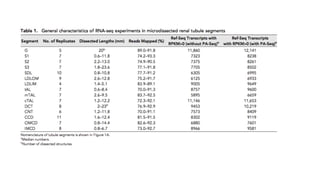
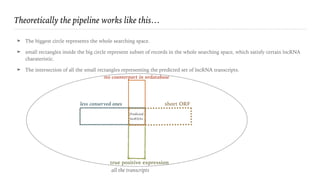
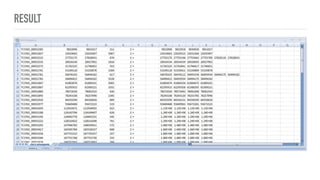
This document describes a pipeline for predicting long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) transcripts from comprehensive rat renal cell-type specific transcriptome libraries. The pipeline applies characteristics of lncRNAs, such as shorter open reading frames, lack of conserved domains, and cell-type specific expression, to filter transcripts from the libraries. Applying this multi-step filtering process identifies transcripts predicted to be lncRNAs based on satisfying all the characteristics. The results are stored in GTF format for further analysis and classification of different lncRNA types.