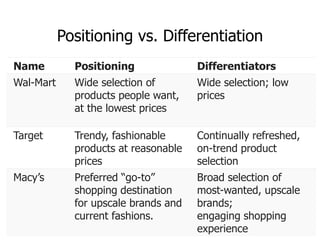
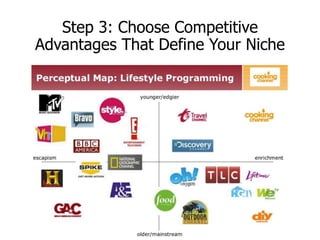
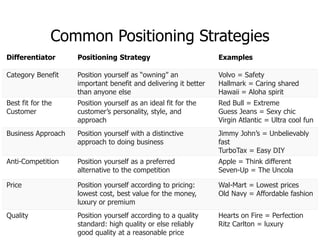
This document discusses positioning and differentiation strategies in marketing. It defines positioning as determining a product's niche relative to alternatives, and differentiation as identifying unique value-adding characteristics that competitors cannot copy. The positioning process involves understanding the market, identifying advantages, choosing a defining niche, developing a positioning statement, and communicating the strategy. Positioning statements target an audience and highlight differentiators. Repositioning may be needed due to competition, trends, or internal changes. Implementation requires aligning all marketing mix elements with the positioning promise.







![Formula for Positioning Statement
To [target audience], Product X is the only [category or
frame of reference] that [points of
differentiation/benefits delivered] because [reasons to
believe].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/principlesofmarketing08positioning2-240125130348-5b1fc4e2/85/PrinciplesofMarketing_08_Positioning2-pptx-11-320.jpg)














