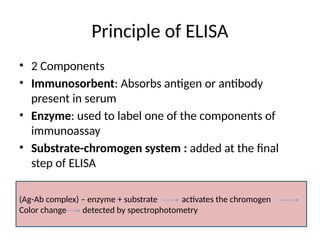
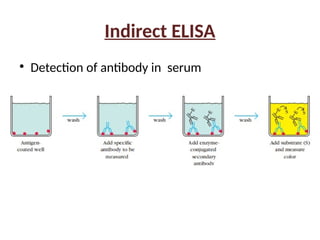
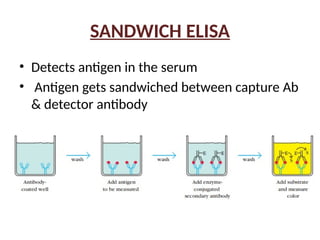
The document outlines the principles and procedures of the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), detailing its components, types (direct, indirect, sandwich, and others), and applications in diagnosing various infections like HIV and dengue. It discusses the mechanics of each ELISA type, their advantages, disadvantages, and the nature of the antigens and antibodies involved. Overall, it emphasizes ELISA's high sensitivity and capacity for large sample testing despite its longer processing time and equipment costs.