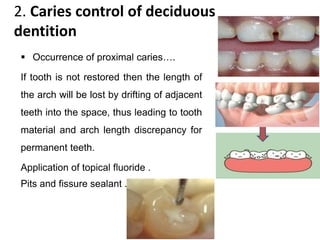
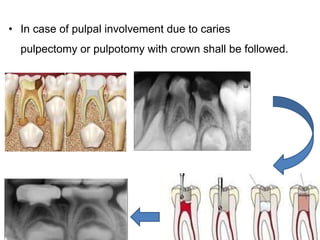
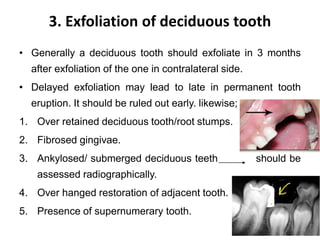
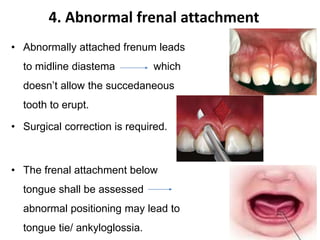
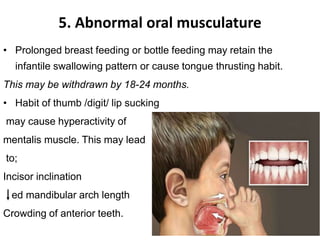
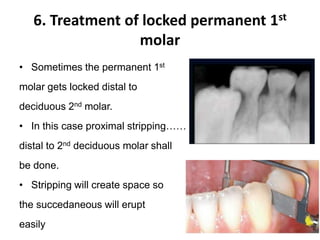
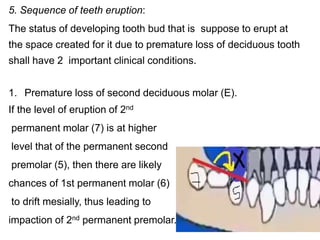
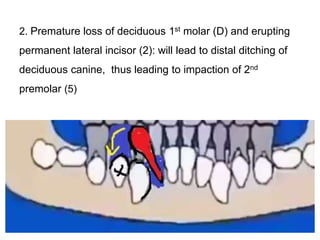
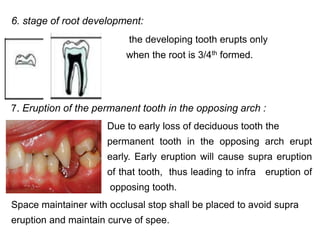
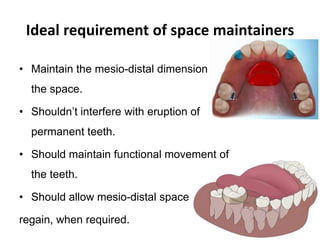
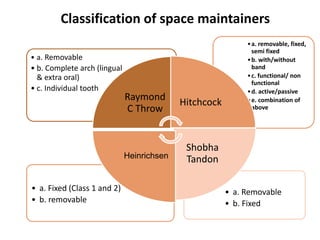
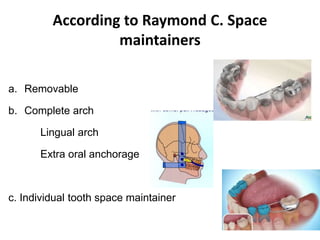
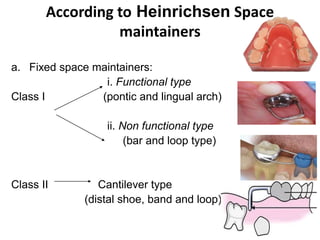
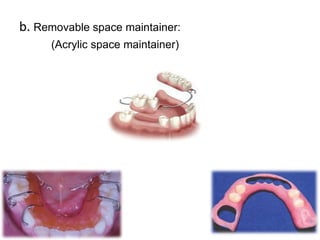
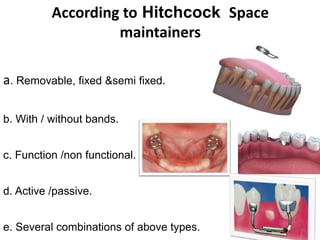
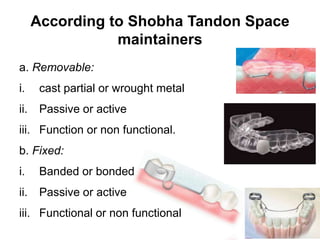
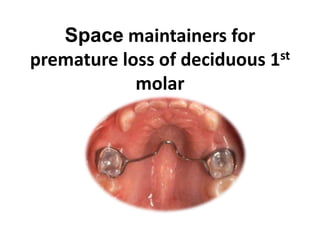
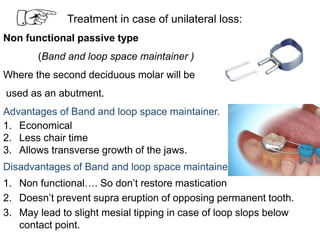
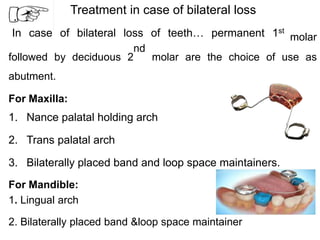
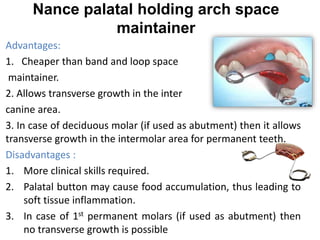
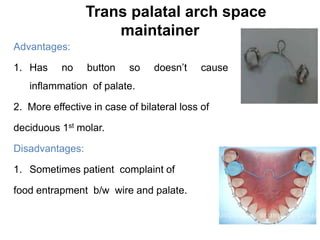
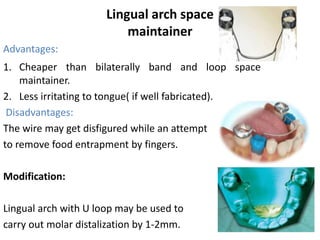
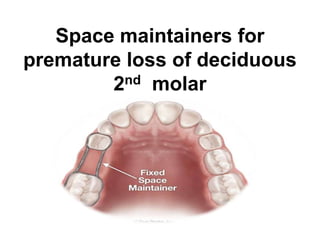
