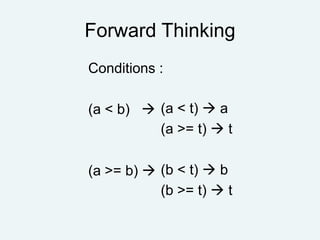
The document discusses problem analysis in algorithm goals, focusing on selecting optimal travel methods (aeroplane, bus, train) based on time efficiency. It presents a maximum-minimum algorithm for determining the fastest option and outlines conditions for problem-solving through forward and backward thinking. Additionally, it offers a grading system based on input marks ranging from 0 to 100, categorizing results into grades 'a' to 'e'.