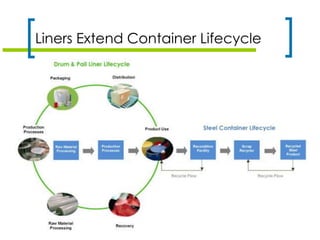
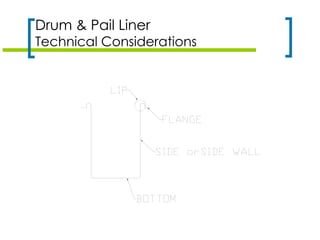
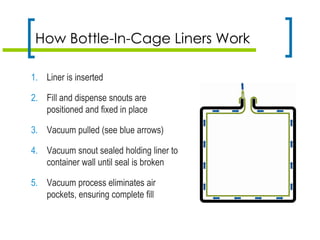
The document discusses various types of liners for drums, pails, and intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) used in the petroleum industry, emphasizing their benefits such as product protection, waste reduction, and sustainability. It highlights technical considerations for different liner types, including form-fit and pillow liners, as well as innovations like bag-in-box and bottle-in-cage systems. Key factors for selecting the appropriate liner are also outlined, focusing on rigidity, filling methods, and environmental impacts.