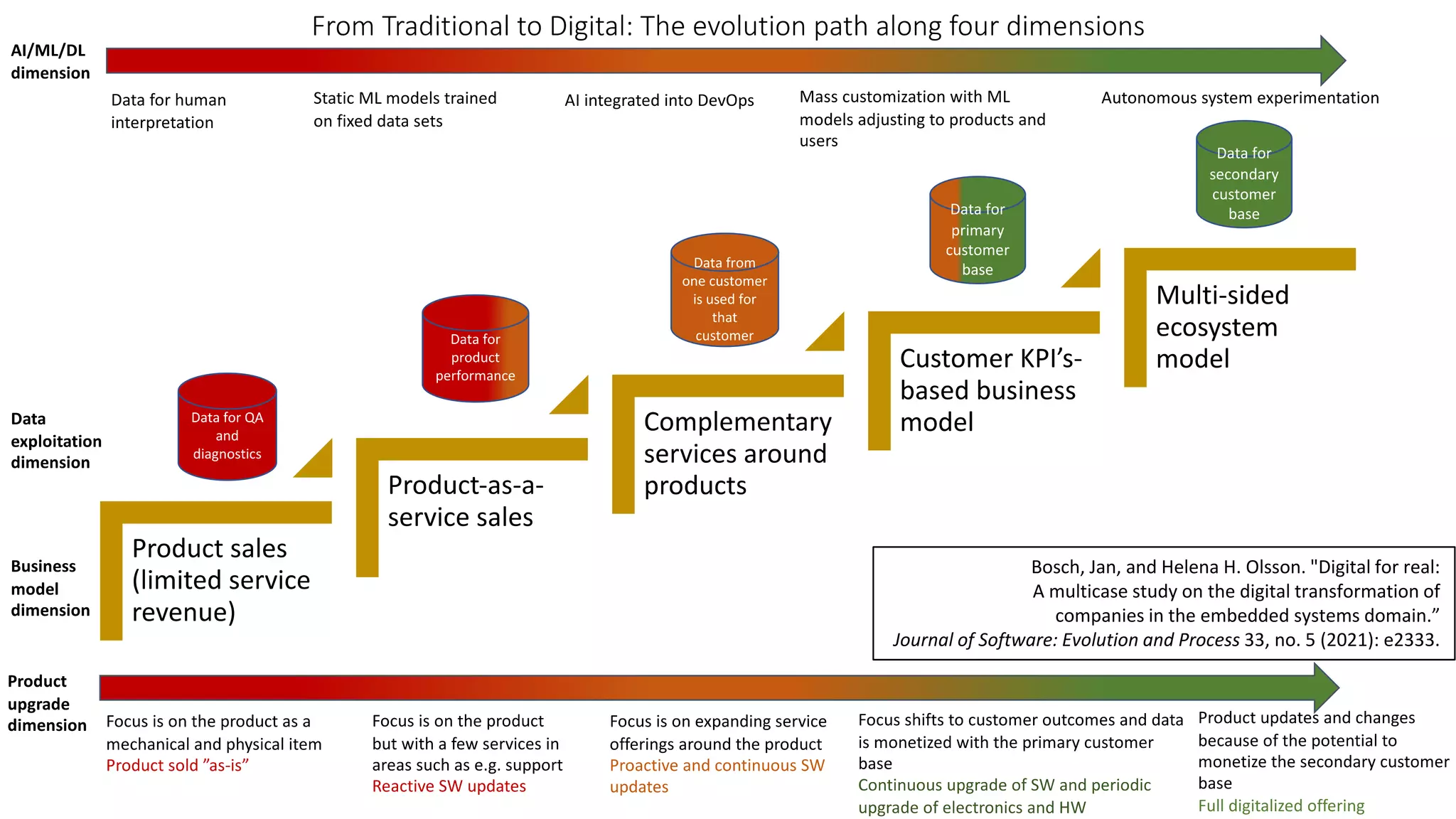
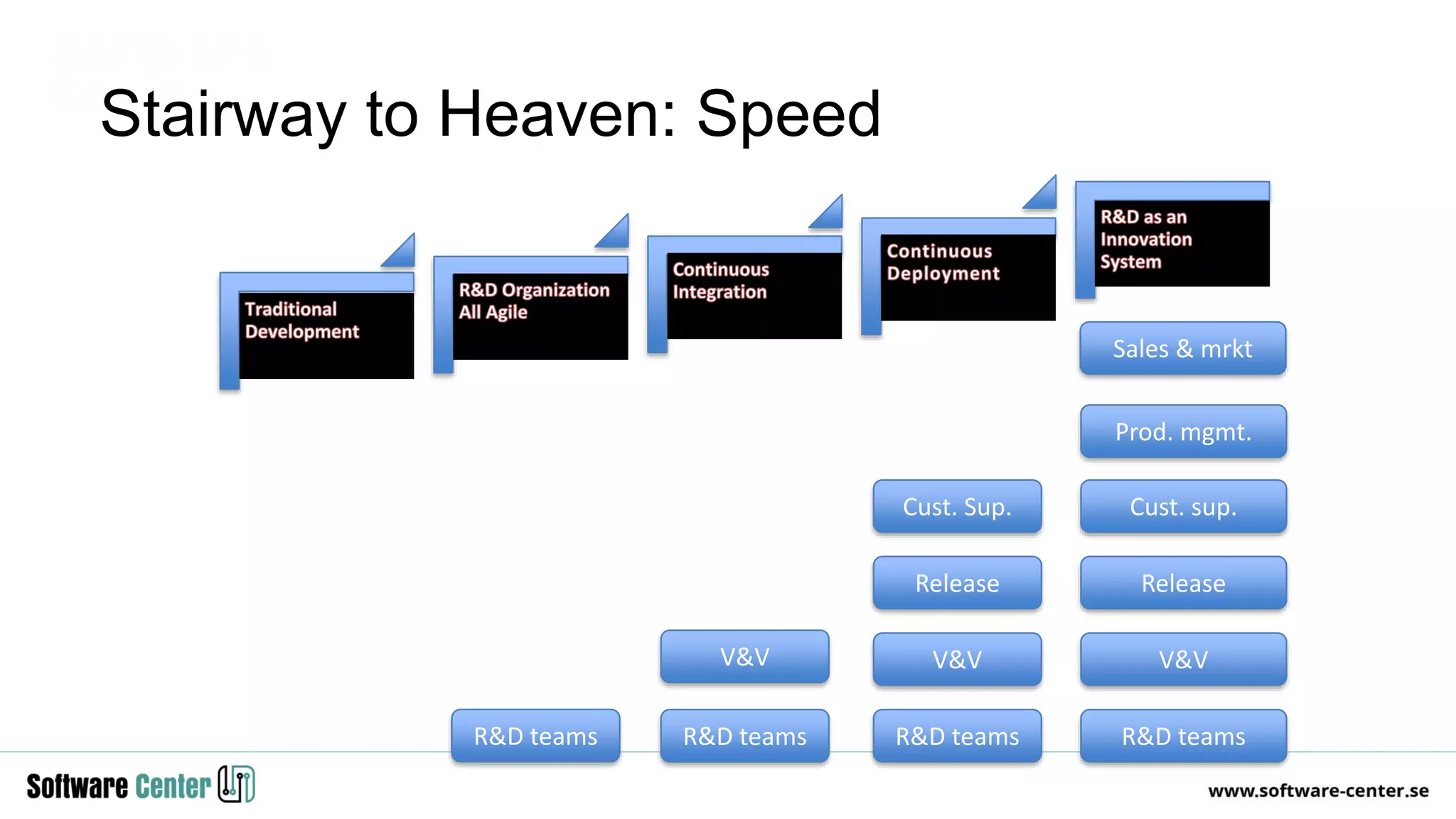
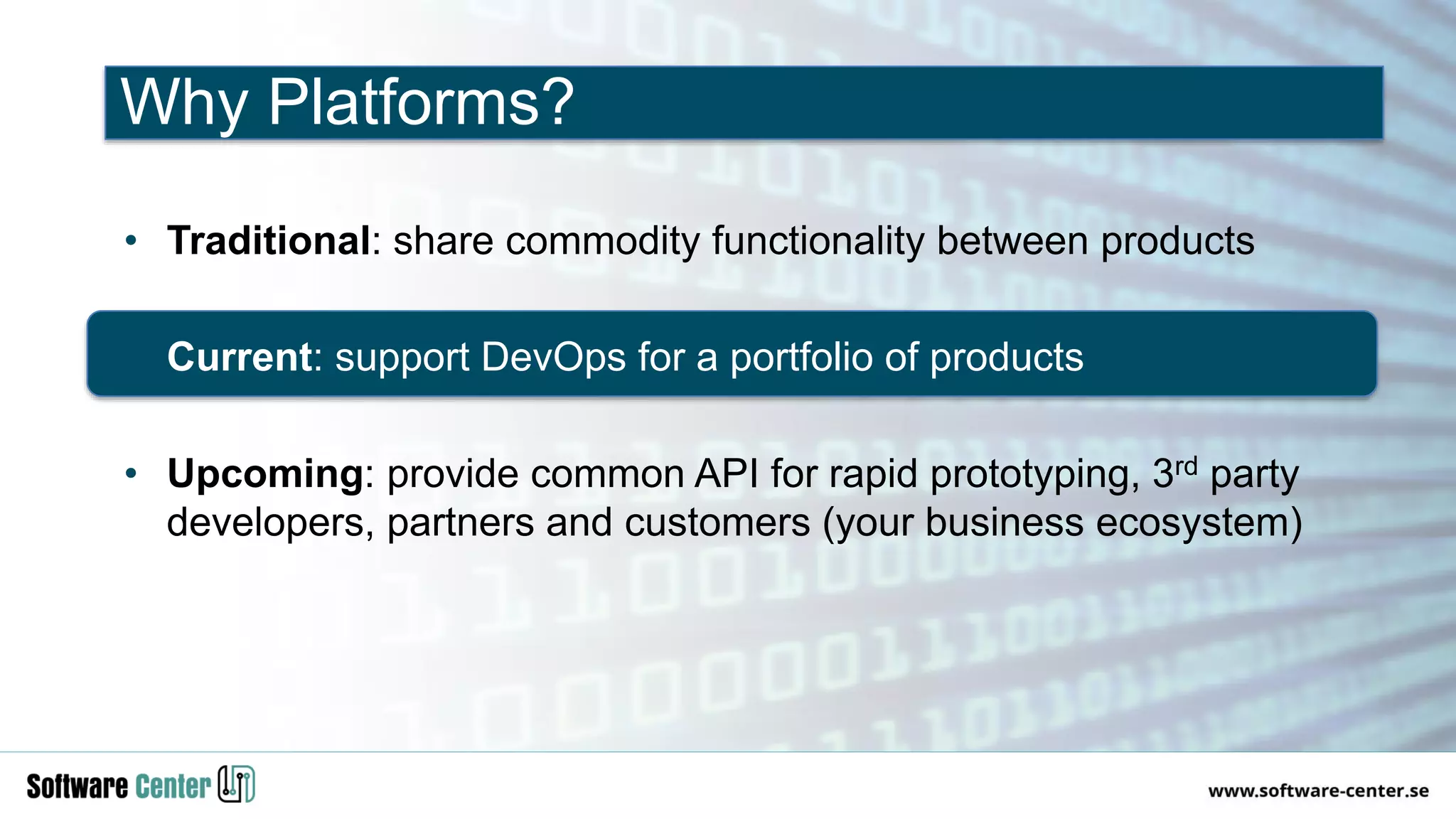
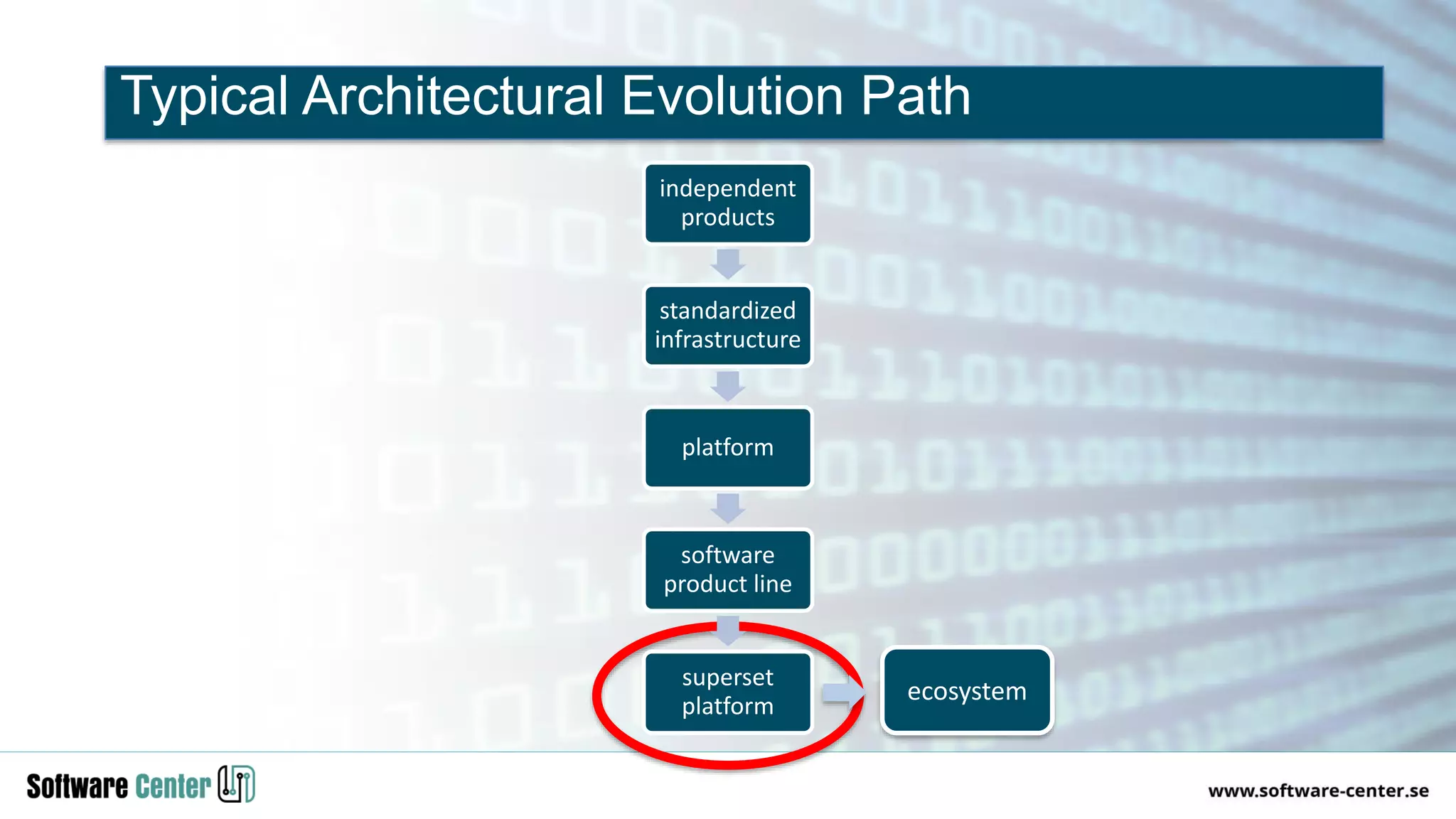
