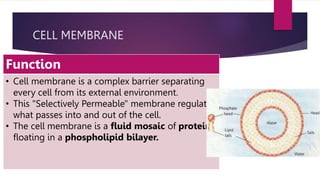
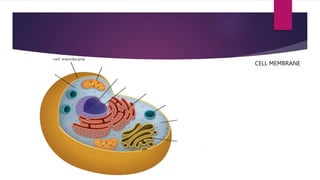
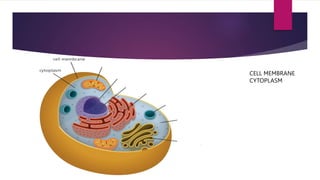
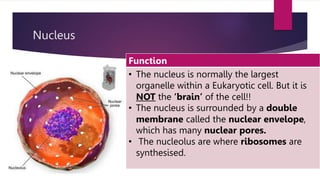
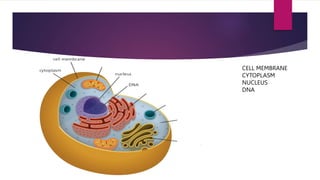
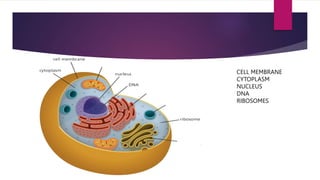
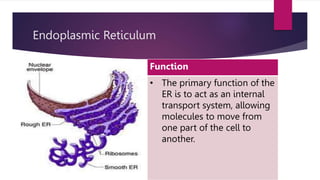
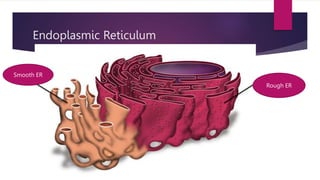
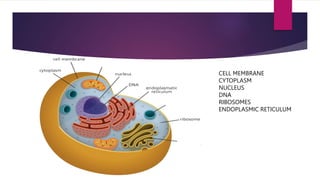
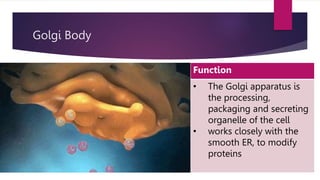
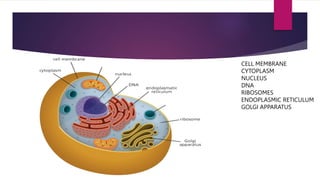
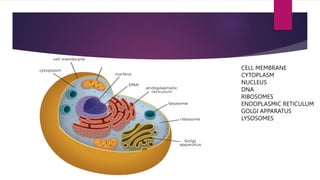
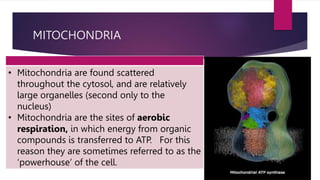
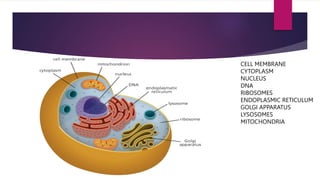
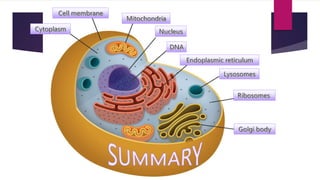
The document provides a detailed overview of animal cell structure, highlighting the three main parts: the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. It outlines the functions of various organelles such as ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and mitochondria, emphasizing their roles in processes like protein synthesis and energy production. Additionally, it clarifies common misconceptions about cell functions and the relationship between organelles.