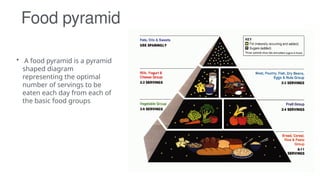
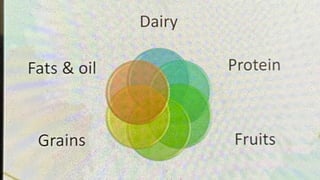
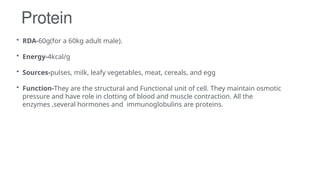
A balanced diet includes a variety of foods to meet nutritional needs for energy, vitamins, and minerals, essential for health and preventing chronic diseases. Dietary guidelines recommend limiting fat, salt, and refined carbohydrates while ensuring adequate protein and fiber intake. Factors such as religion, socio-economic status, and geographic location can influence dietary habits and nutritional deficiencies.