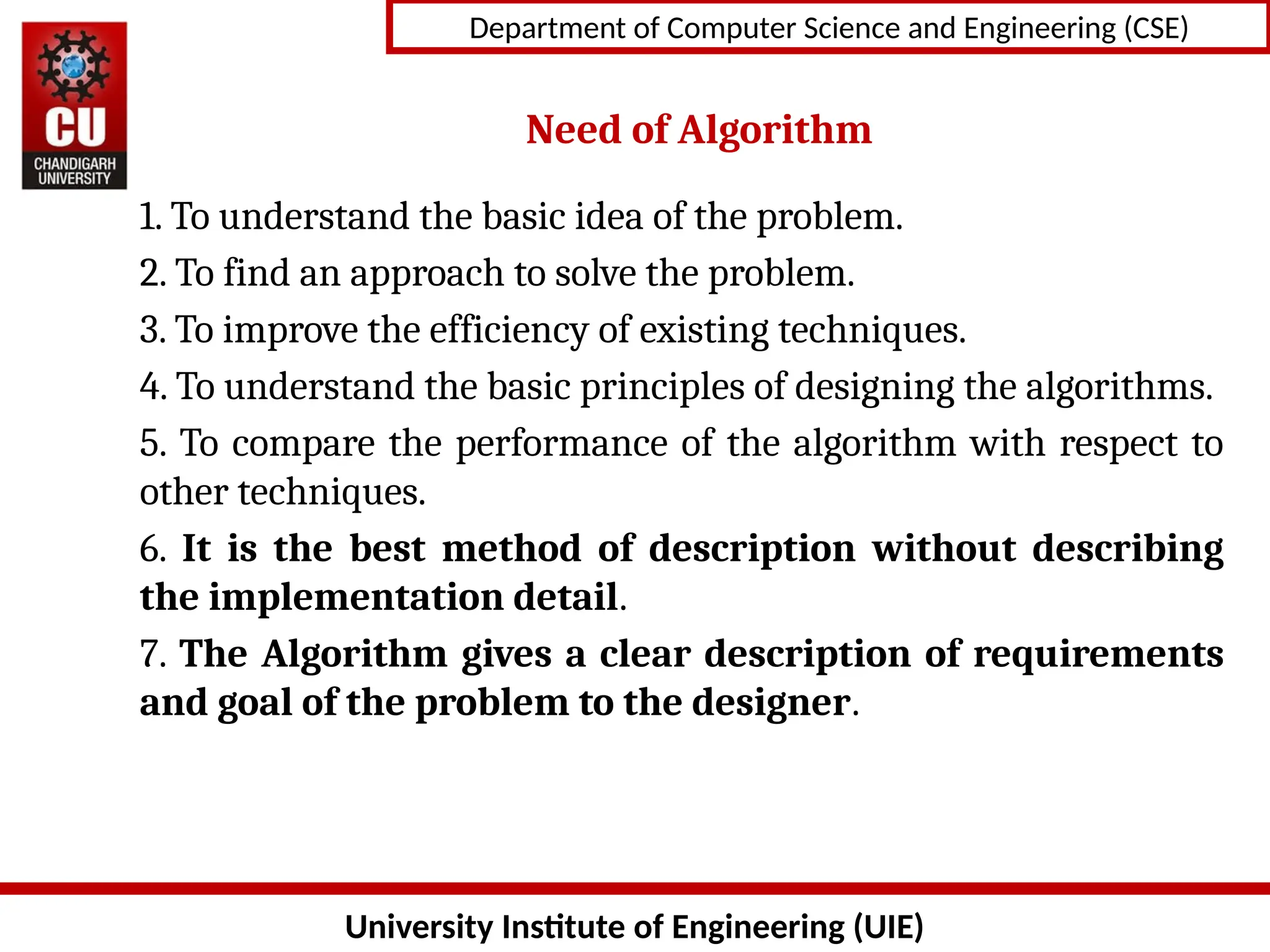
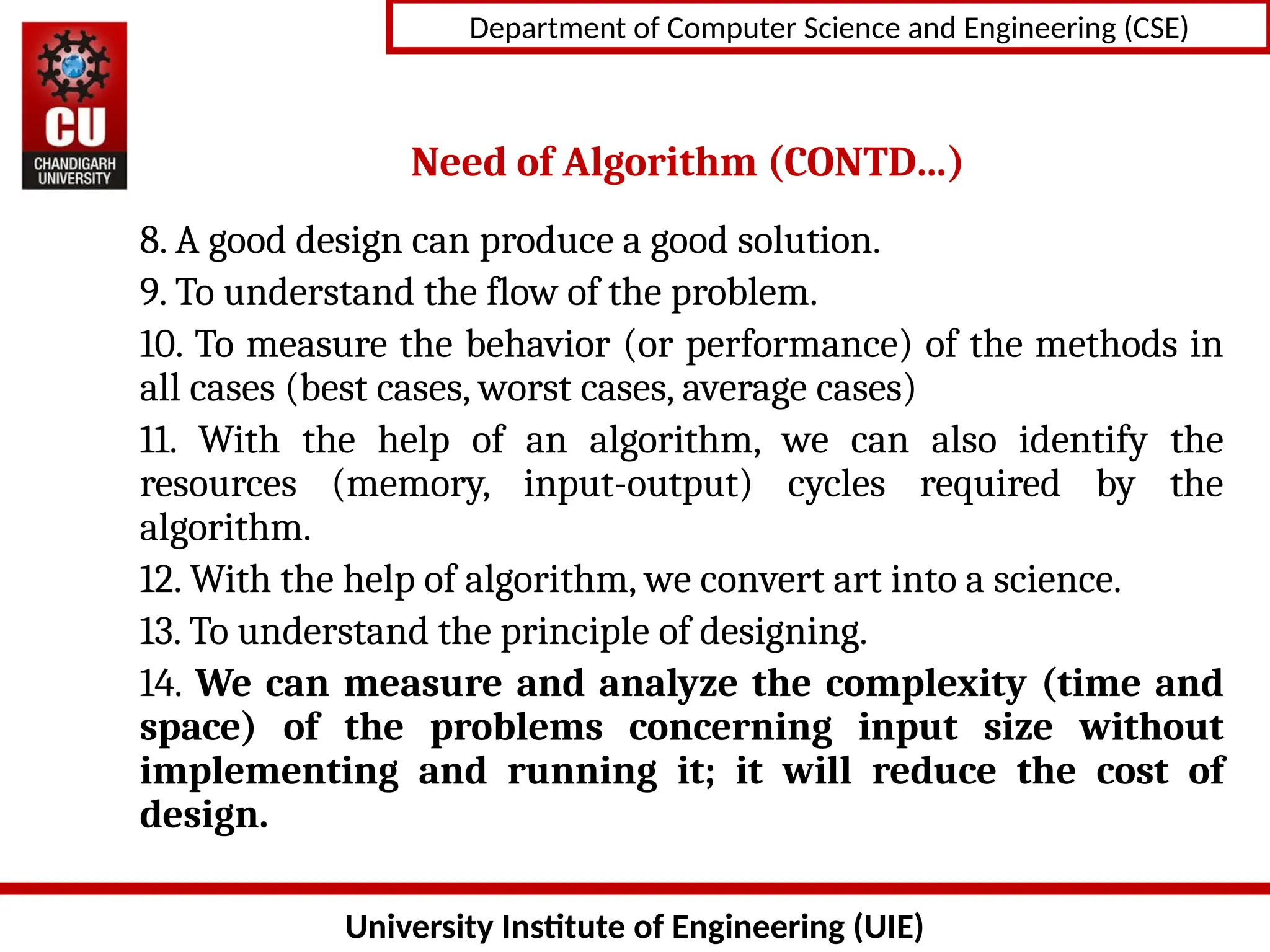
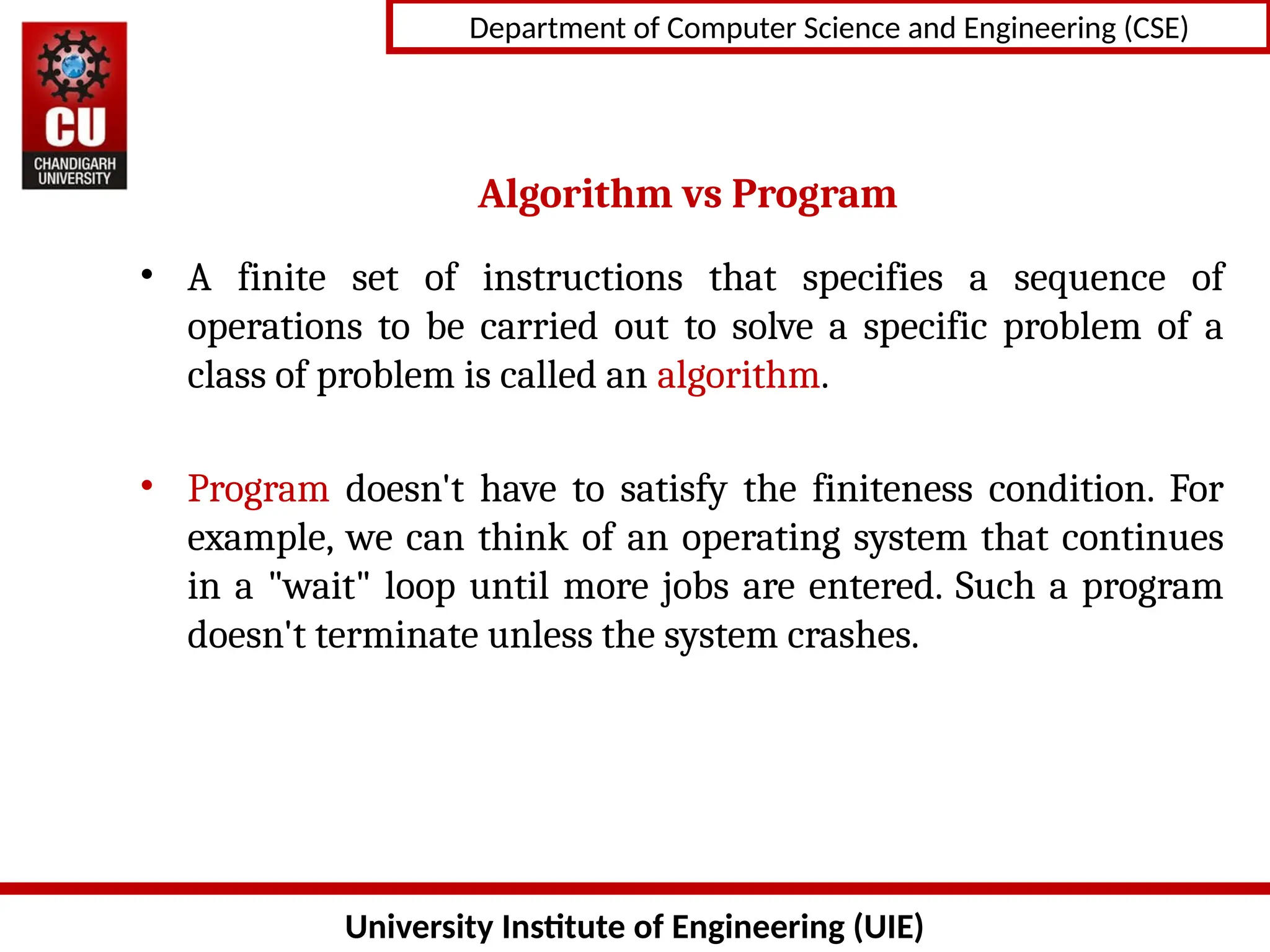
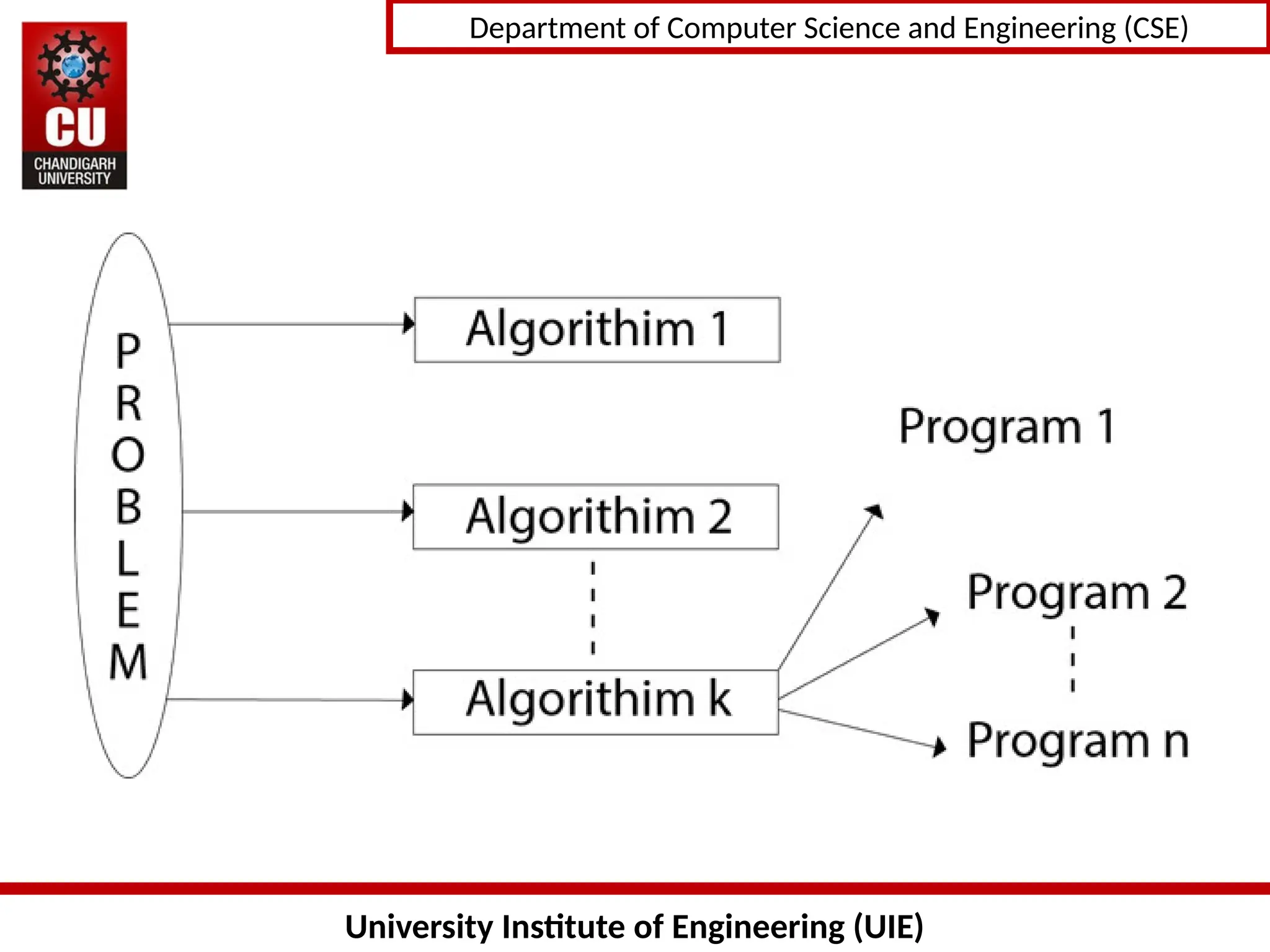
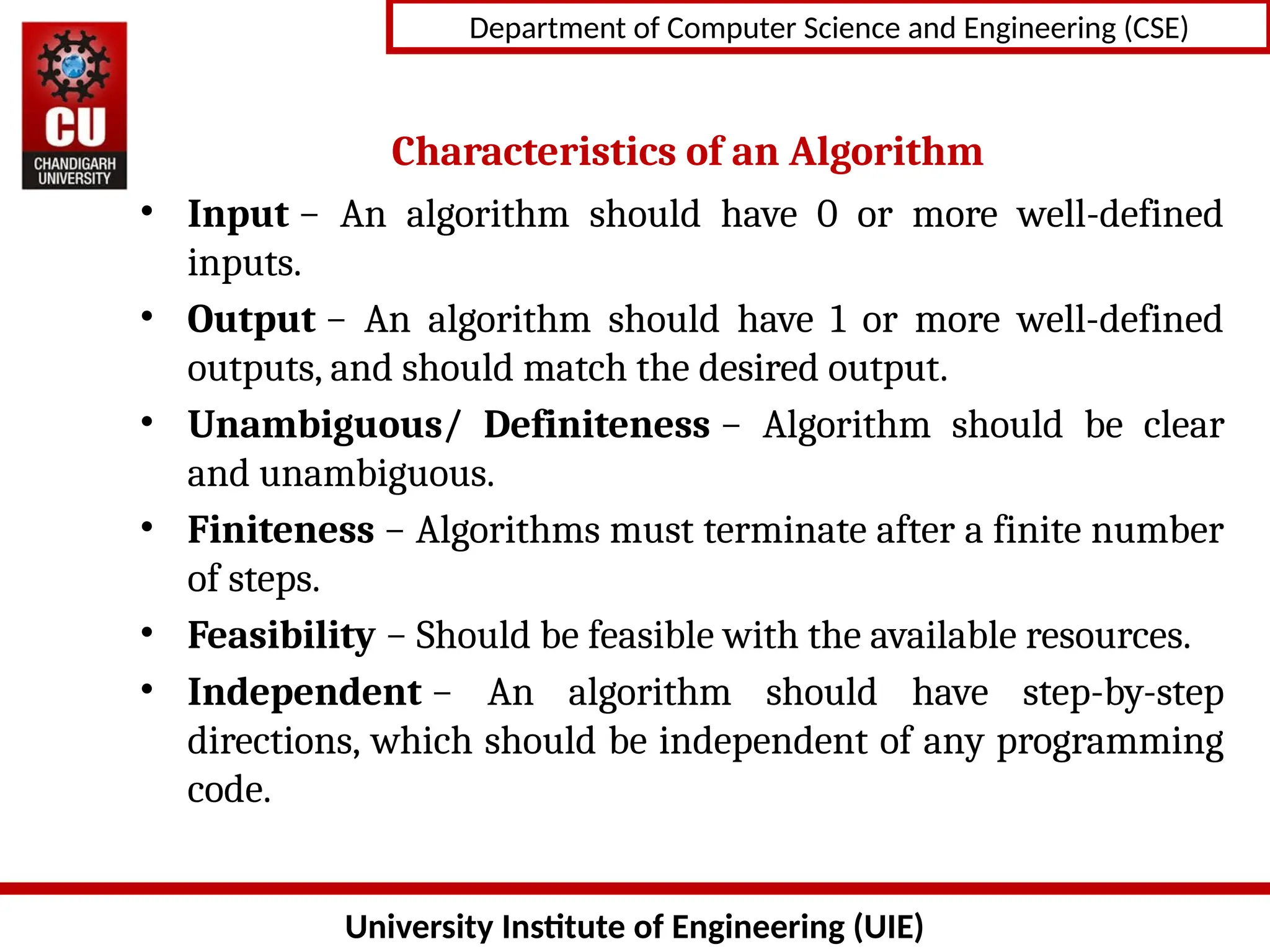
The document provides an introduction to algorithms, detailing their characteristics, specification methods, and the need for understanding and designing algorithms effectively in computer science. Key