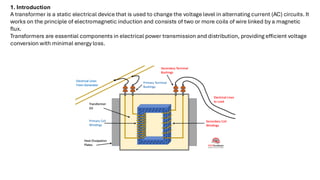
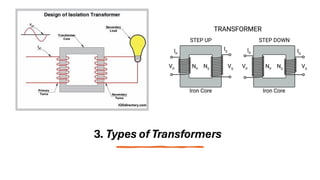
This document is a Class 12 project by Nikunj Krishna Udainiya on transformers, detailing their working principle, types, construction, and applications. It highlights the importance of transformers in electrical power transmission and voltage regulation, illustrating their role in minimizing energy loss. The project emphasizes the principle of electromagnetic induction and provides insights into the construction and practical uses of transformers.