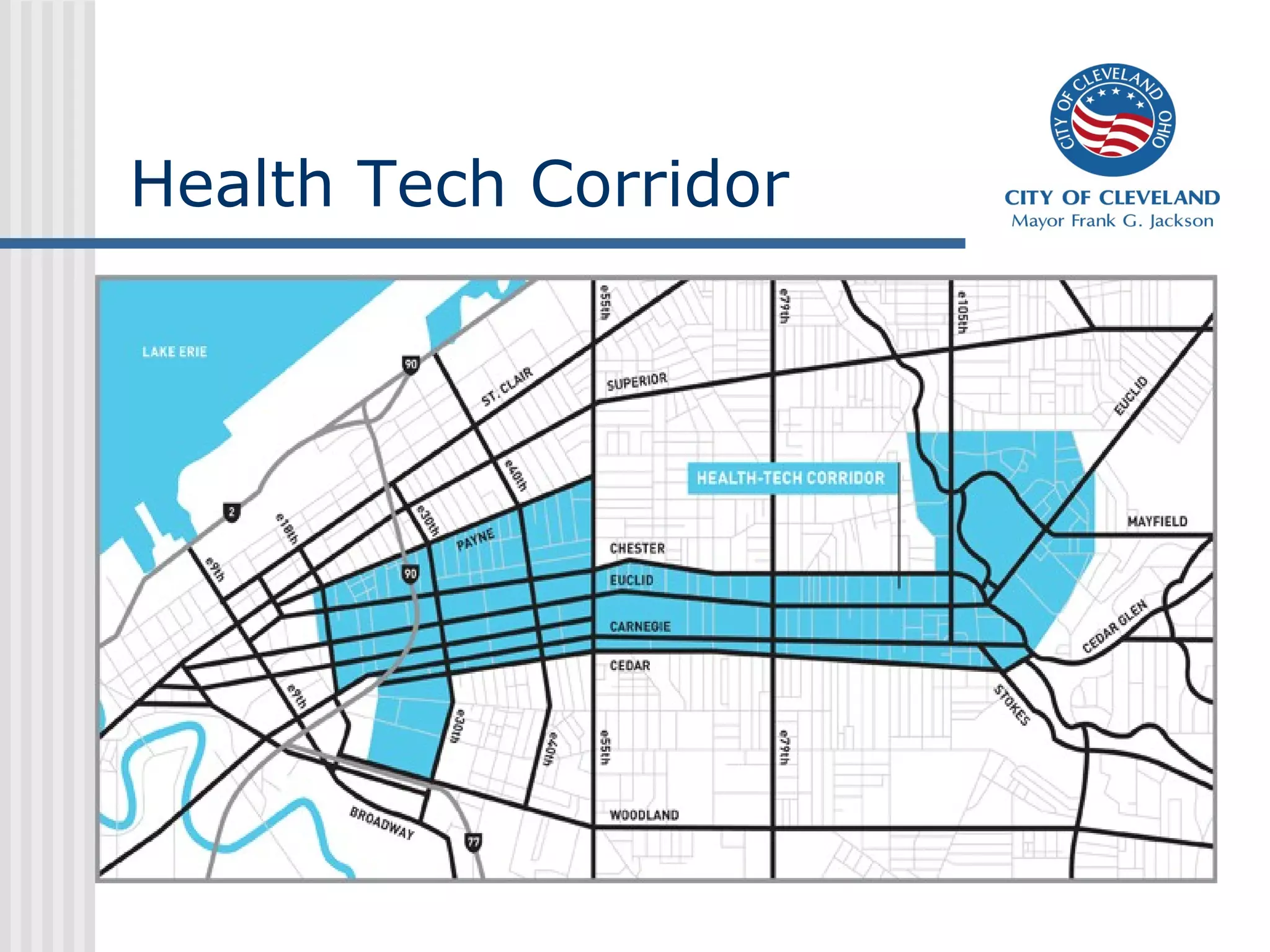
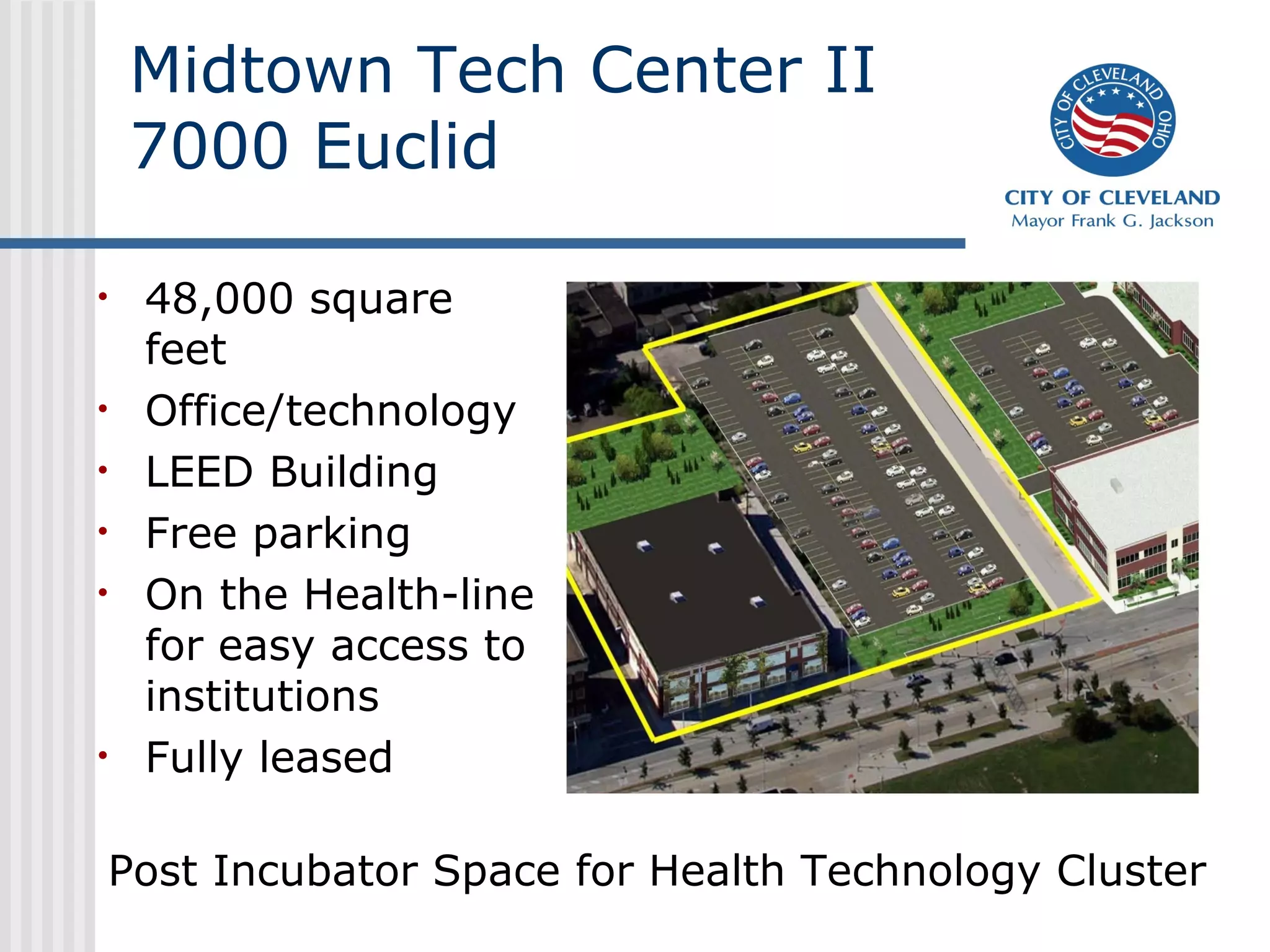
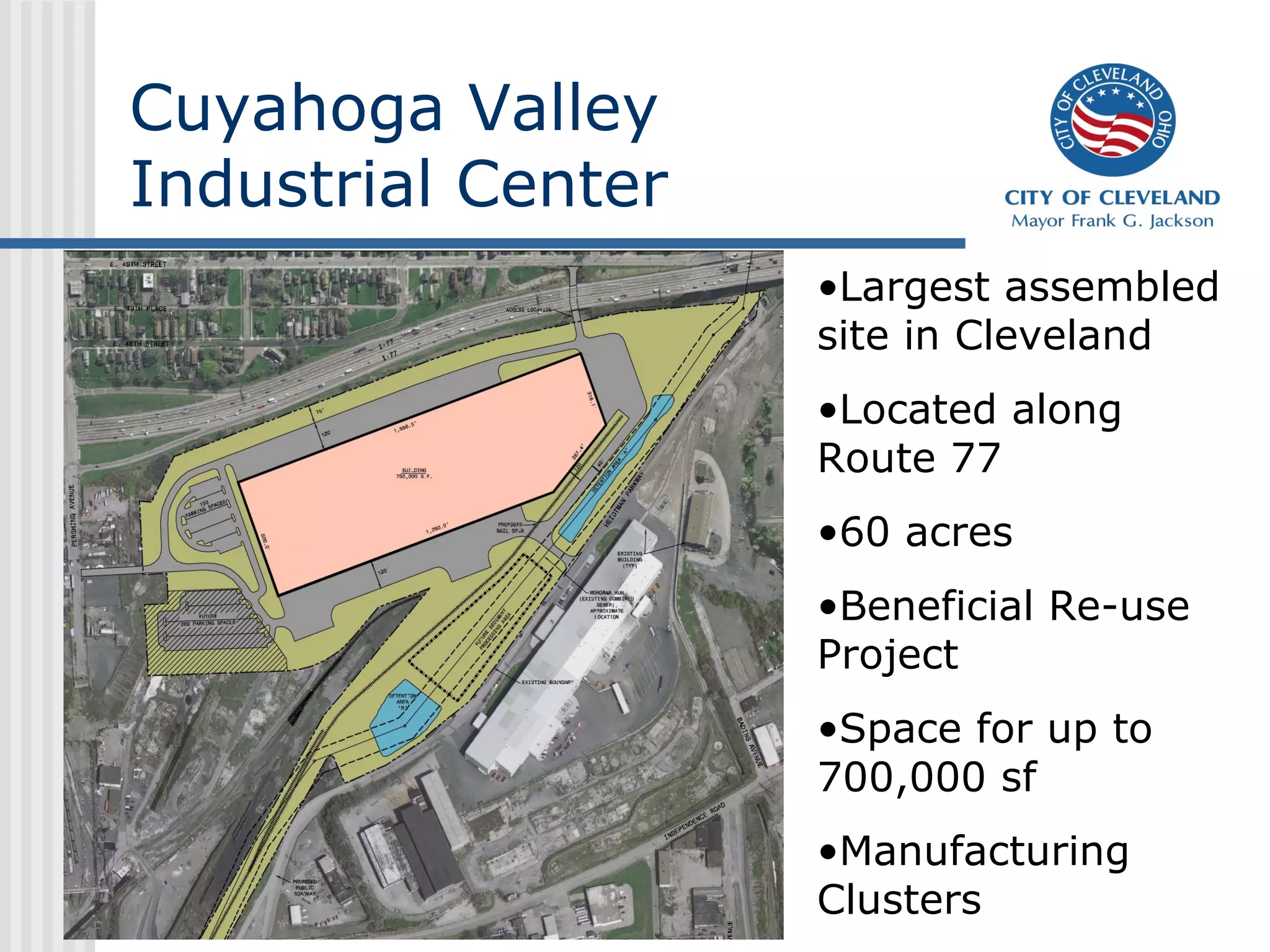
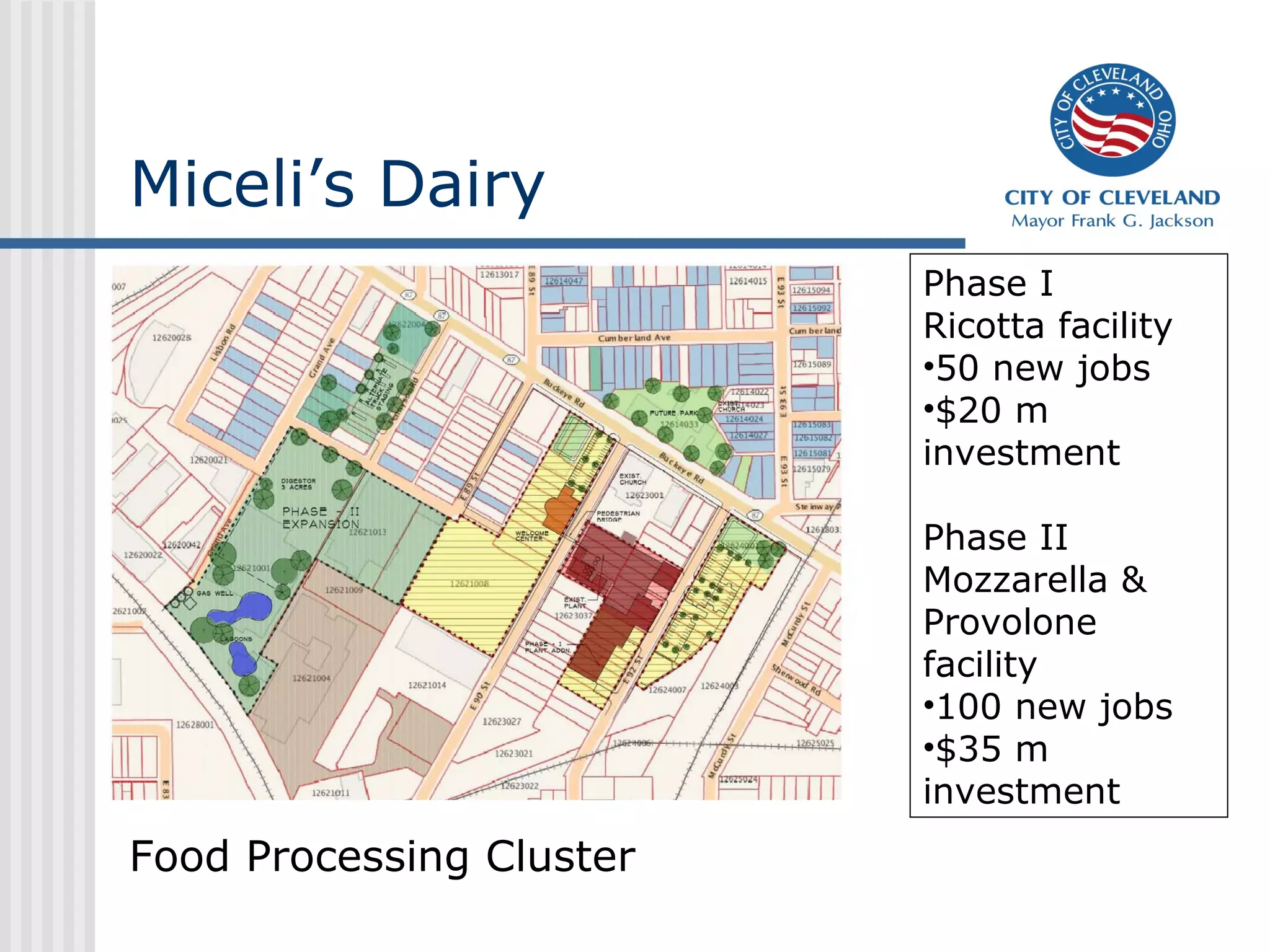
This presentation discusses development challenges facing distressed cities like Cleveland. Cleveland has struggled with job losses in manufacturing and foreclosures, and now deals with vacant and abandoned properties, illegal dumping, and poverty. However, the presentation outlines Cleveland's efforts to address these issues through a unified strategy of education reform, partnerships, and place-based economic development focused on clusters like health technologies. Anchors like universities and initiatives like green cooperatives aim to create local jobs and opportunity.