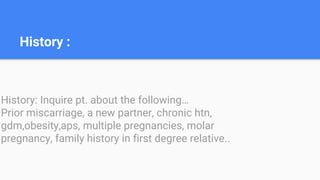
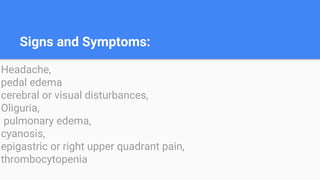
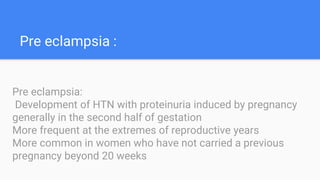
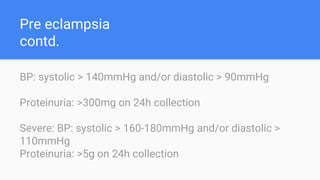
Gestational hypertension, also known as pregnancy-induced hypertension, is defined as new hypertension developing after 20 weeks of gestation without significant proteinuria. It is characterized by diastolic blood pressure over 90 mmHg on two occasions or over 110 mmHg on one occasion. Risk factors include nulliparity, advanced maternal age, obesity, family history of preeclampsia, and previous history of gestational hypertension. Complications can include preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome. Treatment involves monitoring, lifestyle changes like salt restriction, antihypertensive medications, and delivery if gestation is full term or there are severe symptoms.