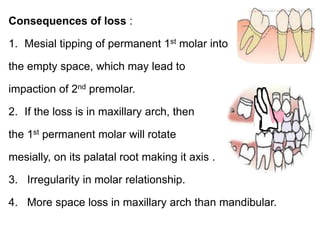
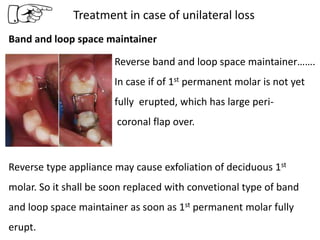
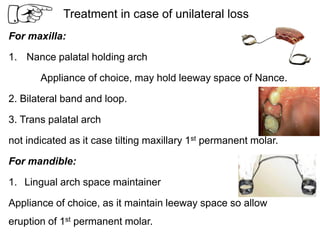
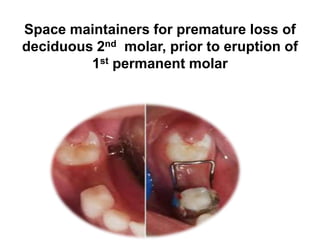
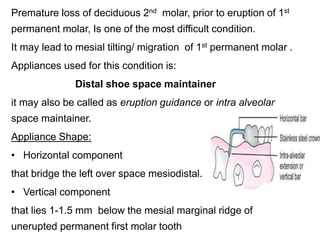
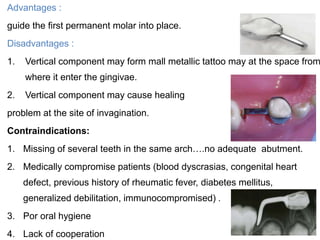
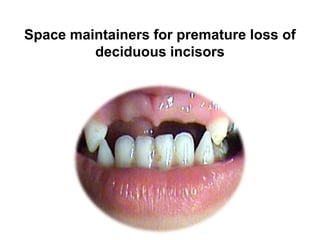
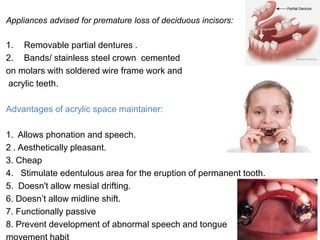
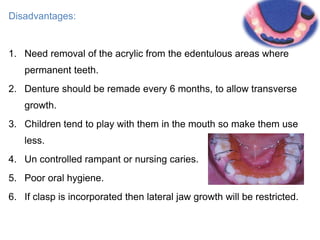
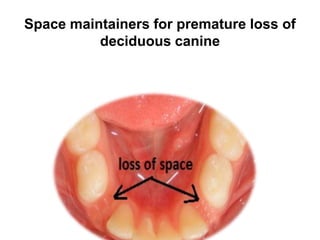
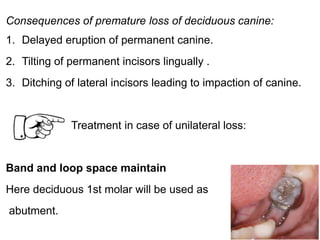
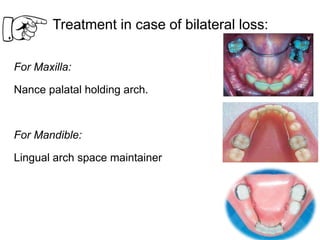
Preventive orthodontics focuses on educating patients and parents about dental growth and habits to avoid future malocclusion, often starting treatment between ages two to six. Key procedures include managing dental health, monitoring tooth exfoliation, and addressing habits like thumb sucking, with the aim to maintain arch integrity. Space maintainers are utilized to manage premature tooth loss and guide proper dental development.