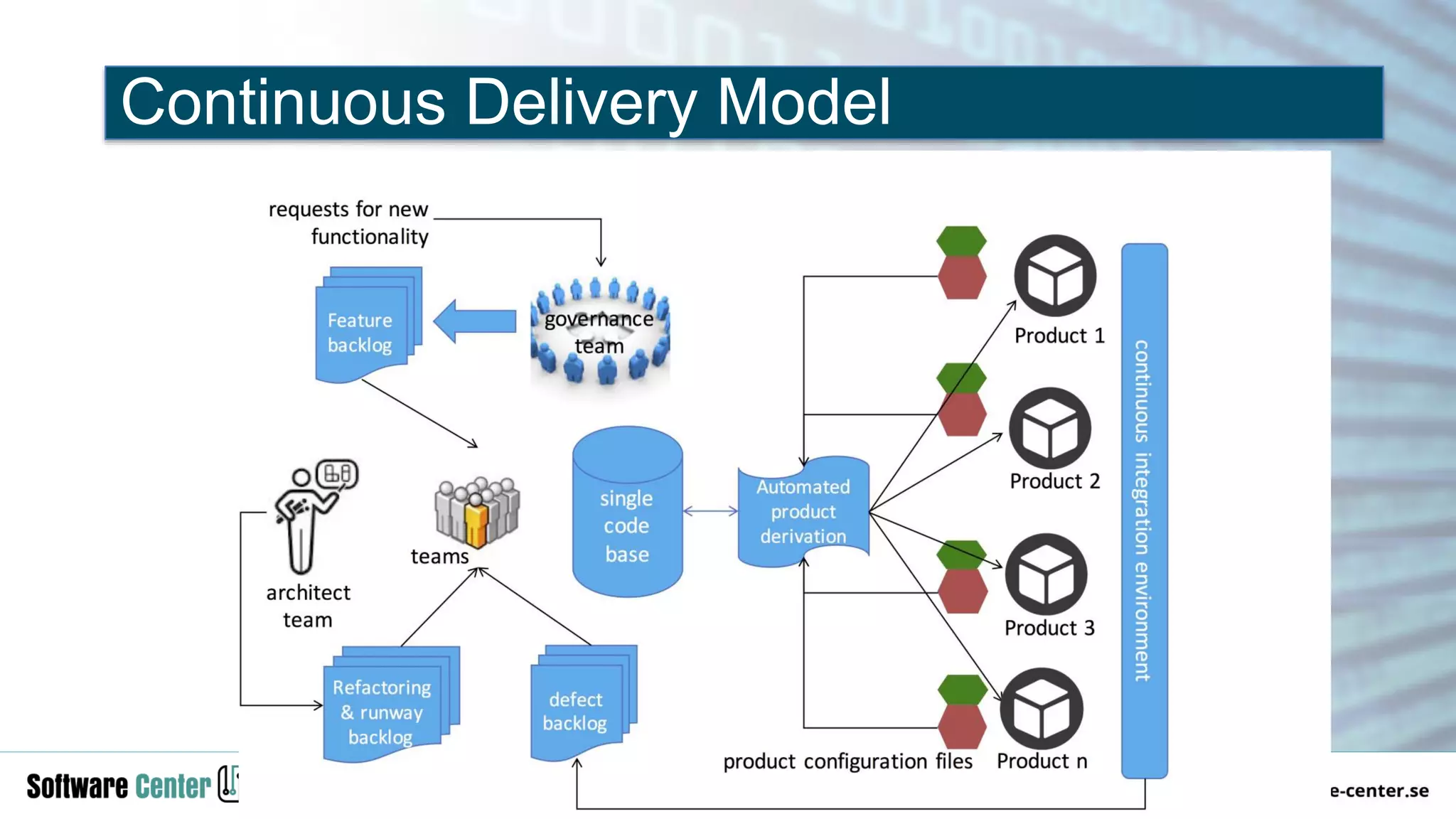
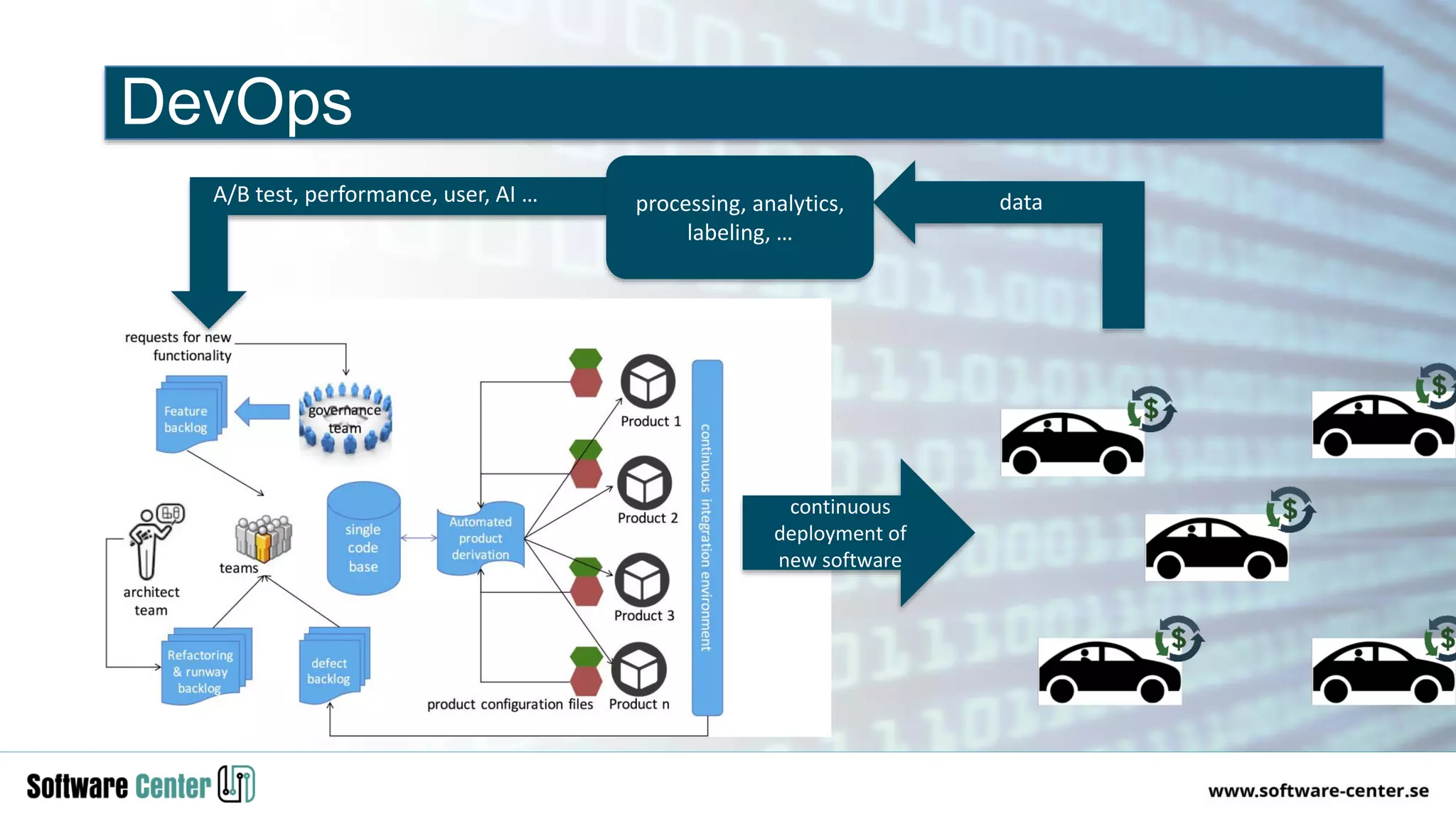
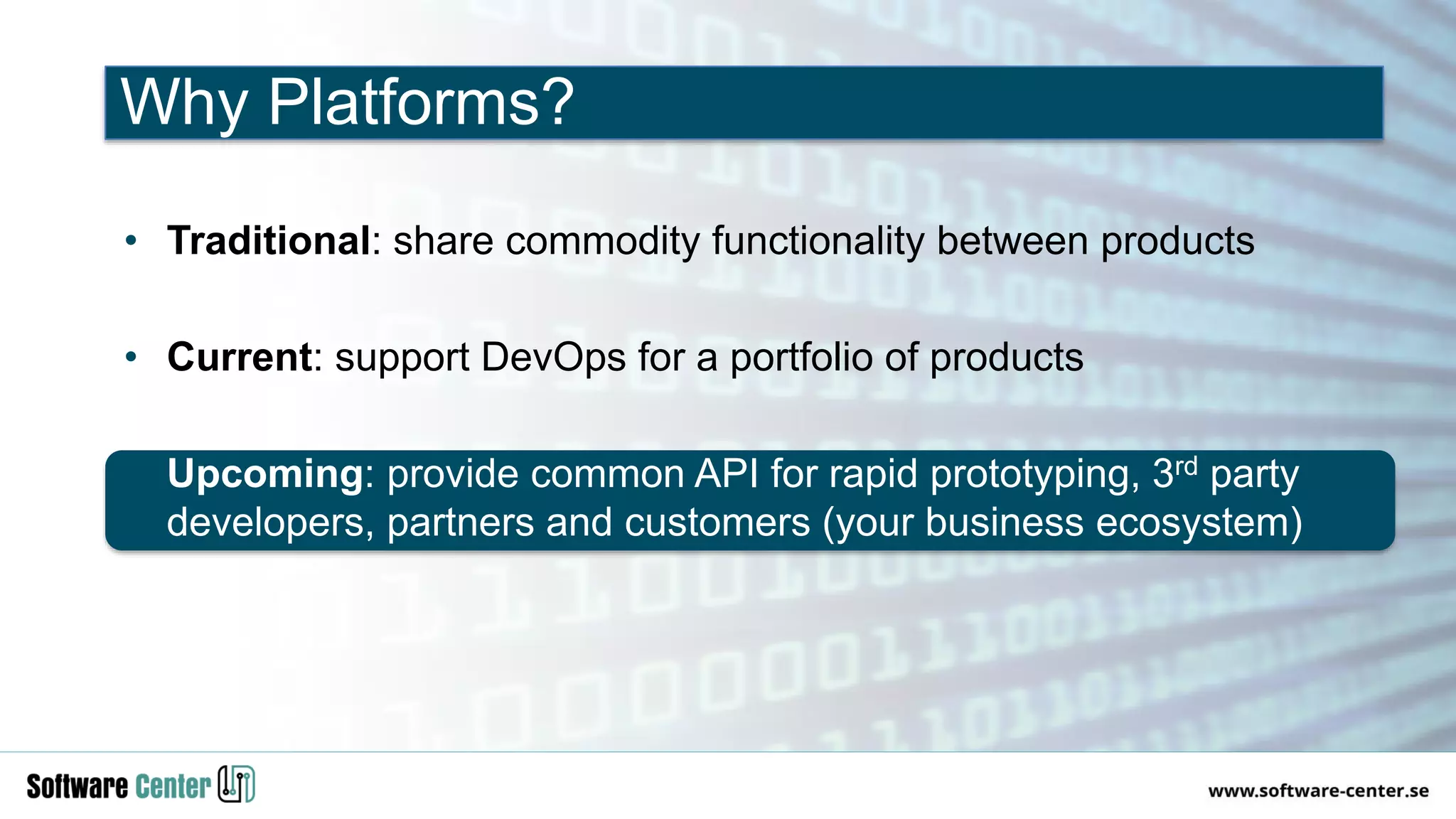
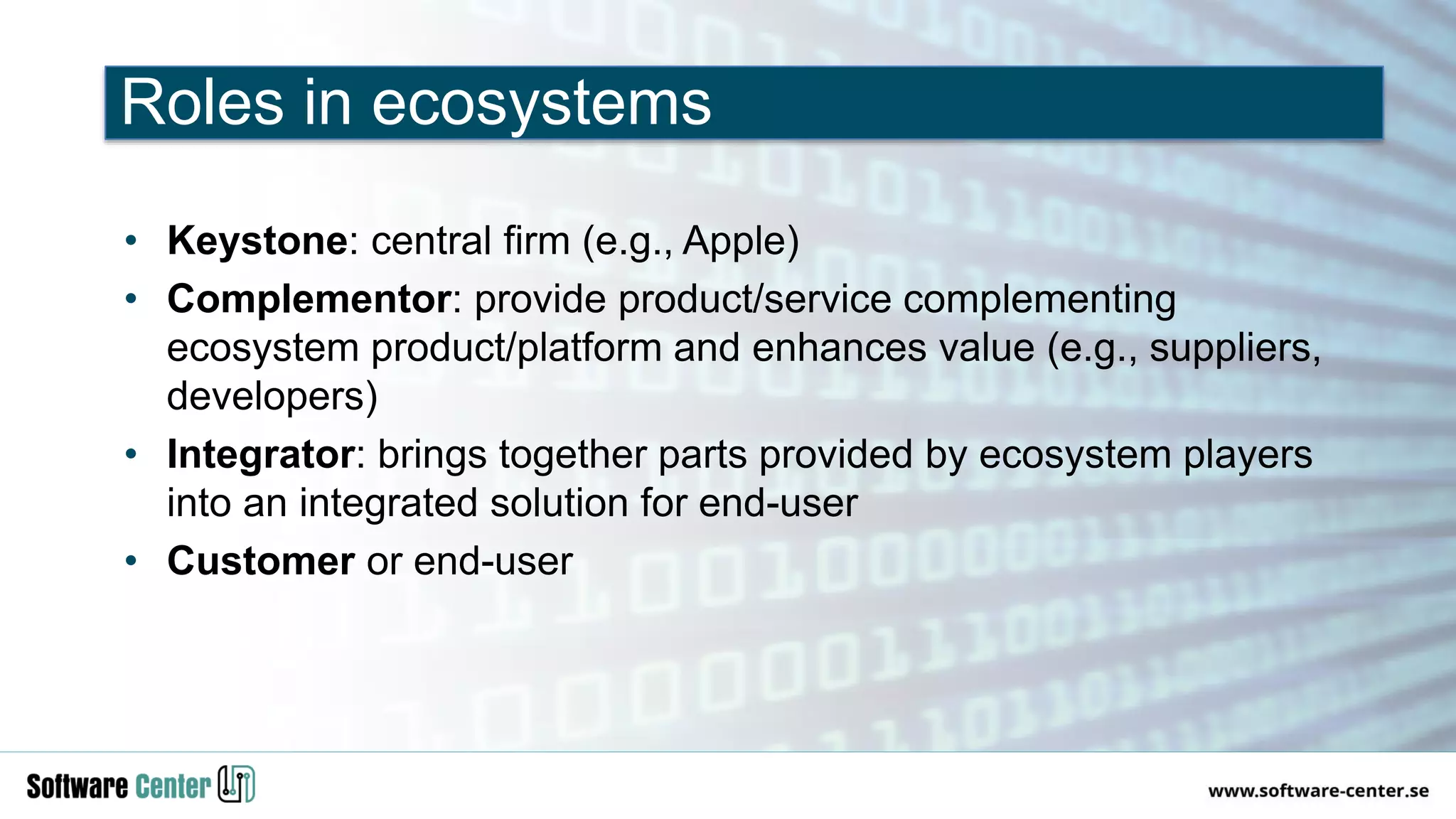