points include the definition of an algorithm as a finite set of instructions, its essential characteristics such as input, output, clarity, finiteness, and feasibility, as well as the various ways to describe algorithms, including natural language, flowcharts, and pseudo-code. It emphasizes the importance of algorithms for problem-solving, efficiency improvement, and performance analysis.

![University Institute of Engineering (UIE)
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE)
Algorithm of linear search :
1. Start from the leftmost element of arr[] and one by one compare x
with each element of arr[].
2. If x matches with an element, return the index.
3. If x doesn’t match with any of elements, return -1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1-240828155326-bc4a082c/75/PPT-1-1-Introduction-to-Algorithms-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![University Institute of Engineering (UIE)
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE)
Pseudocode for Linear Search :
FUNCTION linearSearch(list, searchTerm):
FOR index FROM 0 -> length(list):
IF list[index] == searchTerm
THEN RETURN index
ENDIF
ENDLOOP
RETURN -1
END FUNCTION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1-240828155326-bc4a082c/75/PPT-1-1-Introduction-to-Algorithms-pptx-10-2048.jpg)
![University Institute of Engineering (UIE)
Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE)
int search(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
Program for Linear Search :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1-240828155326-bc4a082c/75/PPT-1-1-Introduction-to-Algorithms-pptx-11-2048.jpg)