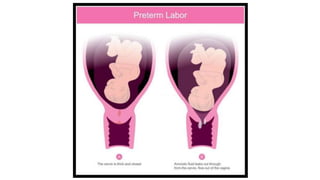
Preterm labor is defined as regular uterine contractions before 37 weeks of gestation that can lead to cervical changes and dilation. It may occur spontaneously or be indicated due to fetal or maternal complications. Common causes include intrauterine infection, cervical incompetence, premature rupture of membranes, and multiple pregnancies. Risk factors include African American race, young or advanced maternal age, prior preterm birth, smoking, and short time between pregnancies. Management involves bed rest, hydration, monitoring, tocolytic medications to stop contractions if possible, corticosteroids for fetal lung maturity, and antibiotics if membranes have ruptured. Complications include increased C-section rates and respiratory, feeding, and developmental issues for preterm infants.