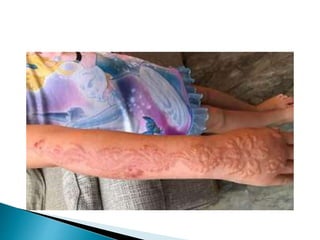
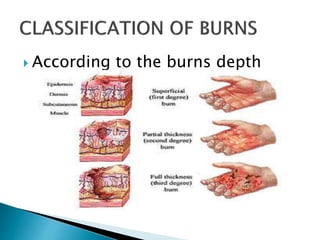
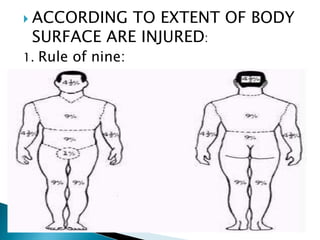
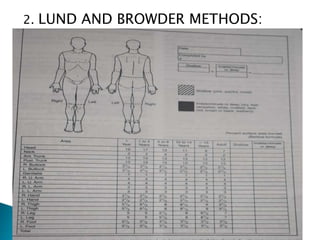
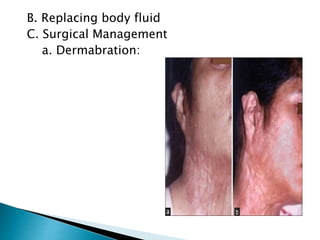
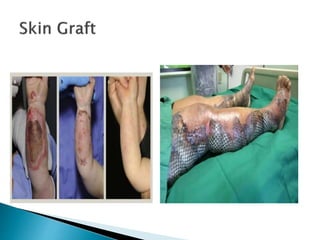
This document discusses different types of burns, including thermal burns caused by fire, heat, or chemicals; electrical burns; and radiation burns. It describes burn severity based on depth and percentage of total body surface area affected. First aid procedures are outlined, such as cooling the burn with water and covering it loosely with a sterile bandage. Hospitalization, pain management, and wound care are also discussed. Surgical techniques like dermabrasion are mentioned as part of longer-term treatment.