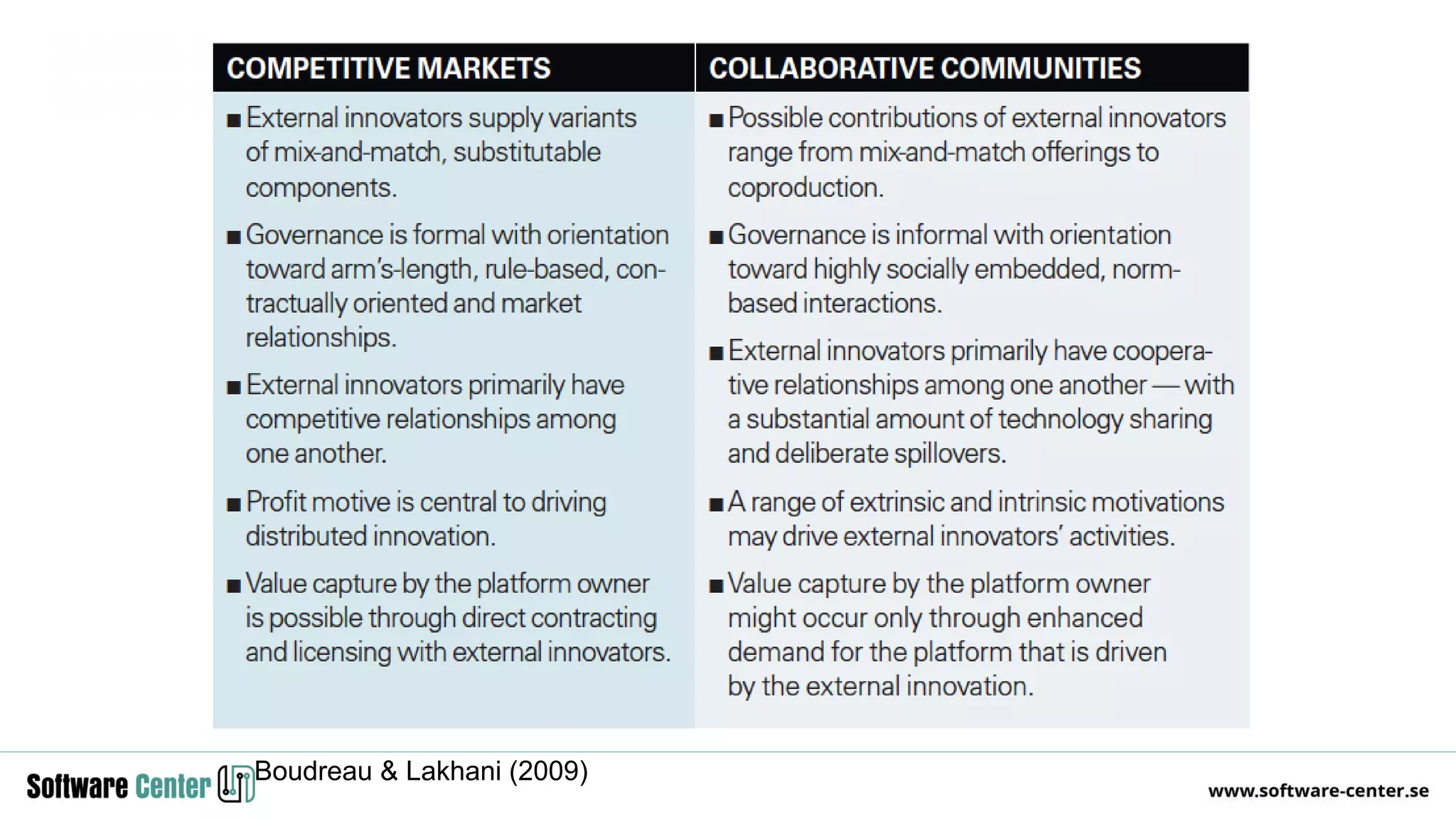
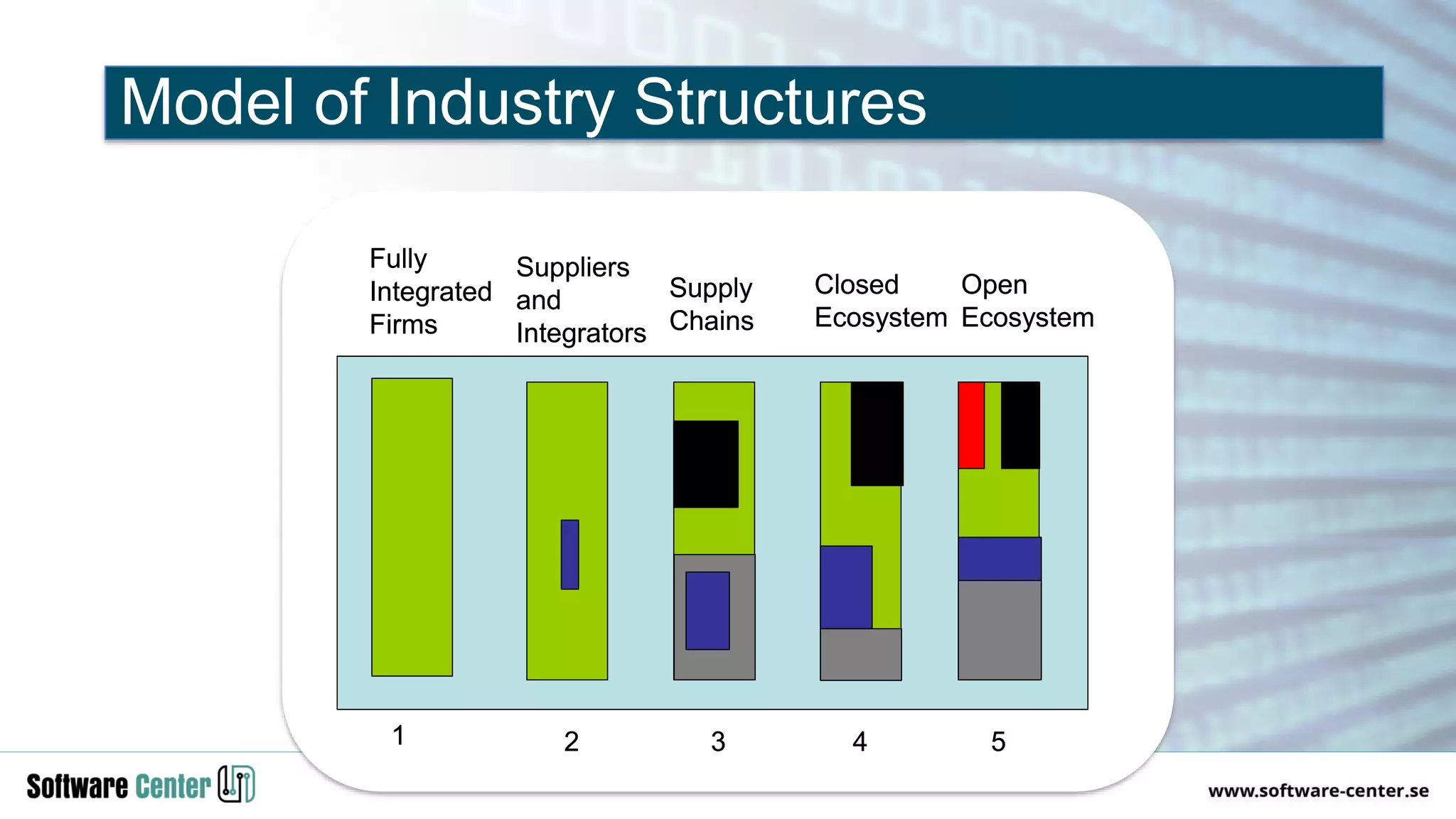
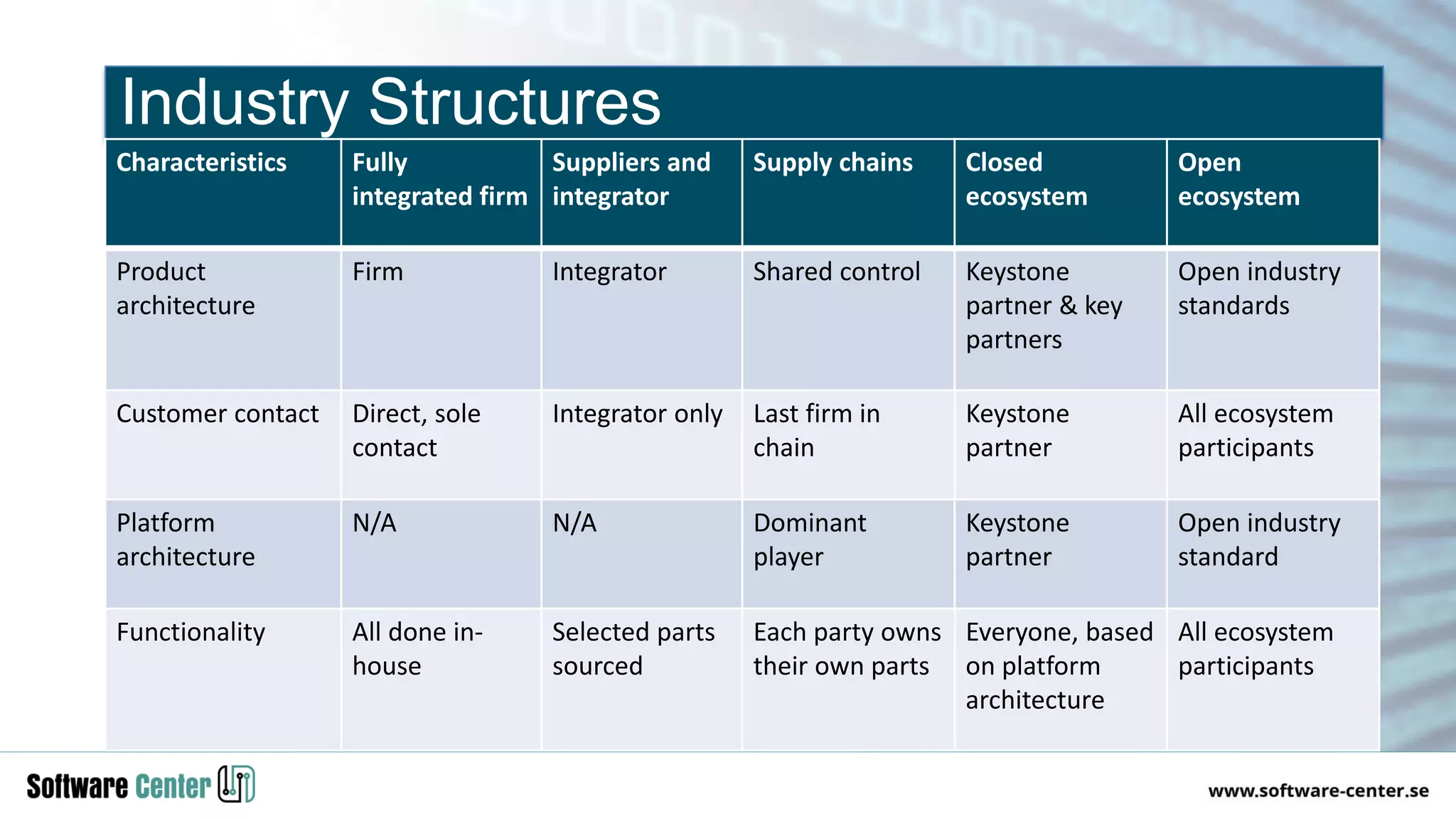
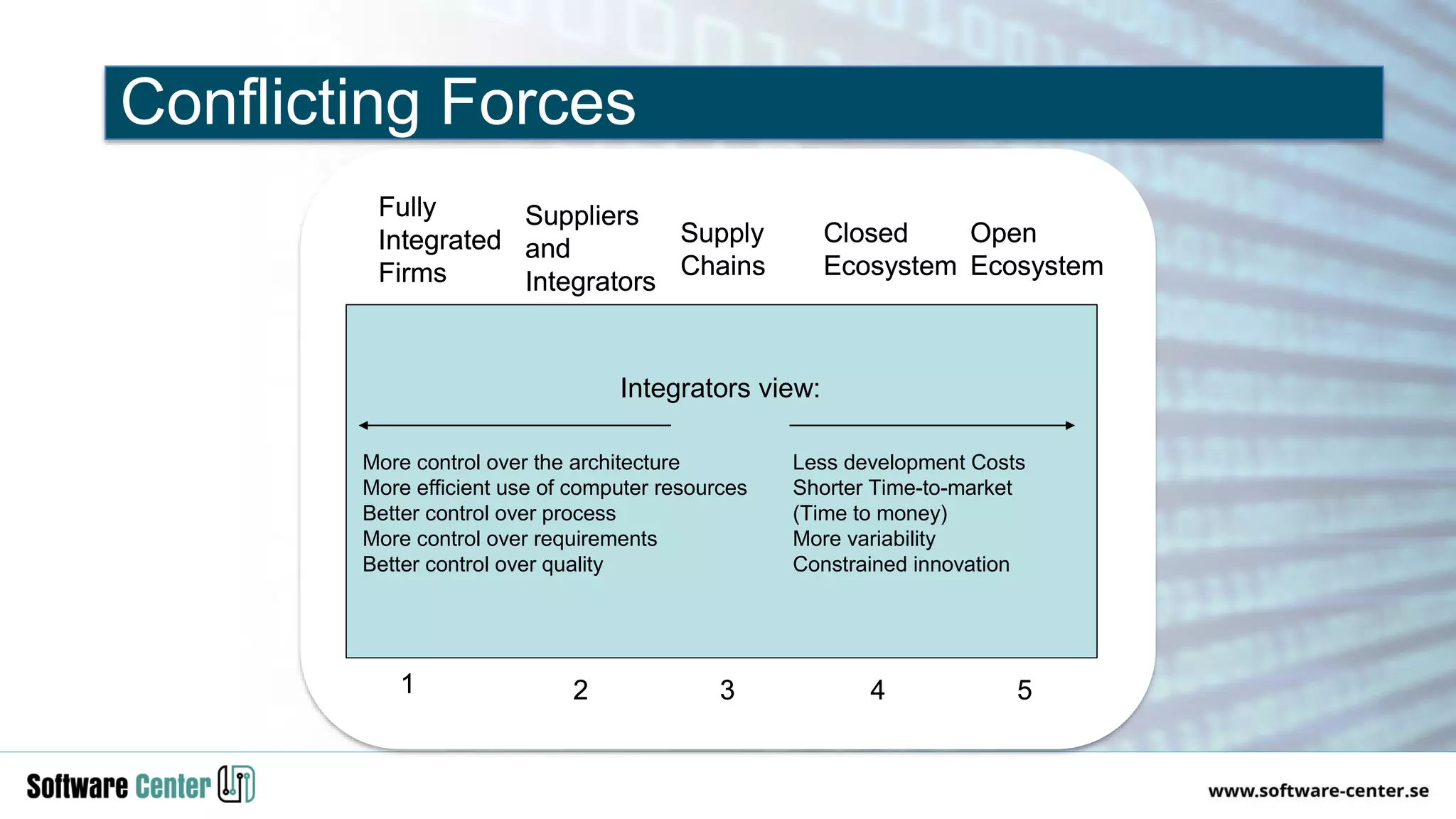
