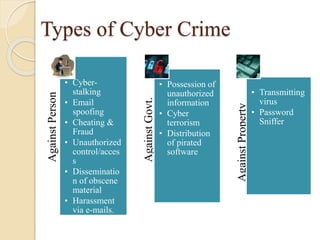
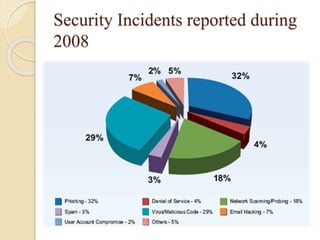
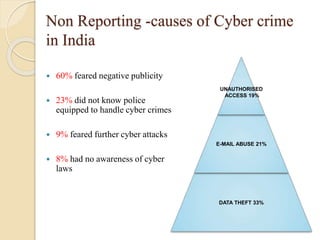
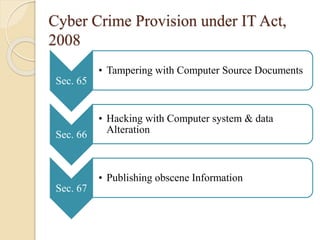
The document provides an overview of the IT Act in India through discussing key topics like the objectives of the Act, cyber crimes and provisions under the Act. It notes that the Act aims to provide legal recognition to electronic transactions and storage of data. It also describes various cyber crimes like hacking, data theft and publishing obscene content, as well as amendments made in 2008 to address issues like data protection. Case studies are presented on crimes such as blackmailing, bank fraud, and hacking into websites to illustrate how the IT Act handles such offenses.