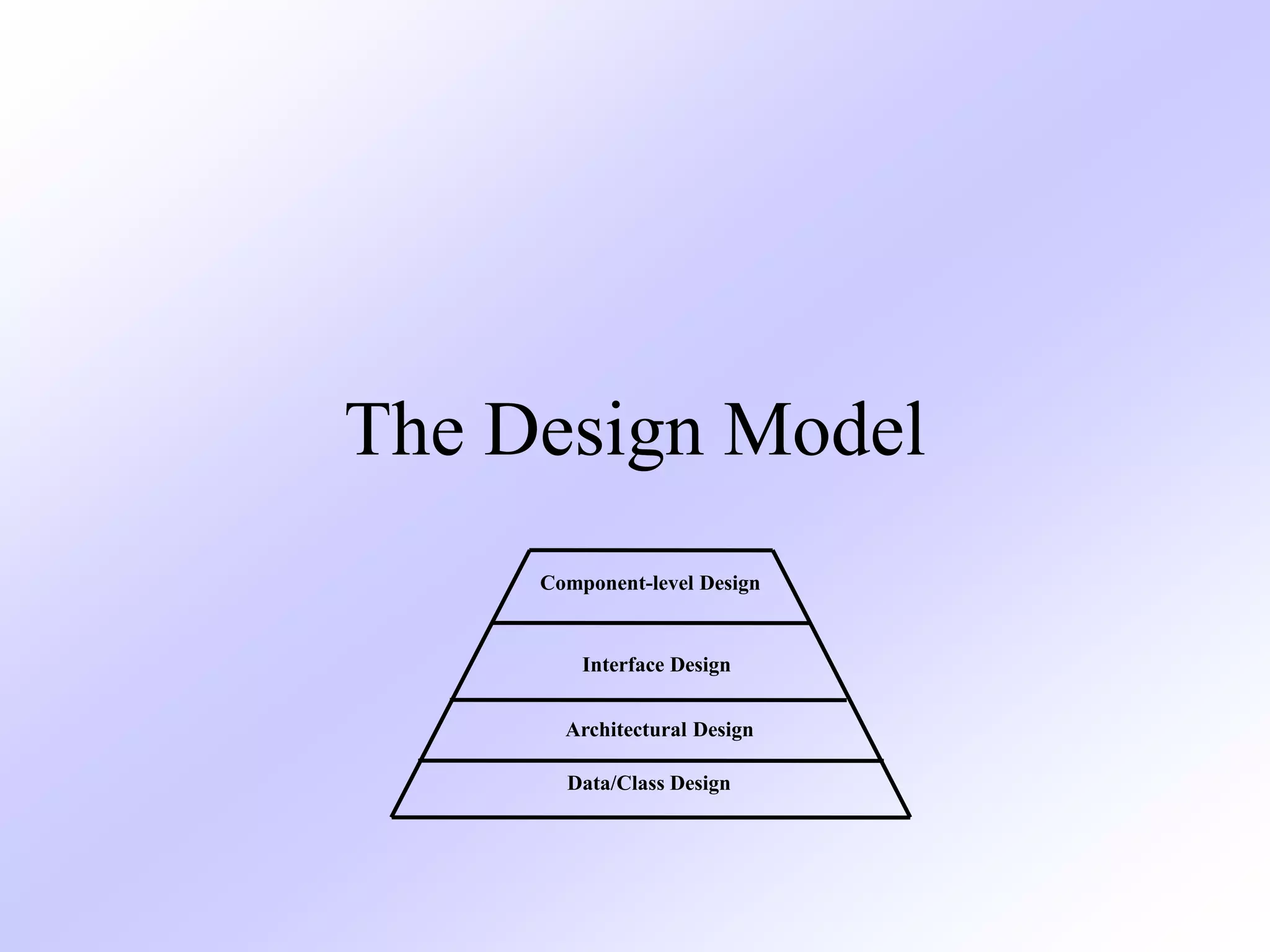
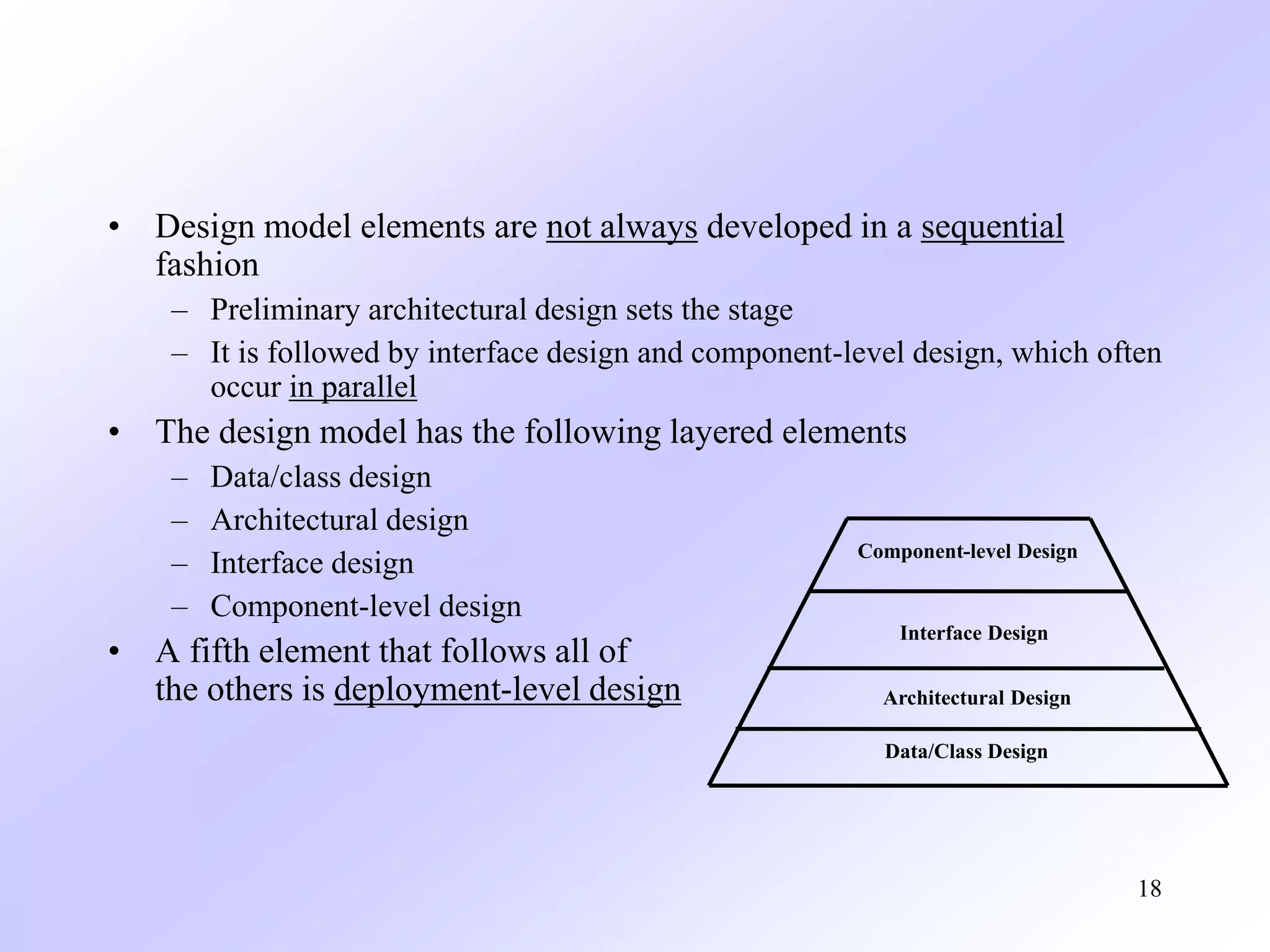
The design model transforms requirements from the analysis model into a blueprint for constructing the software. It includes four main elements: the data/class design, architectural design, interface design, and component-level design. These elements are developed iteratively through increasing levels of abstraction, starting with high-level elements that are traced to requirements and refining into lower-level representations. The design model aims to implement requirements while considering quality guidelines around modularity, patterns, and other design concepts.