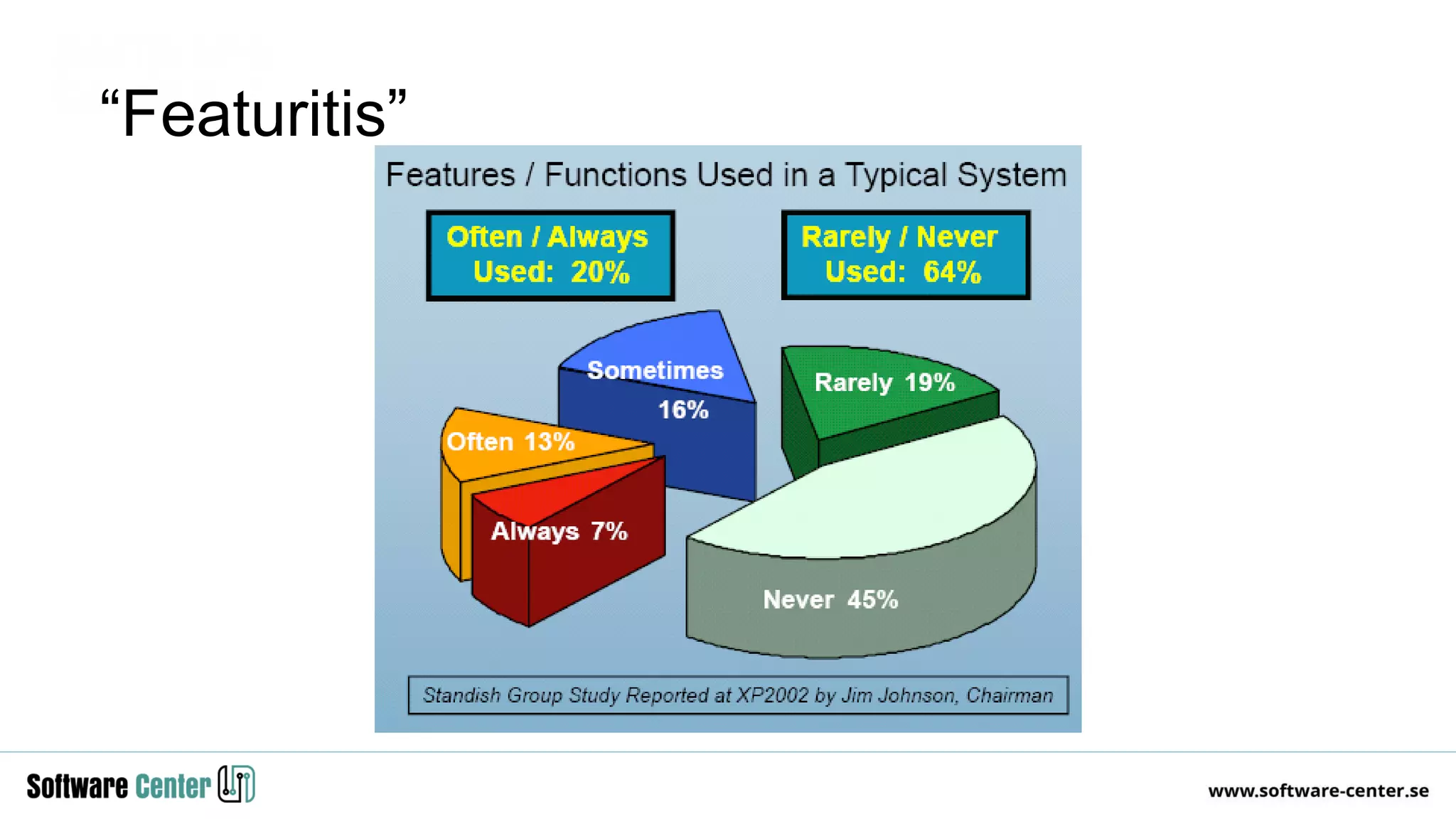
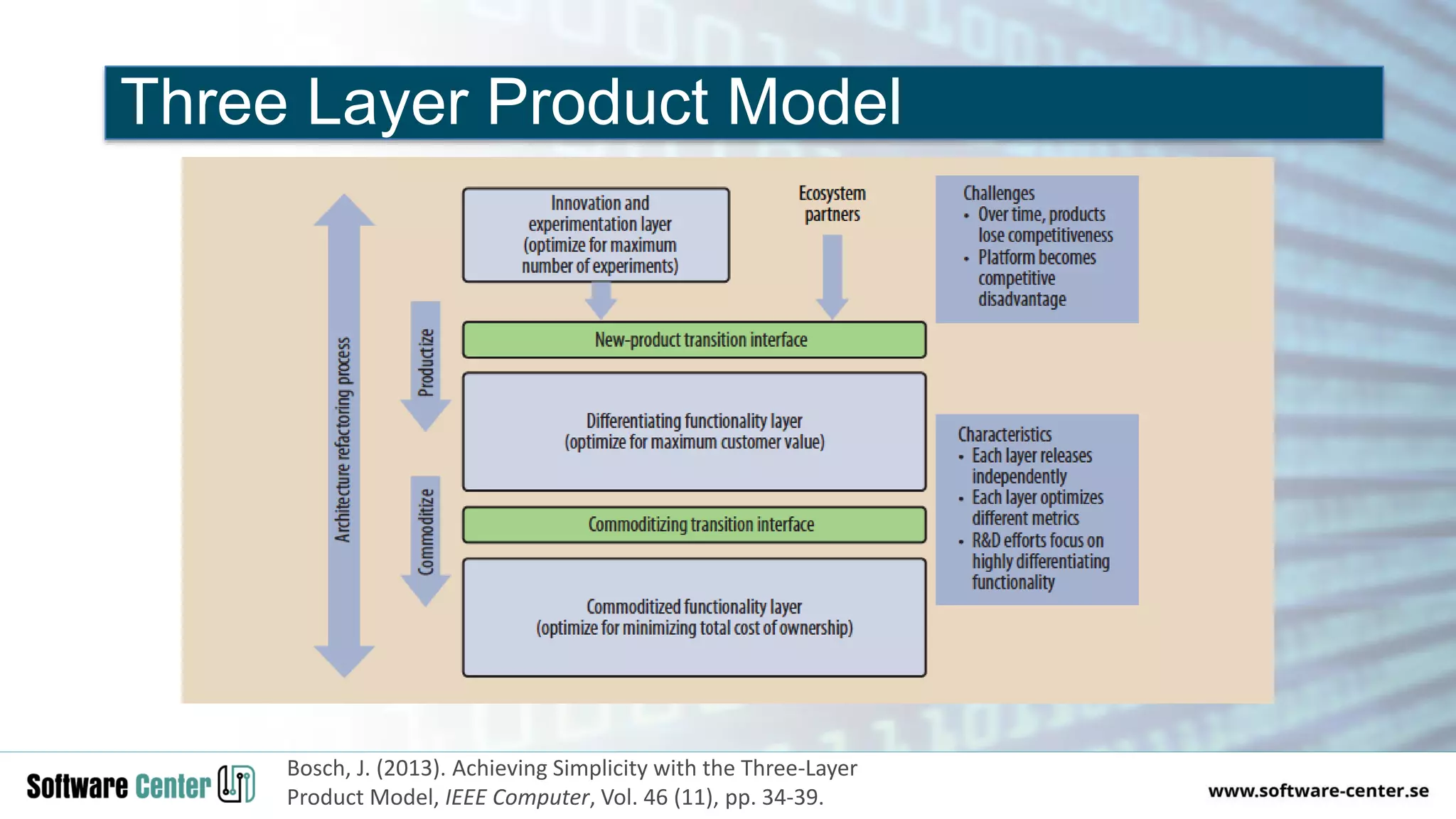
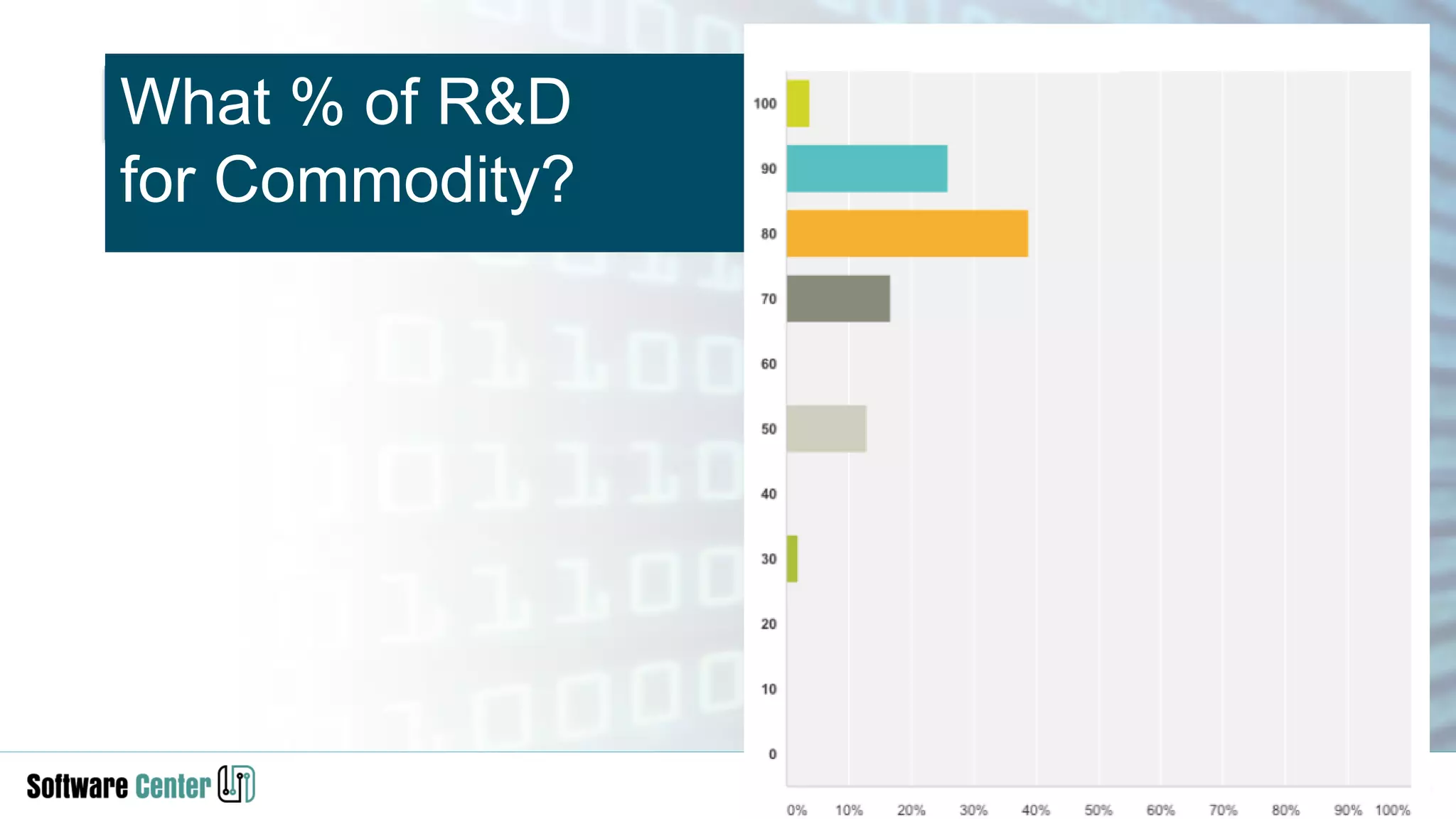
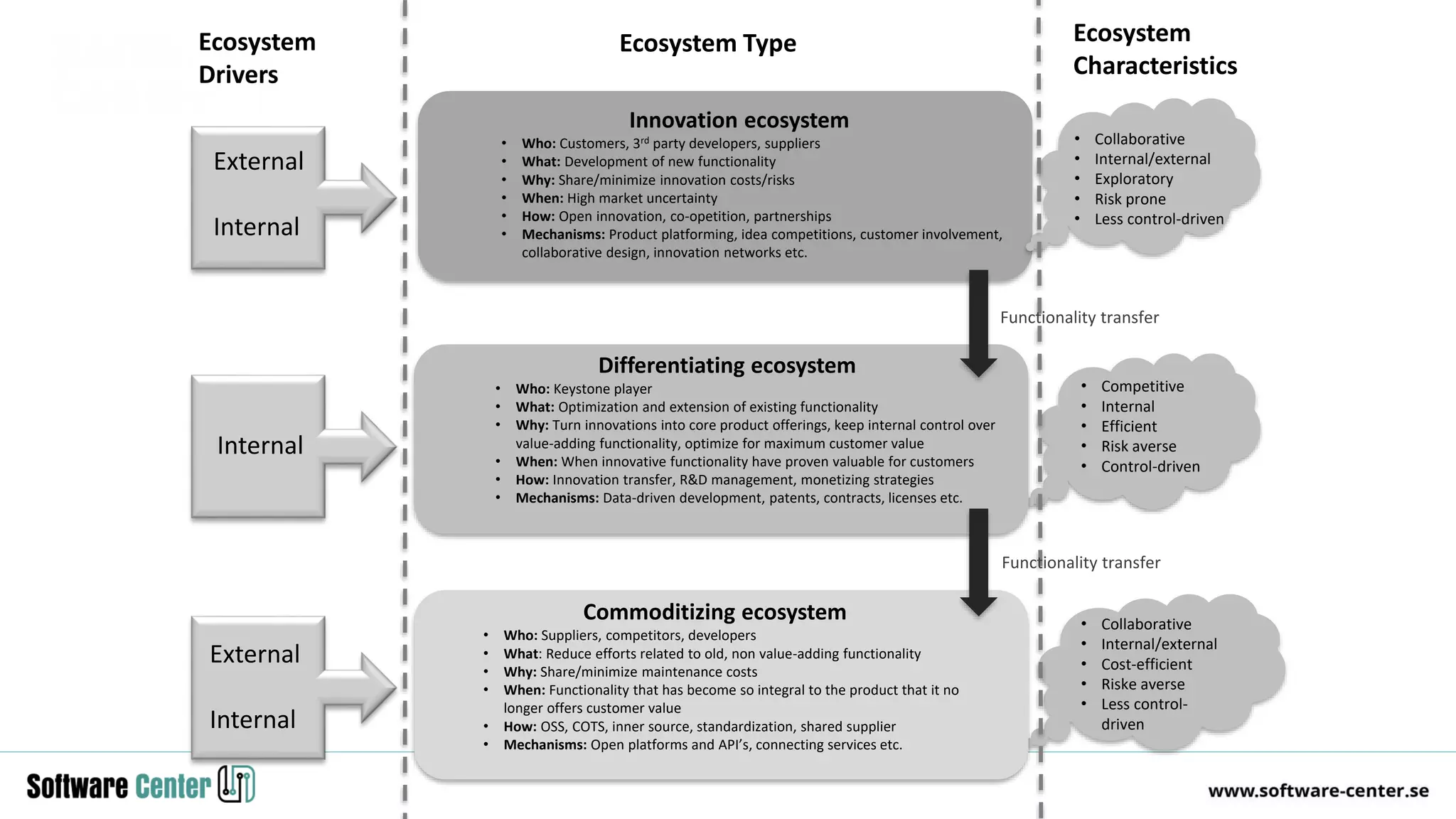
