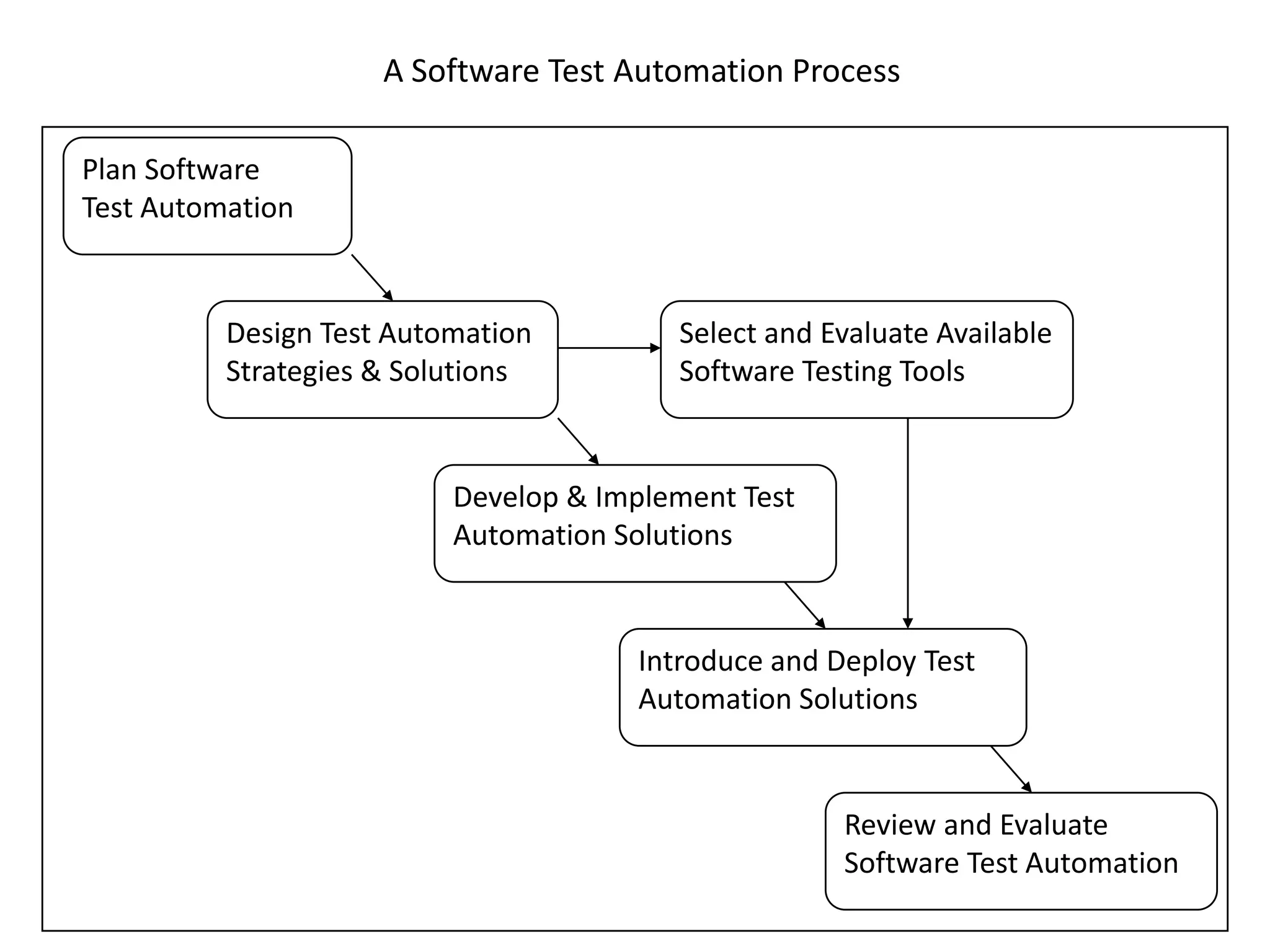
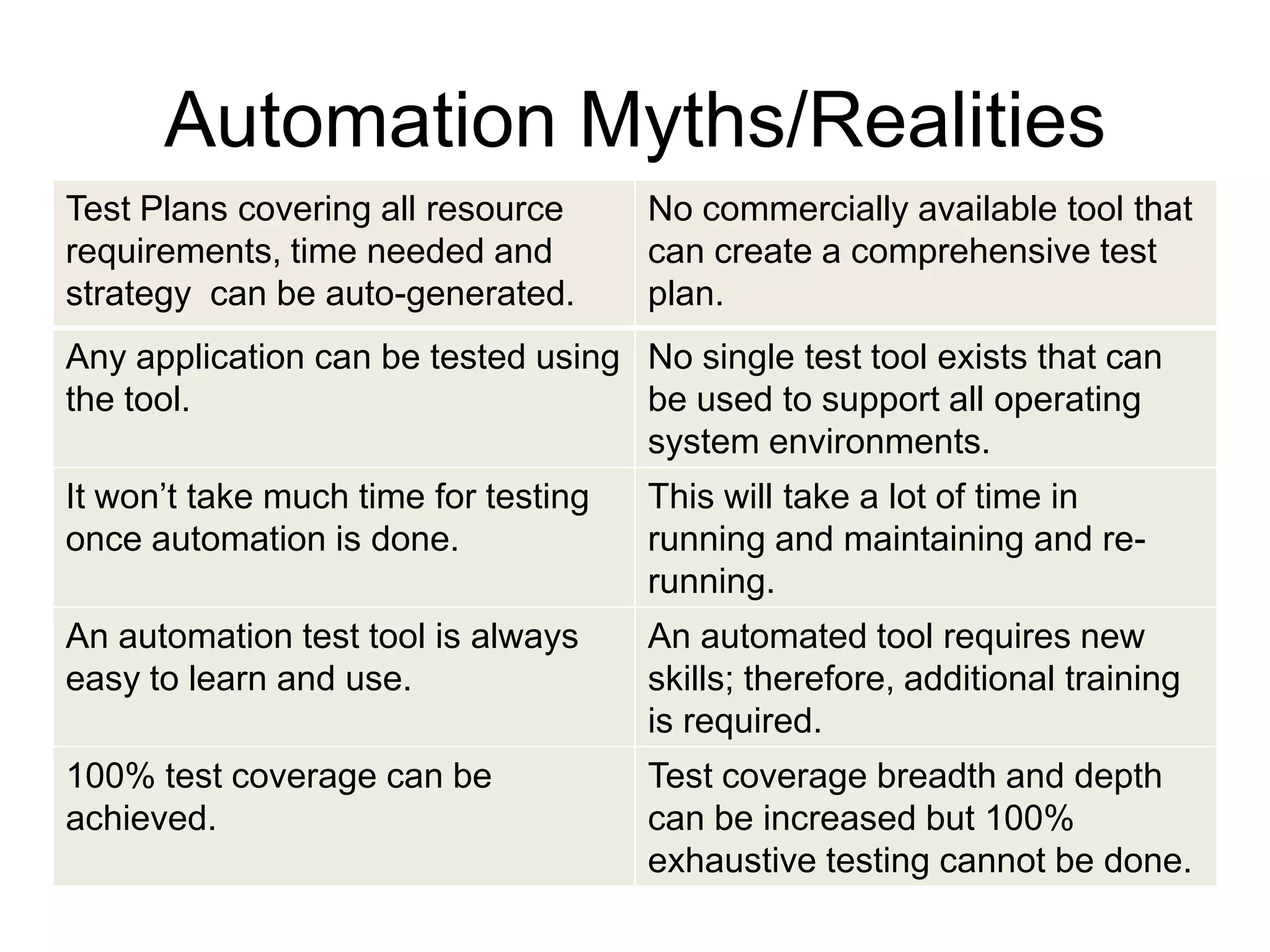
The document discusses how to make automation an asset to software testing organizations by outlining the advantages and disadvantages of manual versus automated testing, providing examples of what types of tests are best suited for automation, and describing best practices for developing an effective test automation process and addressing common myths about automation. It emphasizes that automation can increase testing efficiency and coverage but requires proper planning, resources, and maintenance to be successful.