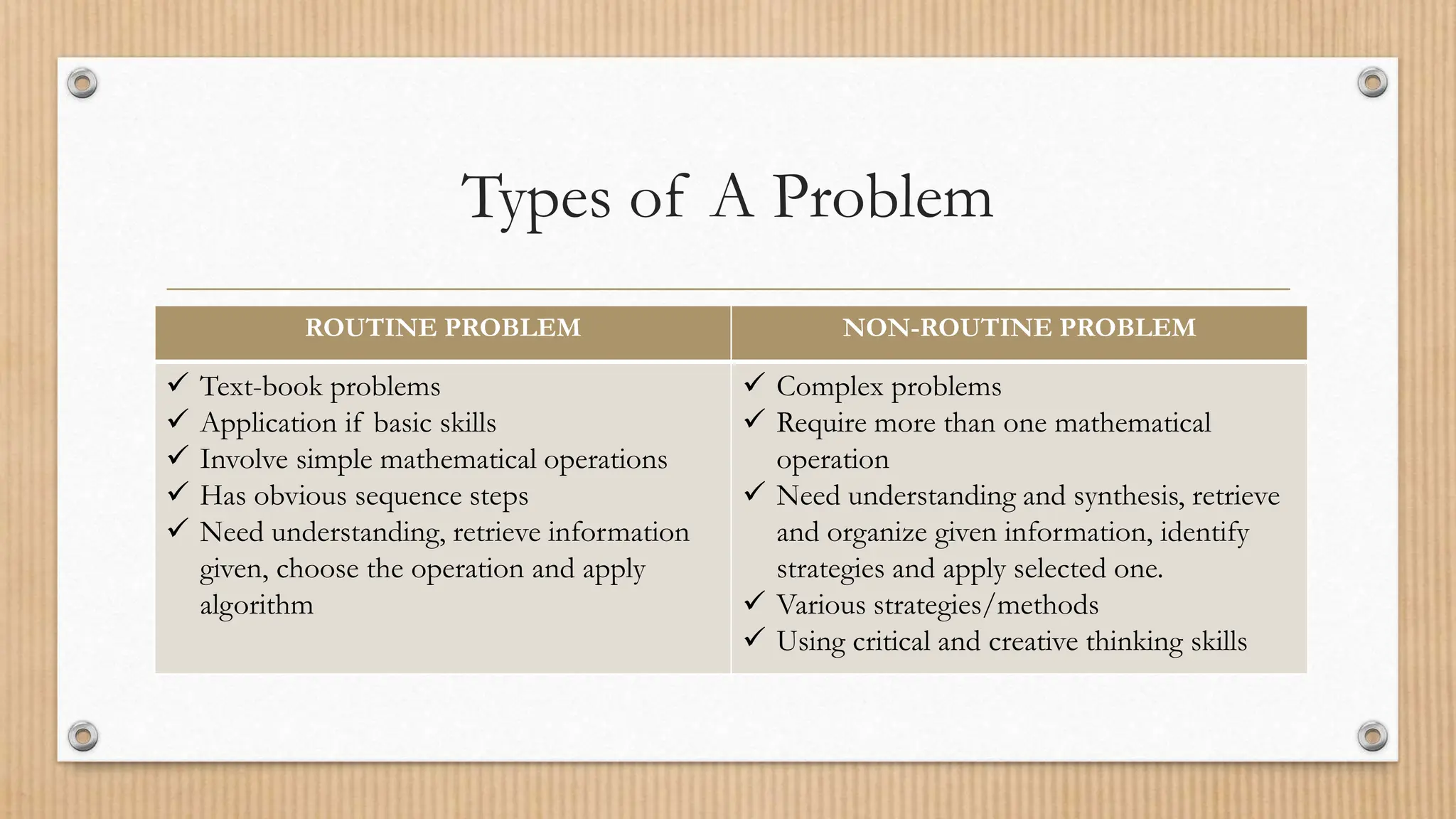
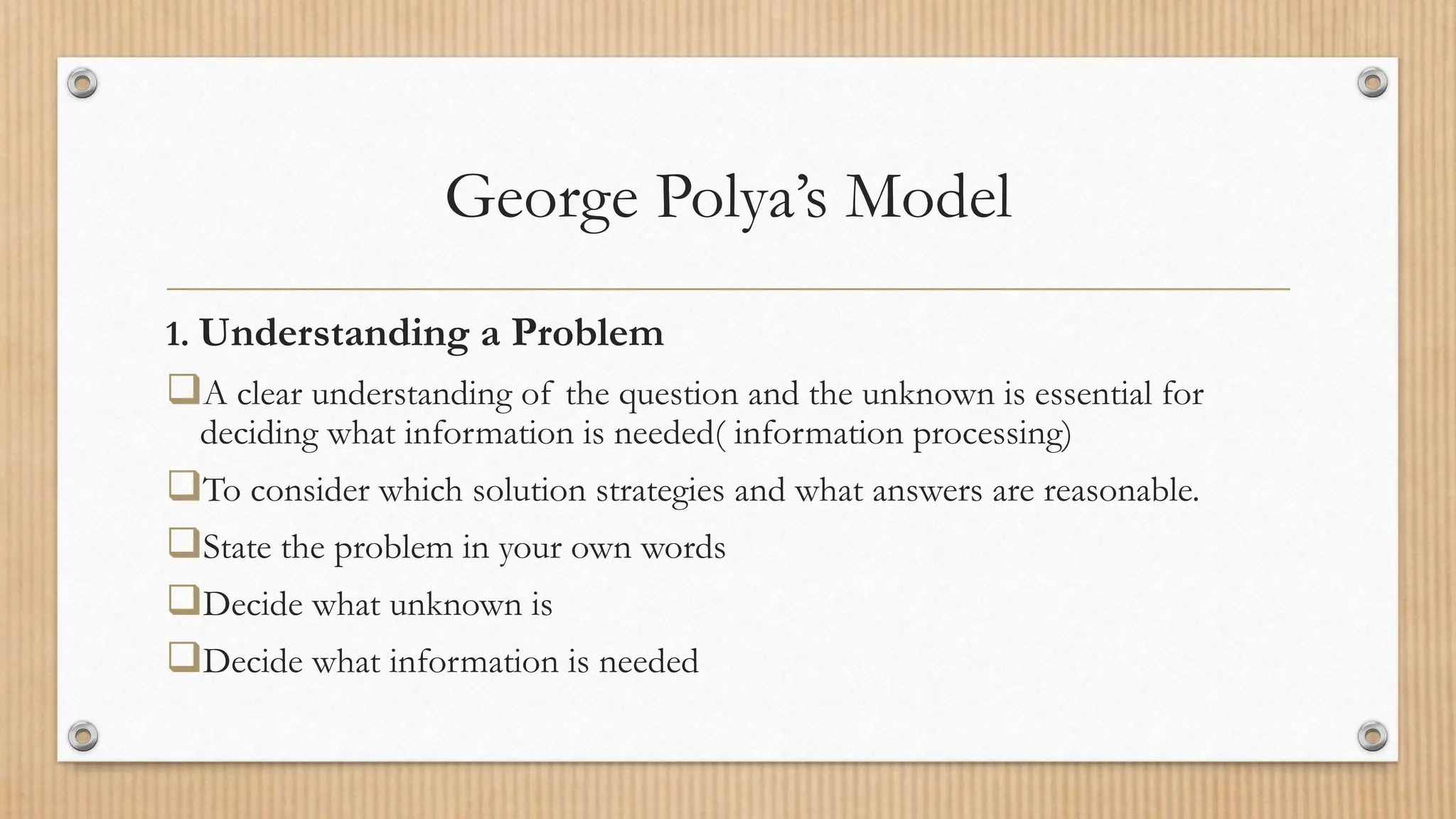
This document discusses heuristics for problem solving. It describes George Polya's model for problem solving, which includes four steps: 1) understanding the problem, 2) devising a plan, 3) carrying out the plan, and 4) looking back. It also discusses Krulik and Rudnick's model, which includes reading the problem, exploring, selecting a strategy, solving, and looking back. Examples of routine and non-routine problems are provided. Heuristics are described as rules of thumb or educated guesses that can help guide problem solving.