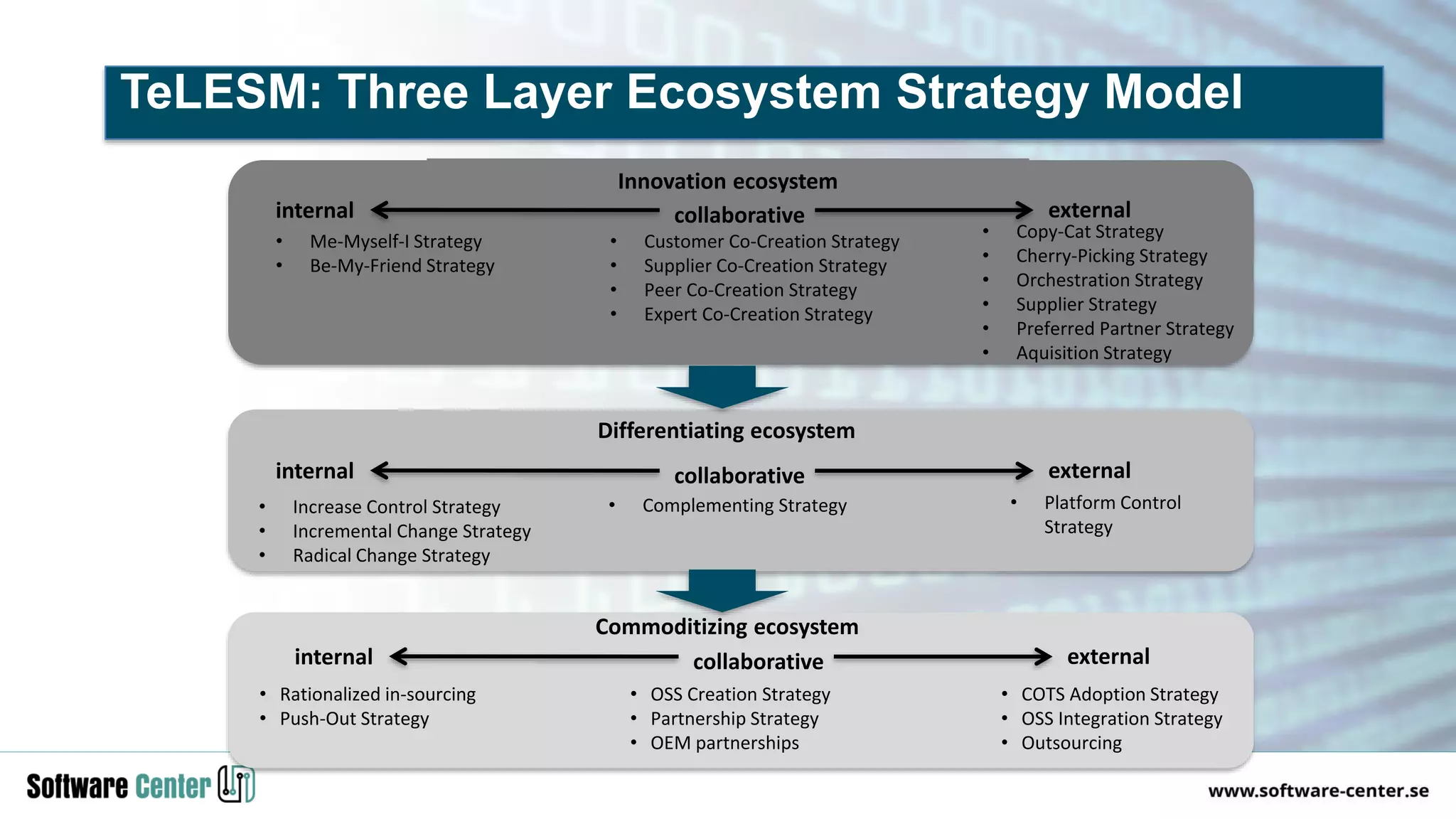
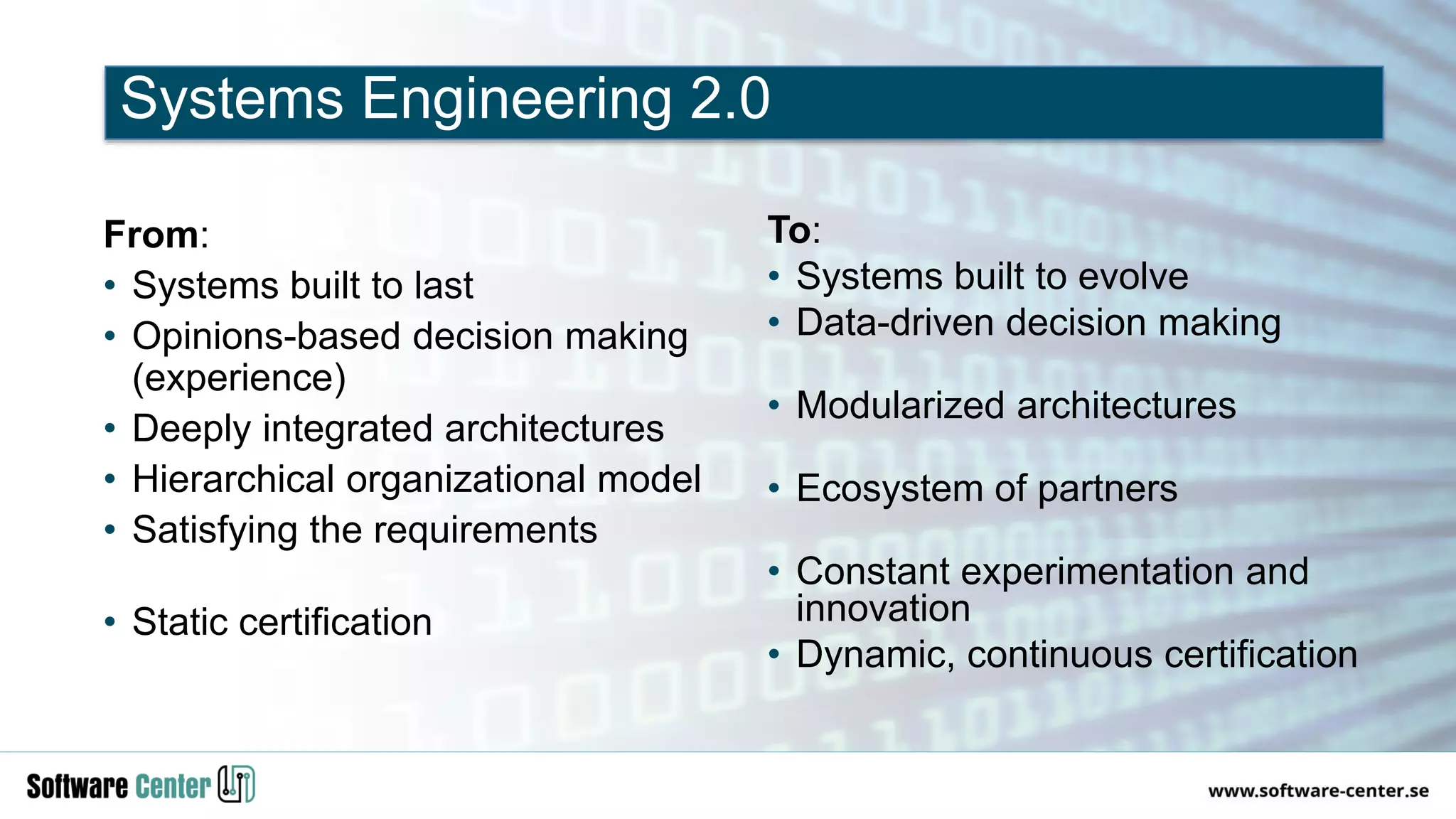
The document discusses the impact of digitalization on software platforms and systems engineering, emphasizing the importance of superset software platforms for implementing DevOps, DataOps, and MLOps. It highlights how digital transformation necessitates a shift in business models and product development strategies to avoid commoditization, with emphasis on collaboration within ecosystems. The key takeaways include the need for continuous innovation, the role of various ecosystem participants, and the transition to software-centric approaches in systems engineering.